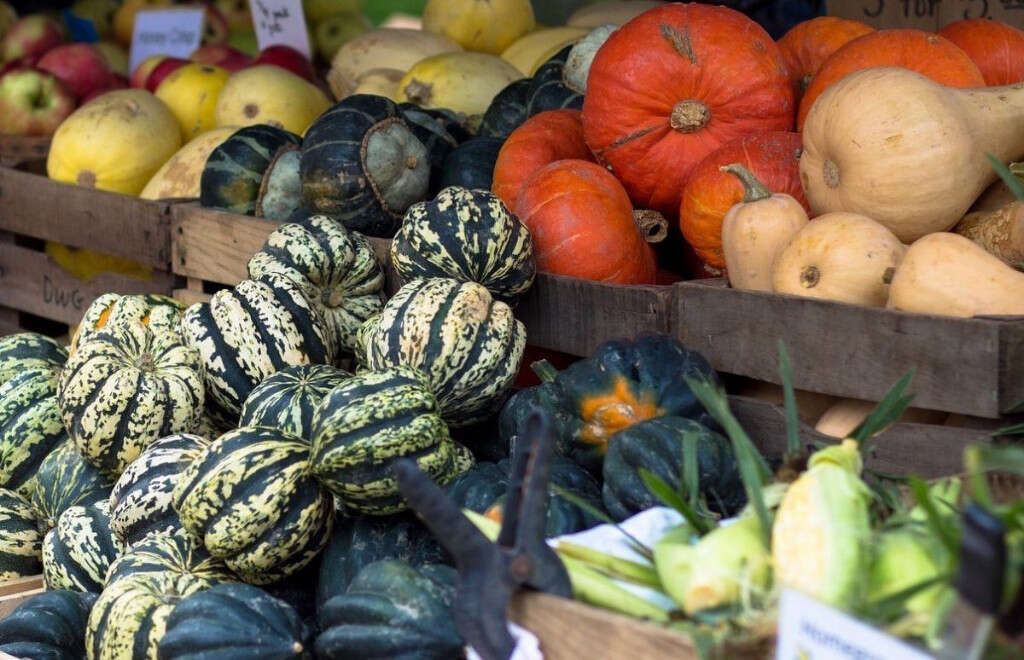
10 Benefits Of Squash
Squash belongs to the cucurbit family. Squash are separated into two categories, winter squash and summer squashes. Popular summer squash includes zucchini and yellow squash, whereas pumpkin and buttercup squash are popular winter ones.
Due to the seeds that accompany the food, squash are technically fruits. However, as they are rarely consumed raw, they are eaten like vegetables.
The difference between summer and winter squash is the texture and the time frame they are harvested. Despite their differences, both categories of squash are very healthy and are great way to replace some of those high calorie non-nutrient dense foods

Squash Benefit #1: Diabetes Management
Diabetes affects thousands of people around the world. Squash is a great option for diabetics because, though known as a starchy vegetable, it is very low in carbohydrates. Winter squash tends to be higher in carbohydrates then summer squash. For instance, 1 cup of cooked pumpkin contains 9 g of carbohydrates, whereas a zucchini only contains 3 grams.
Studies have also traced the vegetable to decreased blood sugar levels. In one human study, individuals with type 2 diabetes took an extract of winter squash. After 5 hours, their blood glucose was measured, and the levels were lower than expected.

Squash Benefit #2: Nutrient Dense
All squash are low calorie and contain little to no fat. They are also high in fiber, water, riboflavin, folate, vitamin C, and vitamin K, and numerous minerals such as potassium and manganese.
Due to its low calorie and nutrient dense profile, squash is a great addition to anyone’s diet. For instance, in one cup of cooked zucchini, which has approximately 124 grams, is only 21 calories. With this caloric amount, one will also get 40% of their daily allowance of vitamin C. This is an excellent amount of vitamin C, which is an essential antioxidant for fighting cancer.

Squash Benefit #3: Improves Digestion
Pattypan is a popular summer squash that is high in fiber. Fiber plays a major role in digestive health because it helps soften and move stool through the digestive tract. Diets low in fiber can often lead to pebble shaped stools that can cause constipation.
In just one cup of squash, an individual can expect to obtain 3 grams of fiber, which is roughly 15% of the daily value. In addition, this only provides 21 calories, which is great for weight management. A healthy digestion system can help prevent irritable bowel syndrome, ulcers, and even colon cancer.

Squash Benefit #4: Healthy Vision
Squash is packed with vitamin A, which plays a huge role in contributing to good eye health. Vitamin A has been proven to protect the cornea and help us see in the dark. With just one cup of zucchini, an individual will consume 15% of the daily amount of the vitamin. Pumpkin is high in vitamin A as well, with 197% of the daily value of the vitamin.
In addition, both types of squash are rich in lutein. Lutein is an antioxidant that has been proven to prevent eye diseases including cataracts and glaucoma. In everyday life, lutein is essential in filtering out high energy wavelengths.

Squash Benefit #5: Rich in Calcium
Butternut squash is rich in calcium. Individuals with poor calcium intake are at risk for low bone density and osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is very common in elderly populations. However, it takes years to develop. Thus, it is essential to ensure calcium is a part of your diet throughout your lifetime for early prevention.
Getting calcium from squash is a great way to avoid excess calories. Dairy is very high in calcium. However, studies have shown the calories and fat that follow may cause more damage than harm. Thus, getting calcium from vegetables, such as squash, may be very beneficial. For instance, a 12-year study conducted by Harvard showed that even though women drank milk three times a day they were actually more prone to bone fractures in comparison to women who rarely drank milk.

Squash Benefit #6: Versatile
There are numerous different types of squash. From sweet dumpling squash to spaghetti squash, there are over 15 edible varieties available. Thus, chances are you will find at least one type of squash that you like.
In addition to the numerous types. Squash can also be prepared in several different ways. Some use squash as a low carbohydrate alternative. This can be seen in dishes such as zucchini enchiladas, as squash fries or squash made into noodles. It can be also prepared in stews, can be baked, grilled, or steamed. Regardless of the way, it is a very versatile food that can be eaten as a snack or as part of a main dish.

Squash Benefit #7: High in Folic Acid
It is very important to get enough folic acid in your diet. This vitamin is linked to proper DNA synthesis, red blood cell creation, and a deficiency in the vitamin can also have mental affects that can lead to depression. Folic acid is also very important in women who are of child bearing age, as the vitamin is essential to proper brain and spinal cord formation in unborn infants.
Luckily, squash is high in folic acid and can help you meet the daily allowance of the vitamin. In one cup of a winter squash you can expect to consume 57 mcg of folate, which translates to 15% of the daily value. Summer squash are slightly lower in folate. 1 cup contains 36 mcg translating to 9% of your daily value.

Squash Benefit #8: High in Potassium
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death in the United States. To maintain good heart health, it is essential to maintain a healthy blood pressure. Getting enough potassium in the diet is one way to ensure this is possible.
Numerous studies have shown a diet high in potassium and low in sodium has been associated with a reduced risk of death from heart disease. Unfortunately, the average American does not consume the recommended daily amount of 4700 mg per day. For those many Americans who suffer from heart disease and are lacking the necessary amount of potassium, squash is a great way to consume the mineral.
Squash Benefit #9: Fights Cancer
Cancer has taken the lives of millions of people worldwide. Numerous research is being done into how to treat the aggressive disease as well as how to prevent it from occurring altogether. A huge part of this research considers what foods can help.
A lot of research has gone into the promising effects of the health properties in pumpkins, which are high in carotenoids, compounds that can function as antioxidants. This allows them to neutralize free radicals, which may protect against certain cancers. An analysis of 13 studies showed that people with higher intake of alpha-carotene and beta-carotene had significantly lower risks of stomach cancers.

Squash Benefit #10: High in Vitamin C
Squash is very high in vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid), which is also an antioxidant and important to immune system health. Numerous studies have shown that consumption of vitamin C can help prevent cold and flu by strengthening the immune system. Though not common any longer, the fatal disease known as Scurvy is the result of a vitamin C deficiency. Recent studies have proven that vitamin C can protect against endothelial dysfunction, high blood pressure, and blood vessel changes that can lead to heart disease.
If you eat enough squash, and other vitamin C rich food, you can reap many of its benefits. Vitamin C is also important for faster healing of wounds and burns. It’s vital to collagen production – keeping skin firm, smooth and youthful-looking.












