What Is Respiratory Acidosis?
It is very important to keep our lungs and the rest of our respiratory system in good working order. This is one reason why regular exercise is recommended – it helps to keep the cardiovascular system strong and healthy. Things can still go wrong, however, even when due care is taken.
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that is caused when the respiratory system is unable to function as well as it usually would. It will be mild in some cases, while it can be very serious in others. Here is a closer look at respiratory acidosis, what can cause it, and what the symptoms and treatment are.
1. Respiratory Acidosis
Every time that we breathe in, we intake a load of oxygen that is essential for us. When we exhale, we breathe out the unused air along with some other gases that are waste products of our body’s metabolism. The main waste gas we emit is carbon dioxide (CO2).
Some people will find that they are unable to remove as much carbon dioxide from the body as they need to in a condition known as Respiratory acidosis. Increased levels of CO2 will cause our blood to become increasingly acidic, and this can cause problems for us. It can be life-threatening in some cases.

2. Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
There are two types of respiratory acidosis: chronic and acute. Chronic respiratory acidosis develops slowly over a long period of time. It can cause some symptoms, although symptoms are usually very mild and will often be barely noticeable. Some people with the condition will not even notice any symptoms at all.
The reason for this is that the gradual development of the condition means the body has time to adjust. In order to help counter the increased acidity of the blood, for example, the kidneys will begin to produce certain substances to normalize pH. The chronic version of the condition will sometimes turn into the acute version, however.
3. Causes of Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
There are several potential causes of chronic respiratory acidosis. One of these is asthma, which will cause breathing problems for the patient, thus potentially resulting in a build up of CO2. Severe obesity is another potential cause because the additional body mass can make it harder for the patient’s lungs to expand fully.
There is also pulmonary edema, which is the accumulation of fluids in the lungs. Another potential cause is an abnormal curvature of the spine known as scoliosis, which can affect the lungs’ ability to function properly. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is another potential cause, as are some neuromuscular disorders, including multiple sclerosis.
4. Symptoms of Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
As mentioned, most people with chronic respiratory acidosis will not notice that they have any symptoms whatsoever. When there are symptoms, they are usually very mild and will have little to no impact on the patient’s quality of life. There are some symptoms that some patients might notice, however.
Some people with the condition will experience difficulties sleeping. This can make things harder for them because they will then be feeling tired the following day. Some people might undergo some very subtle changes in their personality, and others might find that their memory is not as sharp as it used to be.
5. Acute Respiratory Acidosis
Unlike the chronic version of the disease, acute respiratory acidosis will develop very quickly. The symptoms can progress to become very severe and it can pose a very real threat to the patient’s life if it is not treated in time. It should always be treated as a medical emergency.
This occurs because the changes in the acidity of the patient’s blood have been sudden. This means that the kidneys and other organs have not had time to adjust to the higher levels of CO2 in the blood. There are numerous potential reasons that this might happen, some of which can be very dangerous in themselves.

6. Causes of Acute Respiratory Acidosis
One of the potential causes for acute respiratory acidosis is a cardiac arrest, which itself is a condition where the heart suddenly stops pumping. When this happens, the cardiovascular system will no longer be working as usual, and CO2 levels in the body can begin to rise rapidly. A cardiac arrest in itself can be fatal.
Other potential causes include lung problems such as pneumonia and asthma. Conditions that can have an impact on the patient’s rate of breathing can also be an underlying cause. A blockage of the airways can result in the condition, as can a problem with the muscles that affect breathing. An overdose of sedatives is the cause in some cases.

7. First Signs of Acute Respiratory Acidosis
The symptoms of acute respiratory acidosis are likely to develop quickly, and one of the symptoms is a headache. A headache by itself is unlikely to raise an alarm, but the patient should get help if the symptom is unusually severe. The patient will also likely experience other symptoms.
Patients will also sometimes find that their vision becomes blurred, which should cause some alarm if it develops suddenly. Anxiety is another potential symptom and a feeling of restlessness will also arise in some cases. Some patients will also become very confused, which is another indicator that they probably need medical assistance.

8. Advanced Symptoms
If acute respiratory acidosis is suspected then it is important to get treatment for the patient as soon as possible. This is because the symptoms are going to get a lot worse. One of the symptoms is that the patient will develop a shortness of breath, which in itself should be of concern if it happens for no apparent reason.
The patient can also become very lethargic, regardless of how active they might otherwise be. Others may experience extreme confusion and even delirium. Some patients will even go into a coma, which is an extremely serious condition, but they may still be able to pull through if they have the appropriate medical assistance in time.

9. Diagnosis
In order to diagnose respiratory acidosis, it will be necessary to know the pH level of the patient’s blood. Other tests will help to tell how much CO2 and oxygen there is in the blood, while tests may also be performed to help measure the levels of electrolytes in the blood.
In order to treat the condition fully, doctors will also need to know what the underlying cause is. This can include x-rays and other methods of determining how well the lungs are functioning. Other tests may look at how much glucose there is in the blood, and doctors may also look to see if there are certain drugs in the patient’s body.
10. Treatment
If you have chronic respiratory acidosis then medical professionals may look at procedures that will help to improve that functioning of the patient’s respiratory system. This can mean medication to reduce inflammation, to expand the airways, or to reduce excess fluid. Antibiotics may be used to treat any infections that are present.
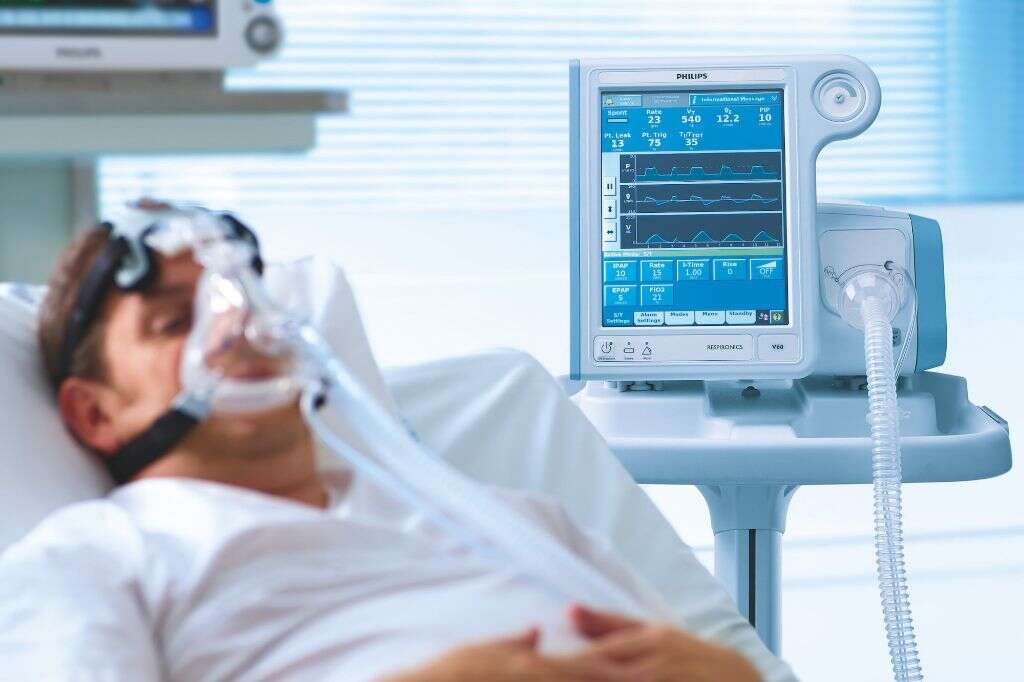
In instances of acute respiratory acidosis, it may be necessary to put the patient on a ventilator to ensure they continue to get the oxygen they need. This will also help to remove excess CO2. It will also be necessary to treat the underlying cause of the condition.