10 Side Effects of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are a class of drugs that can be used in the treatment or management of abnormal heart rhythms, and secondary prevention for myocardial infarction, hypertension, and heart failure.
Beta blockers competitively block the receptor sites for epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) that mediate the sympathetic nervous system.
Some beta blockers affect all types of beta-adrenergic receptors while others are specific for one of three beta receptors: β1—heart and kidneys, β2—lungs, liver, uterus, gastrointestinal tract, vascular smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle, and β3—fat cells. Below are 10 side effects of beta blockers to be aware of.
Side Effect #1: Fatigue
Fatigue is a gradual feeling of tiredness alleviated by rest. Fatigue can be divided into physical and mental fatigue. Physical fatigue describes the temporary inability of the muscles to maintain optimal performance while mental fatigue occurs when there is transient inability to achieve optimal maximal cognitive performance.
Fatigue can manifest as somnolence or lethargy. It is a common and nonspecific symptom that can be seen in various conditions such as dehydration, sleep deprivation, stress, disease, and cancer. It can also be a side effect of some medications such as beta blockers.
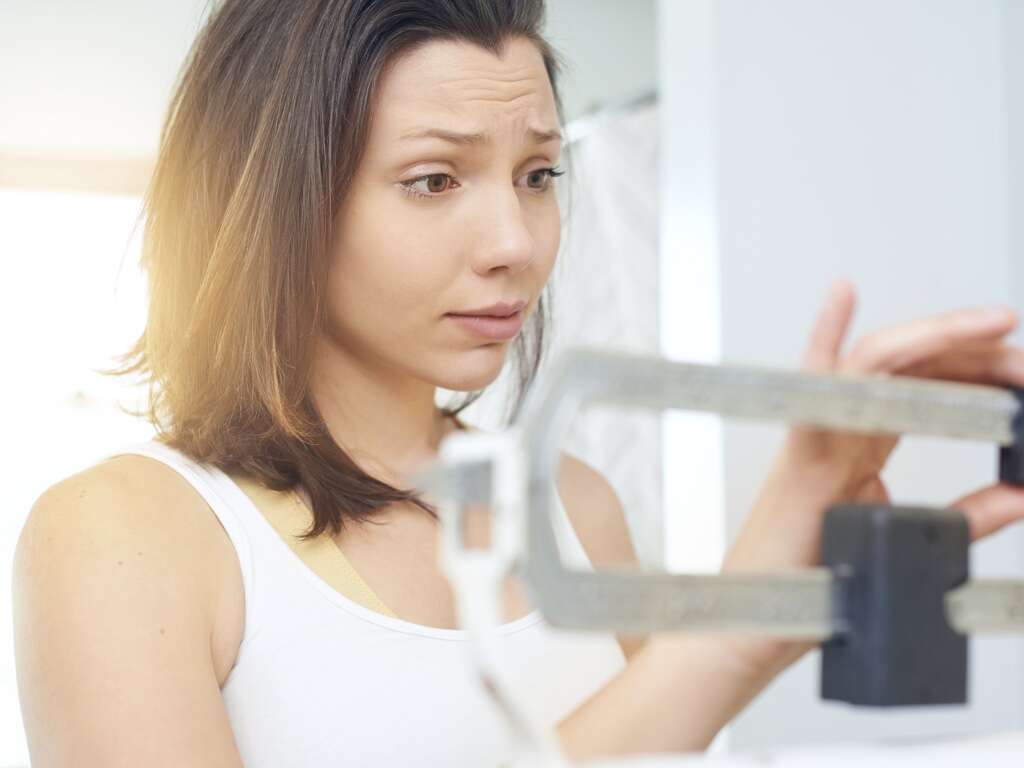
Side Effect #2: Weight Gain
Weight gain occurs when there is increase in body weight due to increase in fluids, muscle mass, fat deposits, or other factors. Weight gain is a known side effect of some beta blockers, especially the older beta blockers such as metoprolol and atenolol.
The average weight gain has been found to be about 1.2 kilograms (2.6 pounds). Newer beta blockers do not usually lead to weight gain. Patients who experience weight gain of more than 1–1.4 kg (2–3 lbs) a day or 2.3 kg (5lbs) in a week after starting beta blockers for heart failure should inform their doctor as the weight gain may mean that there is fluid buildup.

Side Effect #3: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea refers to the sensation when one is unable to breathe well enough. Dyspnea can be evaluated based on the degree of distress, impact on daily activities, and intensity of discomfort.
In 85 percent of patients, dyspnea is caused by conditions such as pneumonia, asthma, interstitial lung disease, cardiac ischemia, congestive heart failure, psychogenic causes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Dyspnea may also occur in patients who take beta blockers due to the effect of the medication that causes bronchospasms or bronchoconstriction.
Side Effect #4: Depression
Depression refers to a state of low mood that can affect behavior, thoughts, feelings, tendencies, and a sense of well-being. While a depressed mood can be normal in certain life events such as death of a loved one, it can also be a side effect of some medical treatments and drugs.
Depression may occur with the use of contraceptives, isotretinoin, beta-blockers, interferon therapy, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics. Patients with a prolonged depressed mood should seek a professional opinion as there may be an underlying psychiatric or medical condition that may require and benefit from treatment.
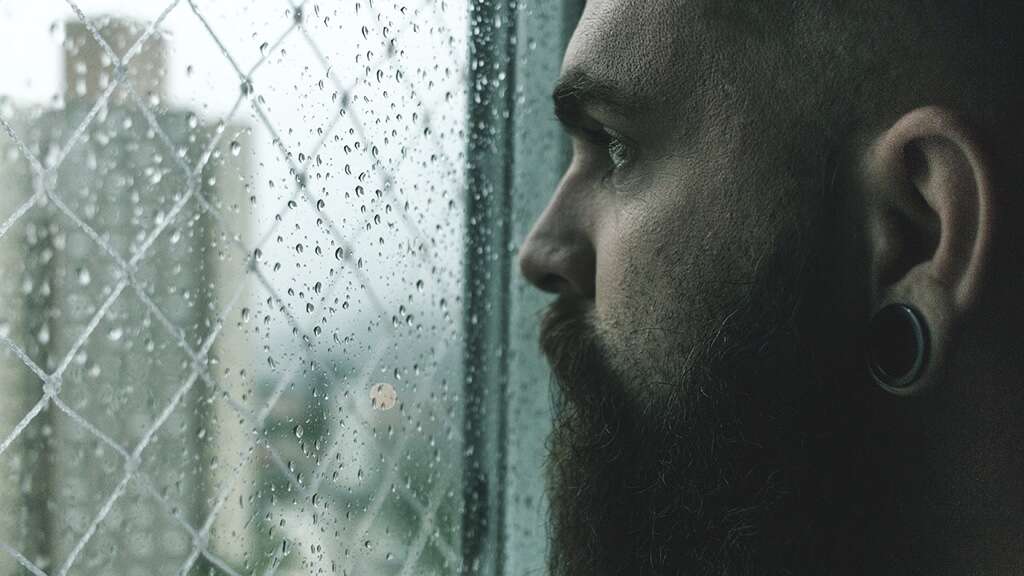

Side Effect #5: Insomnia
Insomnia or sleeplessness refers to the condition where an individual has problems falling asleep or staying asleep. Insomnia usually leads to low energy, drowsiness, depressed mood, and irritability. It has also been associated with increased risks of road traffic accidents and issues with learning and focusing. Insomnia can be short term or long term.
Causes of insomnia include psychological stress, heart failure, chronic pain, hyperthyroidism, restless leg syndrome, menopause, use of caffeine, nicotine use, and side effects of medications such as beta-blockers. This happens in less than 5% of patients taking beta-blockers, especially with acebutolol.
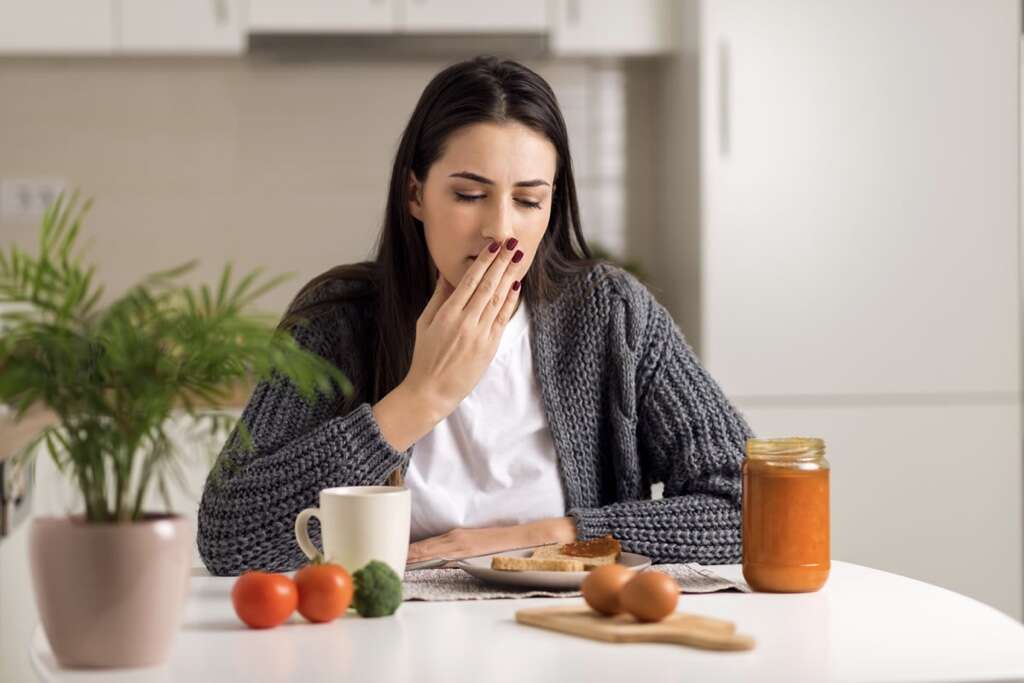
Side Effect #6: Nausea
Nausea refers to the unpleasant and uncomfortable sensation where there is an urge to vomit. While it may not be painful, it can be a debilitating symptom as it places discomfort on the back of the throat, chest, and upper abdomen.
Nausea is a vague and common symptom seen in various conditions such as motion sickness, migraine, dizziness, low blood sugar, fainting, gastroenteritis, and food poisoning. It is also a side effect of many medications like chemotherapeutic agents, antibiotics, and beta blockers. Nausea can be managed using antiemetics such as ondansetron, promethazine, and metoclopramide.

Side Effect #7: Sexual Dysfunction and Erectile Dysfunction
Beta blockers can cause both sexual dysfunction and erectile dysfunction. Sexual dysfunction refers to experiencing difficulty during any stage of normal sexual activity. Sexual dysfunction occurs when the individual feels extremely distressed along with interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunction is an important issue as it can significantly impact the person’s sexual life.
Erectile dysfunction or impotence occurs when there is inability to maintain an erection. Diseases that can cause erectile dysfunction include cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord disease, and vascular disease. Erectile dysfunction occurs due to the effect of beta blockers, which cause peripheral vasoconstriction.
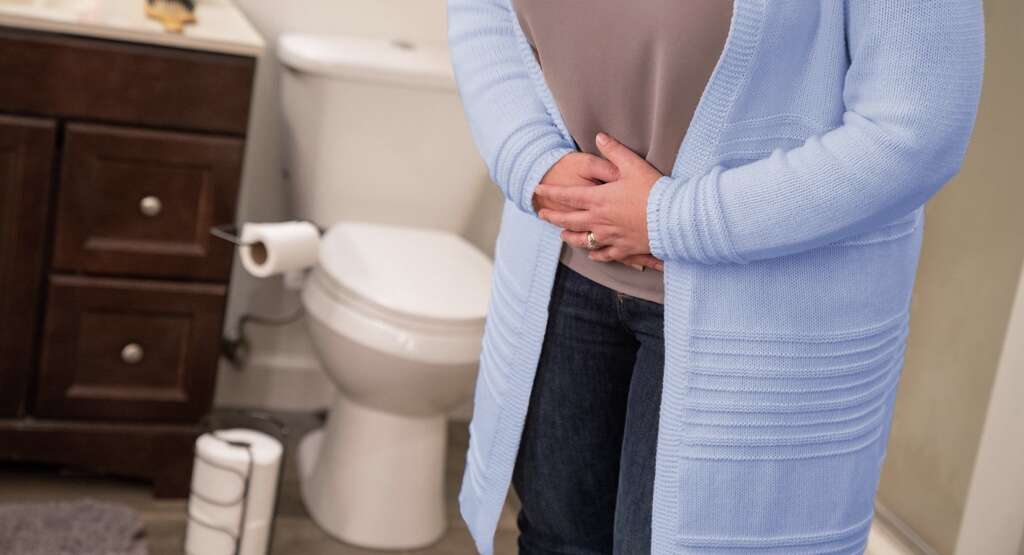
Side Effect #8: Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurs when there is three or more episodes of liquid, loose, or watery stools a day. Diarrhea usually lasts several days and can result in dehydration if there is excessive fluid loss. Excessive diarrhea that causes dehydration can lead to irritability, loss of skin color, tachycardia, decrease responsiveness, and decreased urination.
The commonest cause of diarrhea is an infection of the intestines (viral, bacterial, parasitic). Other causes include irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, and hyperthyroidism. All beta blockers can cause diarrhea.

Side Effect #9: Bradycardia and Hypotension
Bradycardia occurs when an individual (adult) has a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute. In most cases, bradycardia does not generally produce any symptoms until it drops below 50 beats per minute.
Symptoms include weakness, dizziness, fainting, and sweating. Bradycardia can also occur when the dosage of beta-blockers is too high. Hypotension occurs as beta-blockers slow down the heart rate, which in turn decreases blood pressure.
Side Effect #10: Hallucinations and Nightmares
Hallucinations refer to perceptions despite the absence of external stimulus. Hallucinations are usually vivid and occur during consciousness. They should be distinguished from an illusion, which is a misinterpretation of a real perception.
Hallucinations can occur in any modality such as olfactory, visual, auditory, tactile, gustatory, proprioceptive, nociceptive, and thermoceptive. Most hallucinations due to beta blockers usually resolve after several hours of drug discontinuation. Nightmares or bad dreams are an unpleasant dream where there is usually anxiety, fear, sadness, and despair. Nightmares and hallucinations are more likely to occur in patients who receive lipophilic beta blockers such as metoprolol and propranolol. These episodes are much lower in patients receiving hydrophilic beta blockers.