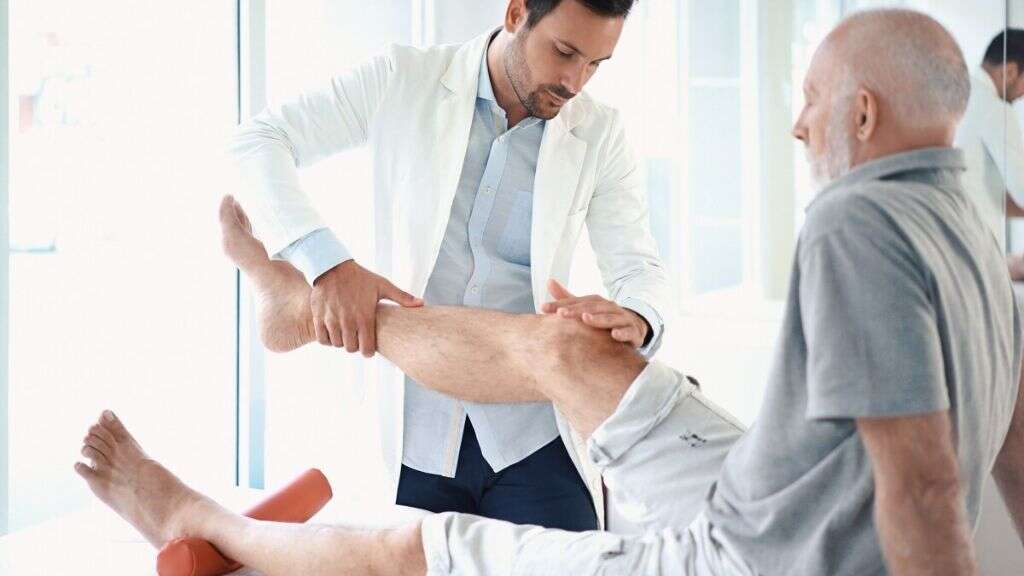
What Is Osteoarthritis?
6. Diagnosis
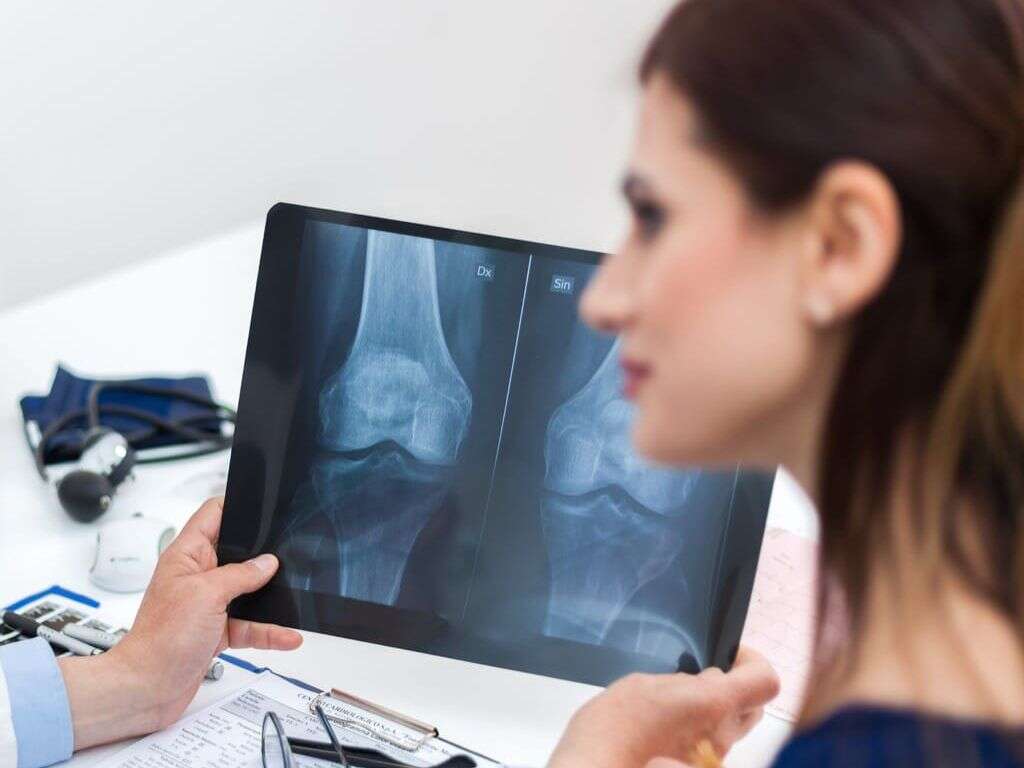
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis can be achieved via a combination of clinical and radiographic evidence. Patients with osteoarthritis do not usually have any specific laboratory abnormalities. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) levels and white blood cell (WBC) counts are generally not elevated.
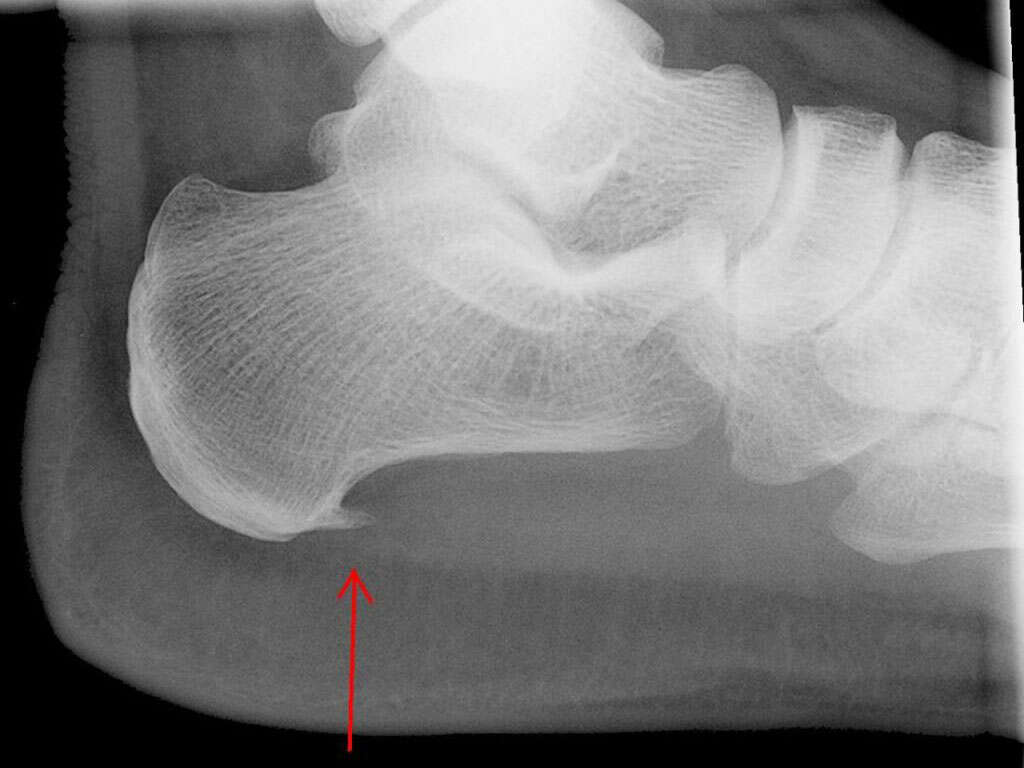
Some cases of erosive inflammatory arthritis may cause slight elevation in these tests. Plain radiographs are the investigation of choice for osteoarthritis as they are cost-effective and easily accessible. Plain radiographs usually show joint-space loss, cyst formation, and subchondral bony sclerosis. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan can show the characteristics that can be seen on plain x-rays but is generally unnecessary unless there are additional pathology that can be resolved through surgery. Bone scans and arthrocentesis are investigations that can be beneficial for diagnosis.
Advertisement