10 Lymphoma Symptoms
Lymphoma is a group of cancers that affect the lymphatic system. It develops from a type of white blood cell known as lymphocytes. While there are many subtypes of lymphoma, the two main categories are Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. The World Health Organization (WHO) has also included immunoproliferative diseases and multiple myeloma as two other categories of lymphoma. Approximately 90% of cases are non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Those with Epstein-Barr virus infection or have a positive history of Hodgkin lymphoma have a higher risk of the disease. For non-Hodgkin lymphoma, risk factors include human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, autoimmune disease, human T-lymphotropic virus infection, pesticides, and those on immunosuppressants.
Diagnosis of the disease can be achieved through blood, bone marrow, and urine tests. Lymph node biopsy may be performed if there are enlarged lymph nodes. Medical imaging can be used to see the extent of metastasis as lymphoma often spreads to the brain, liver and lungs.
Treatment of lymphoma can include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and surgery. In some cases, plasmapheresis (plasma exchange) and expected management may be the treatment of choice. The five-year survival rate for those with Hodgkin’s lymphoma is about 85% and for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, approximately 69%. In 2012, there were 566,000 new cases of lymphoma leading to 305,000 deaths. It makes up for 3 to 4% of all cancers and is the seventh most common cancer among adults, while third most common among children. Let’s explore some of the symptoms of Lymphoma.
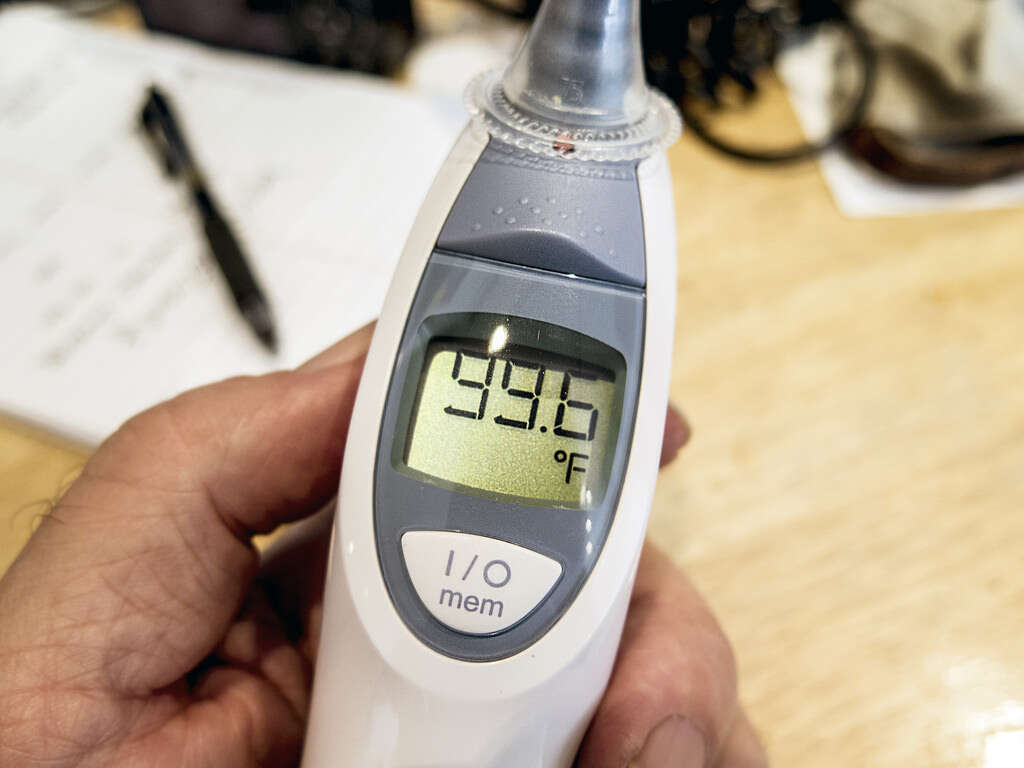
Symptom #1: Fever
In lymphoma, the fever is usually of unknown origin (FUO) or also known as pyrexia of unknown origin (PUO). This refers to a situation were the affected individual has an elevated temperature but although many investigations are performed, there is usually no explanation. Most fevers related to lymphoma are usually low grade and can be accompanied by other symptoms such a night sweats, chills, and more.
Fever occurs as it is the body’s natural way of responding to help the immune system fight against pathogens (bacterial, viral) and also cancers (abnormal cells). The fever is also persistent. This means that taking over the counter medication to relieve fever only lasts as long as the medication is still in the system. Once the medication’s half life is over, the fever returns.
Symptom #2: Night Sweats
Sweating is a natural phenomenon where it is the body’s natural way of cooling itself. It can happen to anyone at any time of the day. However, in night sweats the affected individual experiences increased episodes of excessive sweating at night. It leads to the drenching of clothes and blankets while you are in bed.
Some may even find that it is no longer an option to continue sleeping until the sheets are changed and pillows are aired out. Some patients have likened it to just getting out of a swimming pool. Night sweats only occur if the room is not abnormally warm.

Symptom #3: Weight Loss
A dramatic amount of weight loss is a definite sign to seek medical attention. A dramatic amount of weight loss occurs when you lose more than 5% of your body weight in less than six months without going through a new exercise routine, diets, or intentionally trying losing weight.
While it is a non-specific symptom and can be caused by other medical issues, it can be a sign of lymphoma as the growth and multiplication of cancer cells starts burning up more energy in your body. This results in your body starting to fight back which also burns more energy. Both these factors can lead to dramatic weight loss especially when lymphomas grow quickly. Seek medical attention if you unintentionally lose 5% of your weight in 6-12 months.

Symptom #4: Appetite Loss
Many patients suffering from lymphoma also experience loss of appetite which contributes to weight loss. Appetite loss can occur due to several factors such as the lymphoma affecting the abdomen, causing pain and swelling. It may be due to an enlarged lymph node or enlarging organs that have gotten involved in the disease. The fullness in the abdomen can be due to the build up of a high amount of fluid.
Splenomegaly (or enlargement of the spleen) can increase pressure on the stomach which contributes to the feeling of fullness and loss of appetite. Other abdominal symptoms such as nausea, pain, and vomiting can also contribute to loss of appetite.

Symptom #5: Weakness
The constant growth of cancer cells uses up more energy and nutrients in your body. This can lead to feelings of tiredness, weakness, and lethargy. If the lymphoma has affected the bone marrow, it may also interfere with the production of blood cells.
When the production of red blood cells is affected, the function of carrying oxygen to supply the rest of the body will be affected leading to more feelings of weakness. Anemia causes circulation to not be able to supply adequate oxygen to important organs such as the brain and muscles.

Symptom #6: Lumps or Lymphadenopathy
This is one of the most common and sometimes the sole symptom of lymphoma. The lumps are often felt around regions such as armpits, neck, and groin. Needless to say, these lumps may be enlarged lymph nodes. While it may not always be a sign of lymphoma, it is important to have a doctor examine them.
Most of these bumps are first noticed during bathing or by a partner. The enlarged lymph node is not usually painful, but some patients have reported pain in the lump after alcohol consumption. Swollen lymph nodes have various causes such as infections, other cancers, and more.

Symptom #7: Pruritus
Pruritus or itching can occur in individuals with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Approximately 33% of patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma often experience itching although there is no rash seen. It most commonly affects regions such as the hands, feet, body, or lower legs.
Patients who live in hot climates can find it to be distressing. The itching usually worsens at night. While the exact cause of itching in lymphoma is unknown, many experts believe that it is due to the release of cytokines. However, in cases of lymphoma that affects the skin, the itching of the affected area is due to the disease itself.

Symptom #8: Breathlessness
Lymphoma that starts or originates in the chest or thymus can increase in pressure by pressing on the adjacent structures such as the trachea (windpipe). This can lead to issues such as coughing, chest pain, or difficulty breathing. Another structure known as the superior vena cava is a large vein that functions to carry blood from the arms and head to the heart. It passes closely to the thymus and lymph nodes that are in the chest.
Lymphomas that are in the chest region can push on the superior vena cava causing the blood to be pushed back into the head and arms. This leads to a blush-reddish tint of the skin in the head, upper chest, and arms leading to difficulty breathing and, in some cases, change in consciousness. This is known as superior vena cava syndrome and should be treated as soon as possible.

Symptom #9: Brain Symptoms
When lymphomas affect the brain, it can lead to issues such as difficulty processing, headaches, personality changes, and weaknesses in certain parts of the body. Some patients may also experience seizures.
Once in the brain, it can spread to the spinal cord causing other issues such as facial numbness, difficulty with speech, and even double vision.

Symptom #10: Skin Symptoms
Lymphoma of the skin can present as papules (lesions that look like pimples, patches (lesions that are flat), nodules (lumps or bumps), and plaques (thickened lesions, can be raised or lowered). These lesions on the skin are usually itchy, scaly, and have a reddish to purplish tint. The lesions usually show up on different parts of the skin that are not exposed to the sun. Larger lesions have a risk of ulcerating.
Other symptoms that are seen along with skin issues are lymphadenopathy, fever, weight loss, and itchiness. While having these symptoms are not a confirmation of lymphoma, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible for early diagnosis and treatment.