Health Benefits of Cloves
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Cortes-Rojas, Diego Francisco, et al. 'Clove (Syzygium Aromaticum): a Precious Spice.' PubMed Central (PMC), Feb. 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3819475
- 2. Kuroda, Minpei, et al. 'Hypoglycemic Effects of Clove (Syzygium Aromaticum Flower Buds) on Genetically Diabetic KK-Ay Mice and Identification of the Active Ingredients.' PubMed, Journal of National Medicine, Apr. 2012, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21987283
- 3. 'Spices, cloves, ground.' FoodData Central, U.S. Department of Agriculture, 1 Apr. 2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171321/nutrients
- 4. 'Manganese.' Mount Sinai Health System, www.mountsinai.org/health-library/supplement/manganese
- 5. Santin, Jose, et al. 'Gastroprotective Activity of Essential Oil of the Syzygium Aromaticum and Its Major Component Eugenol in Different Animal Models.' PubMed, 8 Dec. 2010, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21140134
- 6. Hu, Qiao, et al. 'Progress on the Antimicrobial Activity Research of Clove Oil and Eugenol in the Food Antisepsis Field.' Wiley Online Library, Journal of Food Science, 26 May 2018, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1750-3841.14180
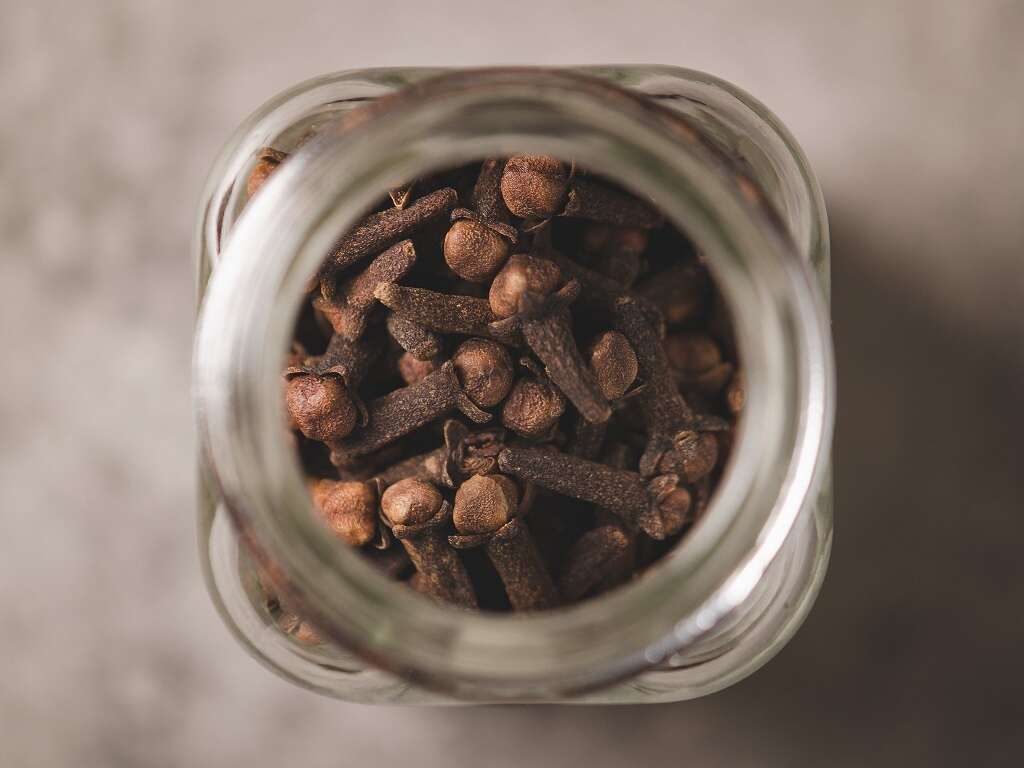
Good Source of Beta-Carotene
Whole cloves are dark brown. When ground up, the brown hue takes on a red-orange tint. This color comes from the beta-carotene in cloves. The human body uses this compound to make vitamin A, which is essential for eye health.
Beta-carotene may also help protect the skin and enhance cognitive function and memory due to its antioxidant characteristics. Those features may slow down the ravages of aging caused by free radicals and limit cell damage.
Advertisement