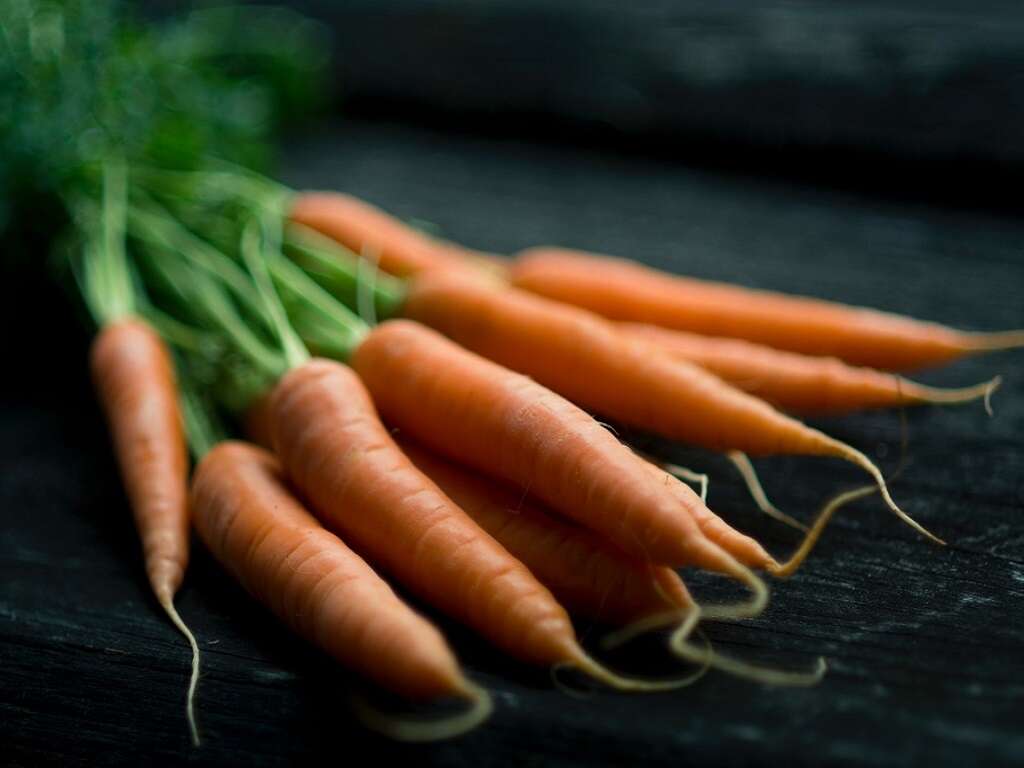
Health Benefits of Carrots
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Rousseau, Nicolas. 'Beta-Carotene.' Fondation Louis Bonduelle, 17 Feb. 2017, www.fondation-louisbonduelle.org/en/nutrient/beta-carotene-or-provitamin-a/.
- 2. 'Office of Dietary Supplements - Vitamin B6.' NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/.
- 3. About The Team Heart Care Team Our team wants to help you keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk for heart problems. We'll provide you with information and tools to help you know your numbers, et al. 'Feeding Your Heart: Foods to Help Lower Cholesterol: Shine365 from Marshfield Clinic.' Shine365, 22 Nov. 2019, shine365.marshfieldclinic.org/heart-care/foods-to-help-lower-cholesterol/.
- 4. 'GI Disorders Functional GI Disorders Motility Disorders Upper GI Disorders Lower GI Disorders Other Disorders FGIMDs and Military Service Kids & Teens.'IFFGD, www.iffgd.org/diet-treatments/dietary-fiber.html.
- 5. Larsson SC;Bergkvist L;Näslund I;Rutegård J;Wolk A; 'Vitamin A, Retinol, and Carotenoids and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: a Prospective Cohort Study.' The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17284749/.
- 6. Khoo, Hock Eng, et al. 'Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments as Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and the Potential Health Benefits.' Food & Nutrition Research, Taylor & Francis, 13 Aug. 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5613902/.
Crunchy carrots are one of the most nutritious and versatile root vegetables. Their complex flavors can be used in a variety of savory and dessert dishes, and they provide a low-calorie snack option. In 100 grams of carrots, there are roughly 40 calories.
When cooked, the nutritional value of carrots increases and makes it easier for the body to digest its vital vitamins. Boasting impressive levels of vitamin A, antioxidants and immunity-building properties, there's so much goodness jammed into one serving of carrots. From purple to orange, carrots truly are one of the most remarkable vegetables.

1. Improves Eye Health
A carrot's claim to fame is its high levels of beta-carotene, a carotenoid that gives certain food its unmistakable red-orange pigment. Other well-known sources of beta-carotene include sweet potatoes, apricots and butternut squash.
The body has the ability to convert beta-carotene into vitamin A, a key nutrient in supporting eye health.1Rousseau, Nicolas. ‘Beta-Carotene.’ Fondation Louis Bonduelle, 17 Feb. 2017, www.fondation-louisbonduelle.org/en/nutrient/beta-carotene-or-provitamin-a/. A lack of vitamin A can cause dry and scratchy eyes and contribute to other degenerative eye diseases. Because vitamin A is fat-soluble, it's a good idea to add oil to help with the absorption of this vital nutrient. Cooking carrots also helps the body absorb more beta-carotene.

2. Boosts Energy Levels
To boost energy levels, grab a handful of carrot sticks! Vitamin B6, together with other micronutrients, is vital for the healthy functioning of the immune and nervous system. It also helps with the breakdown of complex proteins and carbohydrates.
Essentially, vitamin B6 helps the body metabolize food into energy. A standard carrot stick contains 0.15 milligrams of the RDA, which is 1.3 to 1.6 milligrams.2‘Office of Dietary Supplements - Vitamin B6.’ NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/. Just a few carrot sticks per day is enough to meet the daily nutrient requirements.

3. Good for Lowering Blood Cholesterol
Frequent consumption of carrots can contribute to the lowering of blood cholesterol levels. Although the human body needs small amounts of cholesterol, too much cholesterol has been associated with an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes and blood clots. Together with other nutritious foods, carrots are considered heart-healthy vegetables.
What makes carrots good for cholesterol levels? Carrots contain high quantities of water-soluble fiber, which helps rid the body of excess cholesterol. For good heart health, 5 to 10 grams of soluble fiber per day is recommended.3About The Team Heart Care Team Our team wants to help you keep your heart healthy and reduce your risk for heart problems. We’ll provide you with information and tools to help you know your numbers, et al. ‘Feeding Your Heart: Foods to Help Lower Cholesterol: Shine365 from Marshfield Clinic.’ Shine365, 22 Nov. 2019, shine365.marshfieldclinic.org/heart-care/foods-to-help-lower-cholesterol/.

4. Promotes Wound Healing
Vitamin K1 has an important role in blood coagulation and can help individuals heal after major surgery. It's unusual for people to have a deficiency of vitamin K1, but it's still important to include the nutrient in a healthy eating plan.
Before upping the intake of vitamin K1, individuals should consult their physician to confirm it's safe to do so. A single serving of carrots supplies 28 micrograms, which is just under a third of the minimum RDA.
5. Supports Weight Loss
Foods that are high in fiber leave a feeling of fullness, which can prevent overeating. Fiber takes a while to digest, and carrots contain an impressive amount. In addition, carrots are extremely low in calories and considered a superfood.
Half a cup of cooked carrots contains 2.3 grams of fiber, which is quite significant.4‘GI Disorders Functional GI Disorders Motility Disorders Upper GI Disorders Lower GI Disorders Other Disorders FGIMDs and Military Service Kids & Teens.’IFFGD, www.iffgd.org/diet-treatments/dietary-fiber.html. Eaten raw, the same amount of carrots contain 2 grams of fiber. Carrots are also low in calories, making them ideal for a healthy eating regimen.

6. Aids Digestion
For the healthy functioning of the digestive system, 25 to 30 grams per day of fiber from food is required. Fiber assists with solidifying stools by absorbing water and ensuring waste moves easily through the gut.
Carrots are laden with insoluble fibers, which can prevent constipation and keep the bowels regular. Also, carrots can help to balance the gut microbiome by feeding the healthy bacteria. An overgrowth of bad bacteria may lead to digestive ailments.

7. Reduces Risk of Certain Cancers
Carotenoids may reduce the risk of certain gastric cancers, such as prostate, stomach and colon cancer.5Larsson SC;Bergkvist L;Näslund I;Rutegård J;Wolk A; ‘Vitamin A, Retinol, and Carotenoids and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: a Prospective Cohort Study.’ The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17284749/. The compound carotenoid acts as an antioxidant in the human body and helps fight free radicals, which are known for destroying healthy cells.
Carrots are rich in antioxidants that may thwart the development of cancerous cells, according to animal studies. Cooking carrots brings out higher levels of beta-carotene and nutrients because of carotenoid, a fat-soluble compound.

8. Improves Skin Health
The carotenoid beta-carotene is believed to have a positive effect on skin health. Once converted to vitamin A inside the body, it can help improve skin conditions such as acne and oily or dry skin.
Vitamin A has the ability to flush out excess oil, and carrots boast a significant amount of this nutrient. Eaten in moderation, carrots can also help protect the skin from the sun's harmful UV rays.

9. Powerful Antioxidant
Eating antioxidant-rich foods supports the body's immune system in fighting disease. Carrots are a powerhouse of vitamins and minerals and contain noteworthy levels of antioxidants.
Antioxidants are particularly good for cardiovascular health and may also slow cell damage from disease-causing free radicals. Carrots contain carotenoids and anthocyanins, which are the vegetable's primary protectors against free radicals. Anthocyanins give purple carrots their unique color, and just like beta-carotene in orange carrots, they possess powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.6Khoo, Hock Eng, et al. ‘Anthocyanidins and Anthocyanins: Colored Pigments as Food, Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and the Potential Health Benefits.’ Food & Nutrition Research, Taylor & Francis, 13 Aug. 2017, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5613902/.

10. Helps Control Diabetes
The key to a healthy diet for those with diabetes is eating low carb, balanced meals at regular intervals. For a balanced diet, people with diabetes should follow a low-calorie, low carb or low glycemic index (GI) diet rich in nutrients. Carrots are a nutritious option as they're jampacked with vitamins, and raw carrots have a low glycemic index.
Carrots aren't as high in carbs as other vegetables and contain free-radical-fighting compounds. Together with other fruits and vegetables, carrots can help stabilize sugar levels.