10 Side Effects of ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are a group of drugs primarily used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) and congestive heart failure. ACE inhibitors causes the relaxation of blood vessels leading to lower blood pressure and less oxygen demand. This means that the heart does not have to work as hard.
As the name suggests, this medication inhibits the angiotensin converting enzyme, which plays an important role in the renin angiotensin system. By blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, it results in increased venous capacity and decreased arteriolar resistance, cardiac output, stroke work, cardiac index, and resistance in blood vessels.
Some examples of frequently prescribed ACE inhibitors are perindopril, captopril, enalapril, lisinopril, benazepril, and ramipril. Below are 10 side effects of ACE inhibitors to be aware of.
Side Effect #1: Hypotension
Hypotension or low blood pressure occurs when the systolic blood pressure is less than 90 mmHg or if the diastolic blood pressure is less than 60 mmHg. In practice, hypotension only occurs if there are noticeable symptoms. Severe hypotension can deprive the vital organs and brain of nutrients and oxygen, resulting in shock.
Individuals with hypotension may experience breathlessness, tachycardia, chest pain, headache, dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. Some causes of hypotension include hemorrhage, use of diuretics, side effects of ACE inhibitors, and cardiovascular disease. This is one of the most common side effects associated with ACE inhibitors and depending on the specific drug, it can affect up to 10% of patients.

Side Effect #2: Cough
A cough is a protective and repetitive reflex that helps to clear the airways from microbes, irritants, fluids, and foreign particles. There are three phases of a cough: inhalation, forced exhalation, and release of air from the lungs. Frequent coughing may indicate underlying disease.
From an evolutionary perspective, many pathogens benefit by causing the host to cough as it helps the spread of disease to other potential hosts. Some causes of a cough include gastroesophageal reflux disease, respiratory tract infection, post-nasal drip, lung tumors, and medications such as ACE inhibitors. A cough due to ACE inhibitors is believed to be due to the increased bradykinin levels produced by the medication.

Side Effect #3: Fatigue
Fatigue is a gradual feeling of tiredness that can be alleviated by rest. It can be divided into physical and mental fatigue. Physical fatigue is the temporary inability to maintain maximal physical performance while mental fatigue refers to the temporary inability to maintain optimal cognitive performance. Fatigue can manifest as lethargy or somnolence.
Medically, fatigue is a common and nonspecific symptom seen in various conditions such as dehydration, sleep deprivation, nutrition deficiency, cancer, infection, and side effects of medications such as ACE inhibitors.

Side Effect #4: Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia occurs when serum potassium is higher than normal. It is a possible side effect of ACE inhibitors due to the medication’s effect on aldosterone. The suppression of angiotensin II results in a reduction of aldosterone, which decreases potassium excretion.
Hyperkalemia may lead to cardiac dysfunction and neuromuscular issues such as nausea, paresthesia, muscle weakness, and diarrhea. Monitoring of potassium levels in patients who take ACE inhibitors is important to ensure that there is no hyperkalemia.
Side Effect #5: Headache and Dizziness
A headache refers to pain that occurs anywhere in the region of the neck and head. There are many types of headaches such as migraines, cluster headaches, and tension-type headaches. Although headaches are common, frequent headaches can negatively impact employment, school, and relationships. These individuals also have an increased risk of depression.
Dizziness can refer to presyncope, vertigo, and disequilibrium. Dizziness can be associated with nausea, vomiting, feeling faint, and muscular weakness. Both headaches and dizziness have been reported in patients who take ACE inhibitors.

Side Effect #6: Agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis refers to low levels of granulocytes, which include the neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. It occurs when the levels of granulocytes drop below 500 cells/mm3 of blood. It is a serious condition where individuals affected have a very high risk of severe infections due to a suppressed immune system.
Patients with agranulocytosis may have no symptoms or present with sudden chills, fever, rigors, and a sore throat. Any infection present will also progress rapidly. Causes of agranulocytosis include side effects of medications such as valproate, carbamazepine, ACE inhibitors (benazepril), propylthiouracil, carbimazole, naproxen, and indomethacin.

Side Effect #7: Renal Impairment
Renal or kidney impairment has been reported to be a significant potential side effect of all ACE inhibitors due to their mechanism of action. Those who start using ACE inhibitors will usually have some reduction in the glomerular filtration rate, which generally stabilizes after several days.
However, in individuals with conditions where there is decreased renal perfusion such as polycystic kidney disease, renal artery stenosis, volume depletion, or heart failure, the glomerular filtration rate reduction may be significant. In these patients, the glomerular filtration rate maintenance depends on the angiotensin-II-dependent efferent vasomotor tone.
Side Effect #8: Angioedema
Angioedema occurs when there is swelling of the lower layer of the skin and tissue under the mucous membranes or skin. It may occur in the larynx, face, tongue, arms, legs, and abdomen. It is often associated with hives and usually has a rapid onset. It is believed to be due to histamine or bradykinin.
With histamine, it may occur due to allergy to foods, insect bites, or medications. This can be treated with corticosteroids, antihistamines, and epinephrine. When due to bradykinin, it may be due to a lymphoproliferative disorder or ACE inhibitors.

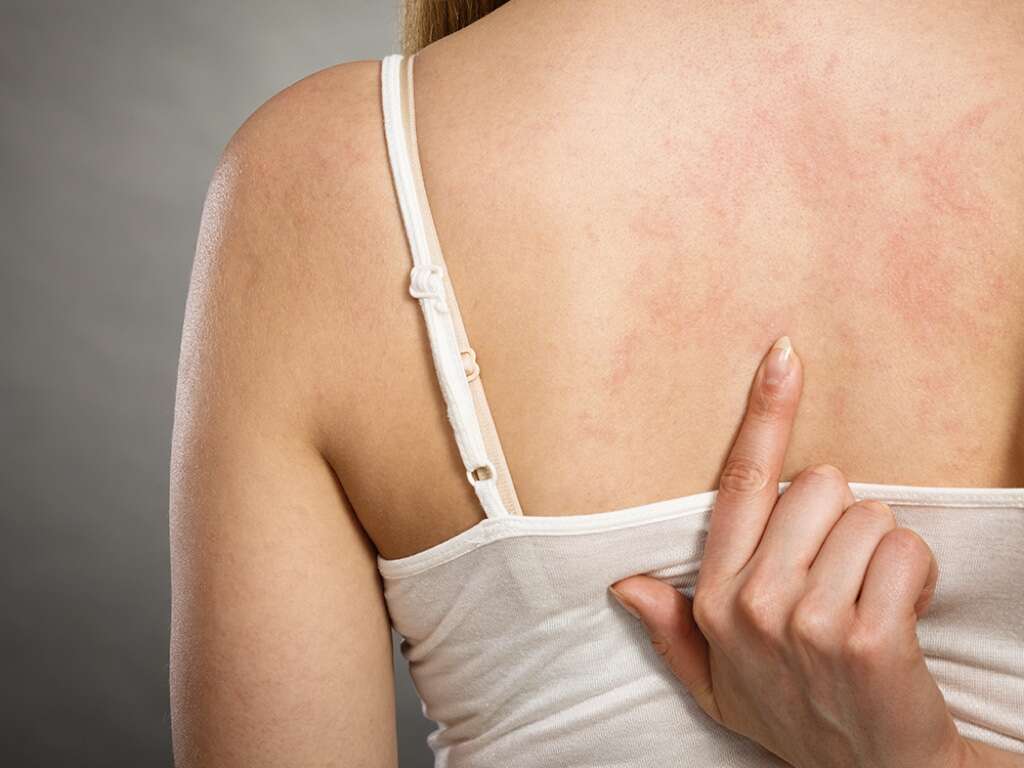
Side Effect #9: Rash
This is a fairly common side effect reported by patients taking ACE inhibitors. Usually the rash is characterized by red papules in the body that may or may not cause an itch. It can be seen in the thorax and back but it can appear anywhere in the body too.
Any skin rash after the administration of a drug most be notified to a medical professional in order to prevent further complications.

Side Effect #10: Pregnancy Side Effects
While there are some drugs that have been proven to be safe if taken during pregnancy, ACE inhibitors have been shown to cause side effects if taken during any of the trimesters of pregnancy. It has been reported to cause neonatal deaths, stillbirths, congenital malformations, oligohydramnios, hypotension, renal dysplasia, intrauterine growth retardation, patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary hypoplasia, and incomplete ossification of the skull.
ACE inhibitors are not safe during pregnancy (C – D category) and should be discontinued if pregnancy is suspected. The most serious side effects during pregnancy occur during exposure in the second and third trimester. ACE inhibitors also enter breast milk; therefore, they are not recommended during lactation either.