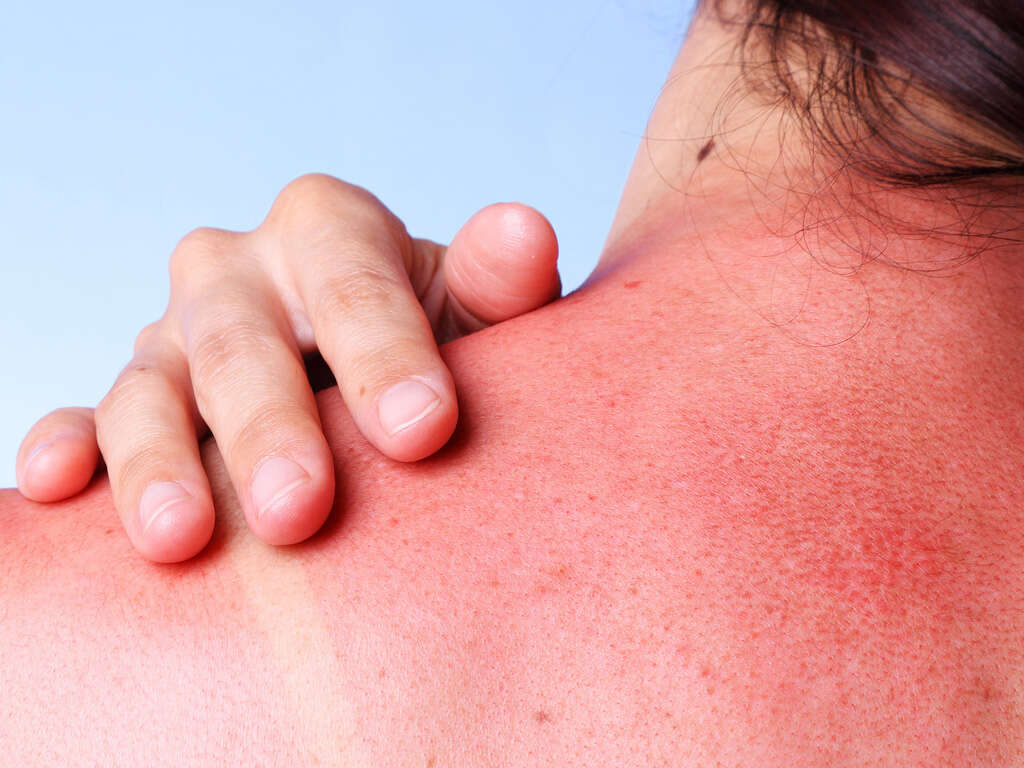
What Is Sun Poisoning?
As summer approaches, more and more people look for ways to soak up the sun. They plan beach vacations, picnics and other outdoor entertainment. A small amount of sunlight every day can be healthy and ensure that you get your recommended dosage of vitamin D. There is such a thing as too much of a good thing, though. Sunburn or its extreme version, sun poisoning, can end a great outing on a sour note.
Sun poisoning occurs when you are exposed to too many of the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Different factors influence whether or not you are in danger of sun poisoning. Understanding the risks and signs of this painful condition can help you recognize it in its initial stages so that you are able to get out of the sun and hopefully avoid further exposure. Here are 10 things you should know about sun poisoning.

1. Some People Are at Higher Risk
The sun’s UV rays do not affect everyone in the same way. Some people can stay outside all day and experience very few negative outcomes. Others must be vigilant about the length of time they stay in the sun and how often they reapply sunscreen.
People who have fair skin and light-colored hair, particularly redheads, are more prone to sun poisoning than those with darker skin tones or dark hair. These people have less melanin, which absorbs UV light and protects the skin from damage. Certain medications can also make you burn more easily in the sun. For example, many birth control drugs, antidepressants, acne medication, heart pills and antibiotics can increase your skin’s sensitivity to sunlight. Certain fragrances in perfumes and body lotion can also intensify the effect the sun has on your exposed skin. Knowing your risk level can help you take the right precautions before spending time outdoors.
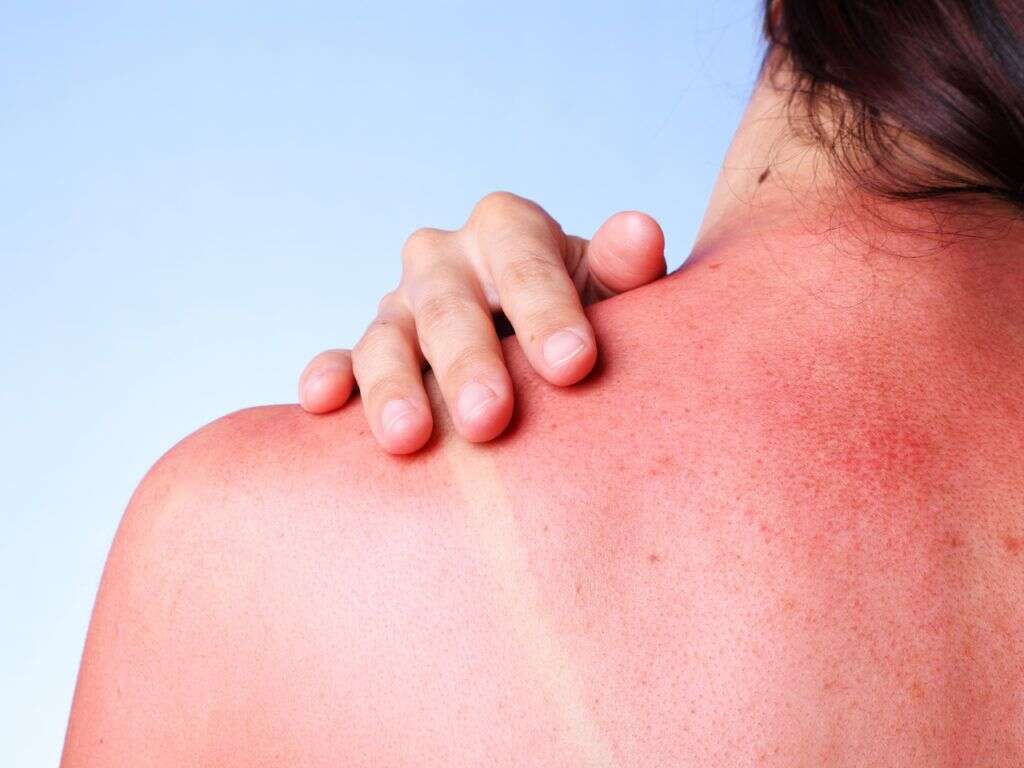
2. There Are Many Symptoms
The most widely known symptom of sunburn is reddened skin. Most people will experience at least a mild sunburn at some point in their lives. Sun poisoning is a severe sunburn that may come with other symptoms. In addition to getting redder, you may notice blisters on your skin, particularly if you get a sunburn while you are in water.
You may have sun poisoning if you feel like you have cold or flu-like symptoms after spending time in the sun. Nausea, headache, dizziness, pain and even fever and chills can result from overexposure to UV rays. Dehydration is another likely side effect, which can exacerbate the other symptoms. If you feel like you’re getting sick after a day at the beach, you may actually have sun poisoning.
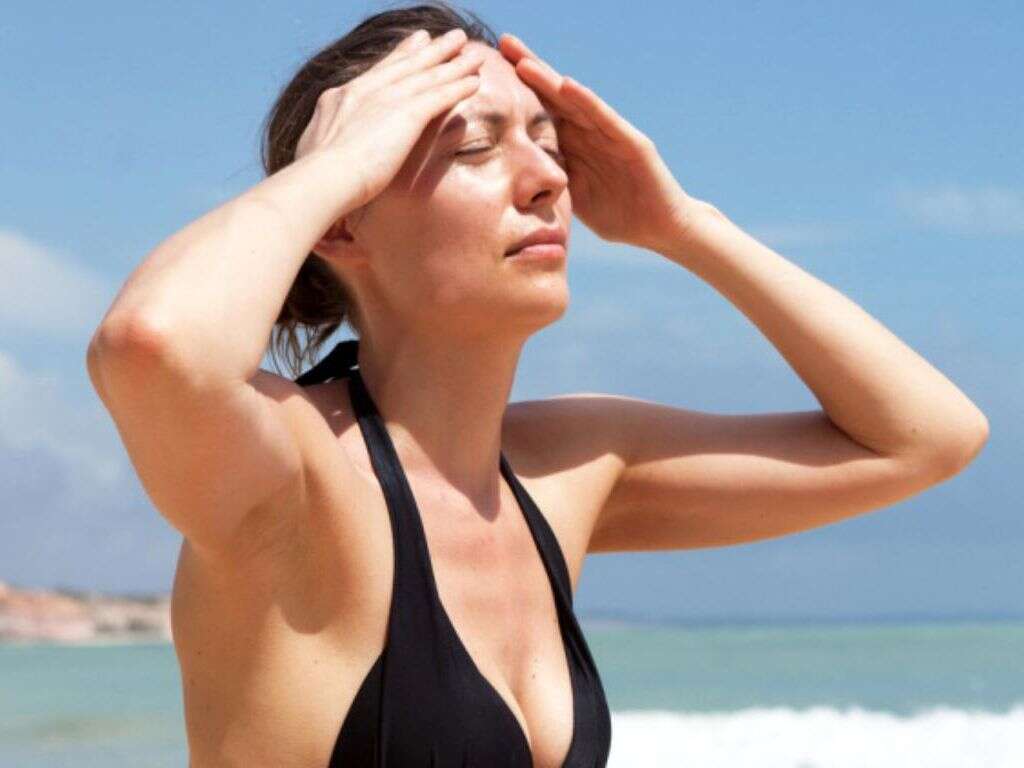

3. Symptoms May Not Show Up Quickly
Despite its ominous name, sun poisoning doesn’t actually poison you. Therefore, you don’t feel the effects as acutely as you would with a regular poison. You are not likely to feel any difference until the damage has already been done. You may not even see a difference in the tone of your exposed skin. Hours later, however, you will definitely notice that something is wrong.
Even though it may only take 15 minutes for a sunburn to occur, different people feel the effects of overexposure to the sun in different ways. Some people may notice that their skin is getting pinker as soon as it happens. Others may not see a visible difference until hours after they’ve gone back inside. Because a lot of sun damage happens under the surface of the skin, it may take it a while for symptoms to appear.

4. There Are Different Types of Sun Poisoning
Polymorphous light eruption is a type of sun poisoning that affects people from climates that don’t get a lot of direct sunlight when they travel to sunny locations. The sudden increase in the intensity of the exposure leaves them more susceptible to the harmful effects of UV light. PMLE is characterized by a rash that appears within hours of exposure. It may appear in the form of small bumps covering the affected area, splotches of bump clusters or even hives.
Solar urticaria occurs in individuals who are extremely sensitive to sunlight. A rash can develop within minutes of intense exposure. In extreme cases, people who suffer from solar urticaria can become dizzy or even pass out. Anyone experiencing these symptoms should get emergency medical care.
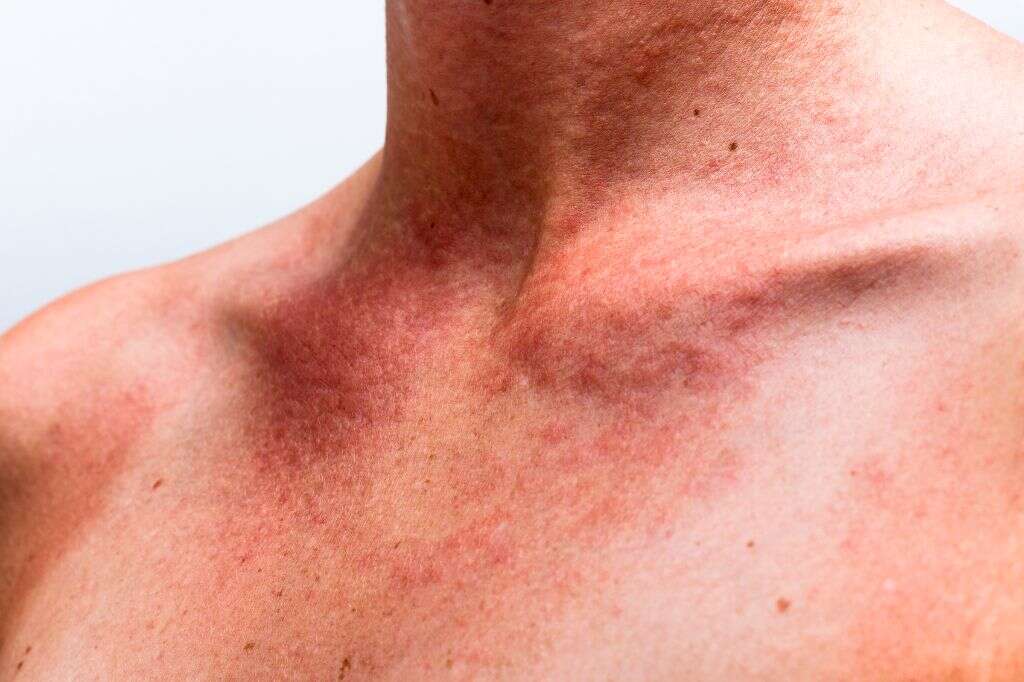
5. Most Treatments Can Be Done at Home
Minor symptoms should be treated the same way that you would handle a regular sunburn. The most important thing you can do if you have sun poisoning is to cool the affected area. While it’s vital that you avoid shocking your skin with cold water, if you are able to take a cool bath, it can pull some of the heat out of the burn. You can also apply cool compresses to your skin to achieve the same effect.
After you have cooled your skin down, you need to replenish its moisture. Drink extra water to hydrate your whole body. Apply aloe vera gel or some other soothing moisturizer to the burned skin for relief. If you have a fever or pain, an over-the-counter pain reliever such as ibuprofen should do the trick.

6. Affected Skin Should Be Shielded From Further Exposure
Another important step to take is to stay out of the sun as much as possible while you are healing. If you can avoid going outside, do so. Avoid windows, as they can let in UV light that could make the problem worse.
If you must go out, make sure that you cover your burned skin as much as possible. Avoid tight clothing over the burn so that you don’t irritate the rash. Wear loose clothing over the burn so that it’s shielded from the rays. Try to dress in heavier materials, as UV light can get through gauzy fabrics.

7. Severe Symptoms May Require Professional Treatment
With any luck, you will be able to handle the effects of sun poisoning from home. But if you have more severe symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical care. The earlier you get treated, the faster your doctor can help you find relief for your symptoms.
There are several signs that you need to go to the doctor or emergency room. Severe burns that include blisters or charred, discolored or broken skin need stronger treatments than a cool bath or compress. If your fever or nausea persists after you have been out of the sun a few hours, you may need more help than OTC medications can provide. If you are experiencing respiratory distress or intense swelling, you may need to visit an urgent care facility so that you can get help right away.

8. Sunburn Can Usually Be Prevented With the Right SPF
The best treatment is always prevention. It is not feasible that you can avoid the sun altogether, and spending time outdoors frequently is actually good for your health. You just need to take the appropriate precautions before you go out.
Your primary defense against UV rays is a good sunscreen. Choose a broad-spectrum formula that guards against both UVA and UVB rays. You need a lotion or spray with at least 30 SPF. Plan ahead well enough that you can apply it liberally to any exposed skin at least 15 minutes prior to going out in the sun. This gives it time to soak into the skin and provide the best protection. Reapply sunscreen every two hours or more often if you are in water or are sweating a lot.

9. Avoiding Midday Sun Can Lower Your Risk
Another way to avoid bad sunburns or sun poisoning is to limit your exposure during the time of the day when the sunlight is the most intense. Specifically, you should take extra care between the hours of 10:00 in the morning and 2:00 in the afternoon. The sun is highest in the sky during this time and thus exposes you to more direct sunlight.
This practice is especially important in certain scenarios. Water, sand and snow all reflect light. When you are outside in the middle of the day in these elements, you are not only getting the direct sunbeams from above but also being exposed to extra sunlight from the reflection. Save your skiing and sand volleyball for the early morning, late afternoon or evening.

10. Untreated Sun Poisoning Can Lead to Complications
As with any condition, you need to take sun poisoning symptoms seriously. Ignoring symptoms does not make them magically disappear. In fact, in many cases, it could worsen your condition. For example, chronic dehydration can lead to many other problems. Everything your body does requires water. When you are dehydrated, your body’s ability to regulate its temperature and function normally is compromised.
Another problem that can result from untreated sun poisoning is infection, particularly if your burn is severe. Any time the skin is irritated, it is more susceptible than usual to the bacteria in the air or on the surface of your skin. Make sure the affected area is cleaned and monitor it closely so that you can seek medical care if the problem gets worse.