10 Foods High in Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 sometimes also called cobalamin, is an essential micronutrient in the human body. It has a role in brain and nerve functions, production of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. Vitamin B12 also helps maintain healthy blood through prevention of megaloblastic anemia. Its deficiency can lead to brain and nerve dysfunction, confusion, depression, numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, among other symptoms 1https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/. It is therefore necessary that you regularly take adequate amounts of vitamin B12.
An average adult requires 2.4mcg of vitamin B12 per day 2https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-Consumer/. And although you may take vitamin B12 supplements, it is generally healthier and less costly to eat foods that contain adequate amounts of the vitamin. Vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal-based foods. However, other food products may be fortified with cobalamin and other vitamins. Here are 10 foods high in vitamin B12.

Vitamin B12 Rich Food #1: Shellfish
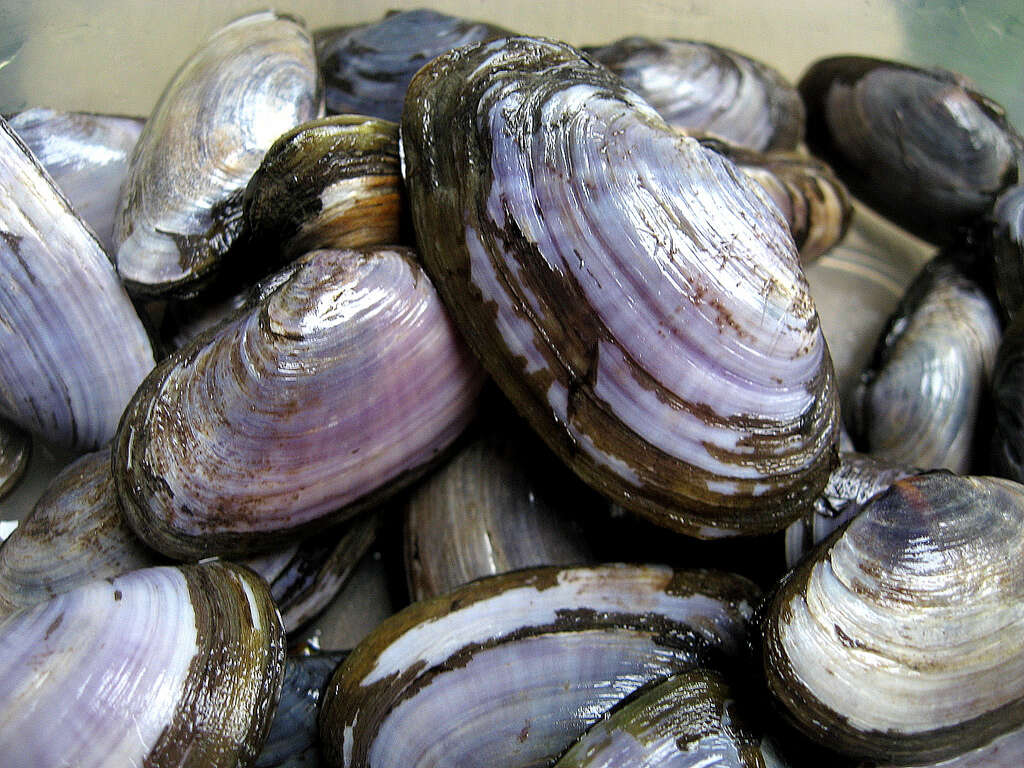
According to the USDA, National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, shellfish such as oysters and clams, contain very high amounts of vitamin B12. For instance, 3 ounces of clam contain 84.06 micrograms of B12. This is more than 35 times the 2.4 mcg recommended dietary allowance, or RDA. Other shellfish like oysters and mollusks are also high in vitamin B12.
Additionally, shellfish are high in protein, iron and antioxidants. Other food products made with shellfish are also high in vitamin B12. For instance, 3 1/2 ounces of canned clam broth contains more than 100 % of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12.

Vitamin B12 Rich Food #2: Liver
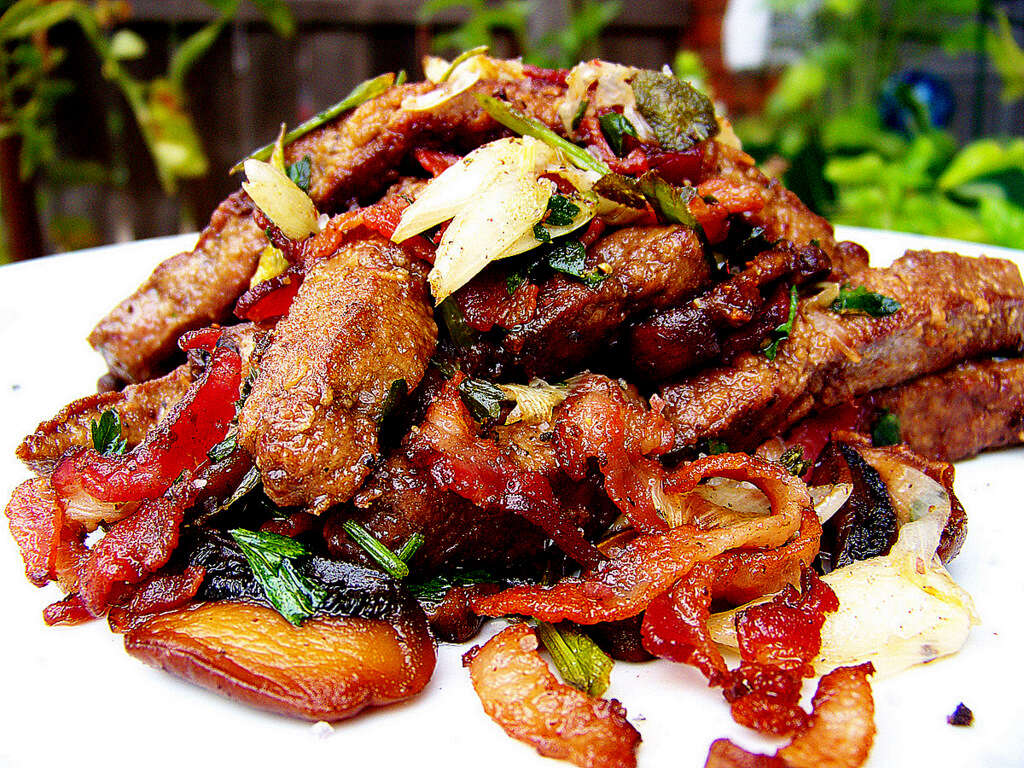
The liver from beef, lamb, pork and chicken are very high in vitamin B12. 3.0 ounces of boiled beef liver contains 81.60 micrograms or 34 times the RDA of vitamin B12. Cooked lamb liver contains 67.07 micro grams of B12, while raw goose liver contains 50.76 micrograms of vitamin B12. You can also get similar amounts of vitamin B12 from the livers of other animals.
Liver is also rich in protein, iron, vitamin B2 and minerals like selenium. Besides the liver, other organ meats such as kidneys are also high in vitamin B12. 3.0 ounces of cooked lamb kidney contains 67.07 micro grams of vitamin B12.

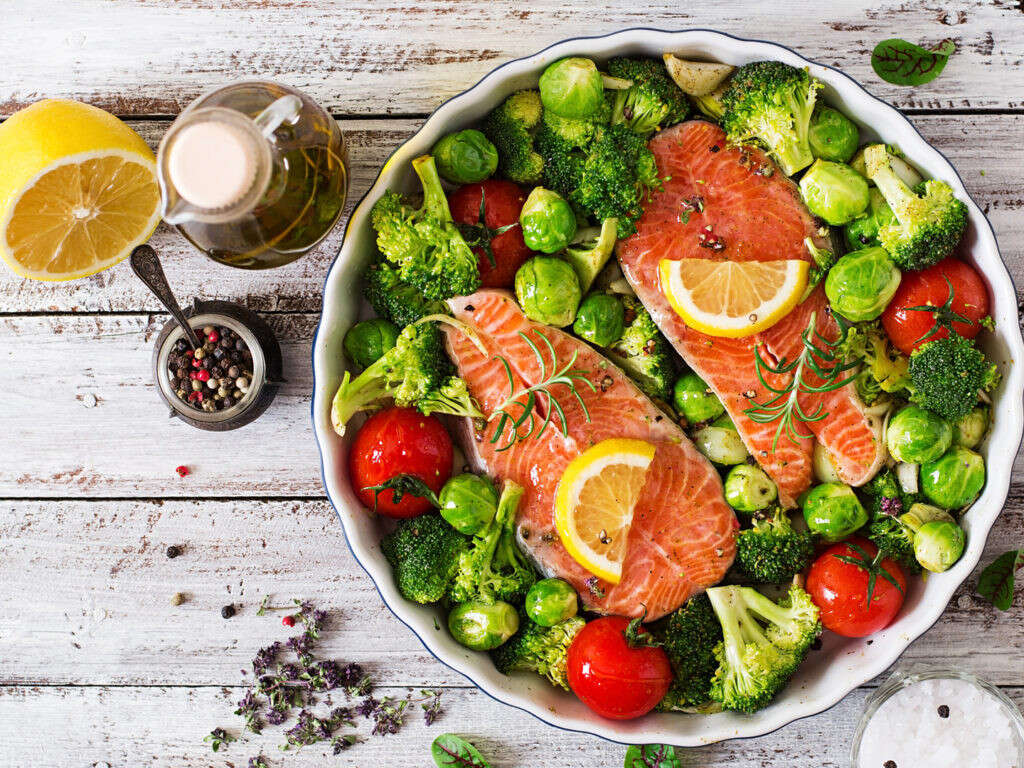
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #3: Salmon
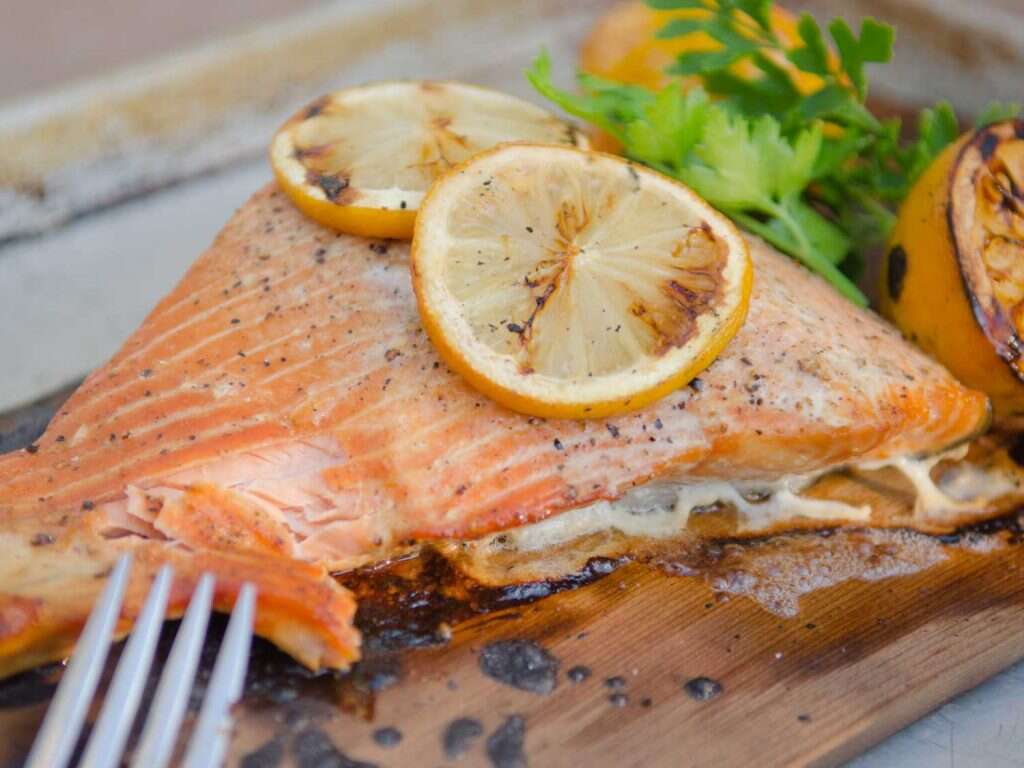
Small fish such as salmon, sardines, tuna, herring, mackerel, and trout contain high vitamin B12 foods. One smoked fillet of the red sockeye salmon provides 19.55 micro grams, or 8 times the RDA of vitamin B12. One fillet of cooked Atlantic herring fish contains 18.79 micrograms of vitamin B12; while one fillet of cooked mackerel provides 16.72 micrograms of the cobolamin vitamin.
Besides vitamin B12, oily fish like mackerel and salmon are rich sources of omega 3 fatty acids and vitamins B2, B6, folate, D, E and K. They also contain protein and minerals like iron, calcium, magnesium, selenium, phosphorus, potassium and zinc. It is worth noting that wild caught fish are better sources of vitamin B12 and other nutrients than their farmed counterparts.

Vitamin B12 Rich Food #4: Crabs and Other Crustaceans
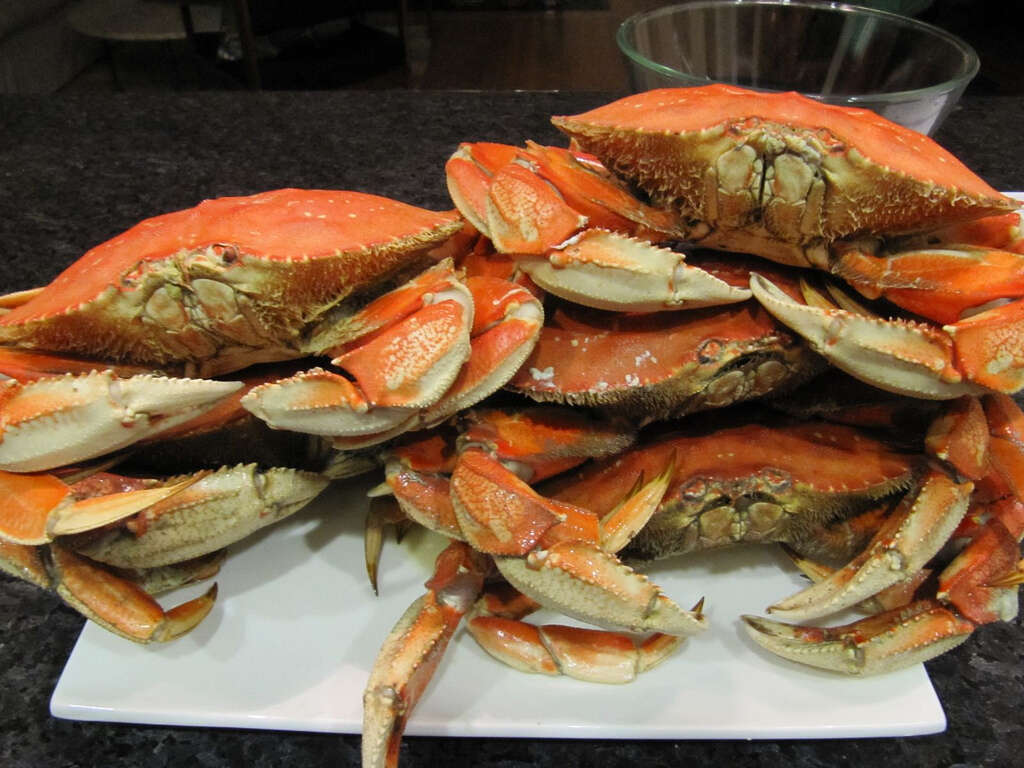
Crustaceans like crabs, shrimps, lobsters, krill, and crayfish are aquatic animals which are used as food. They are excellent sources of vitamin B12 beside other nutrients. One leg of an Alaskan king crab, weighing about 134 grams, contains 15.4 micrograms of cobalamin. This is a lot more than the recommended daily allowance of 2.4 micrograms. 4 ounces of shrimp provides 1.88 micrograms of vitamin B12. Other crustaceans have similar amounts of vitamin B12. Note that if you eat crabs regularly, they contain very high amounts of sodium.
In addition to cobalamin, crustaceans contain other vitamins including A and C, cholesterol and fat. They are also good sources of protein and minerals like iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, zinc and magnesium.

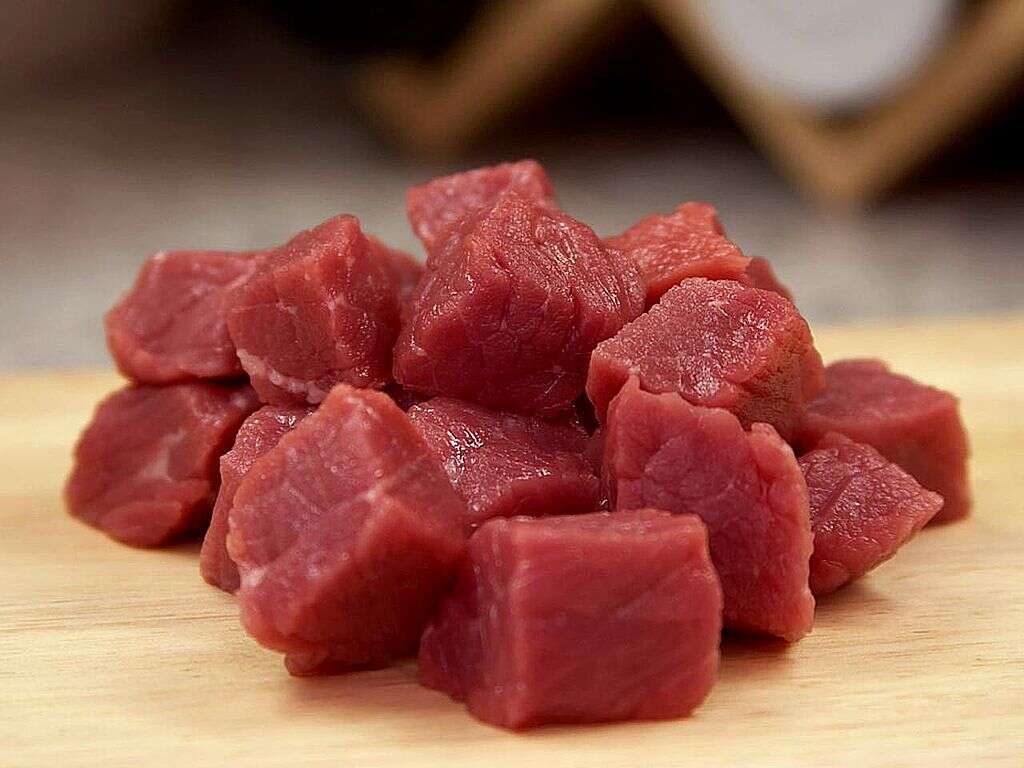
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #5: Red Meat
Red meat such as beef and lamb is a rich source of vitamin B12. A 3.0 ounce cut of grilled beef steak without fat provides 6.95 micro grams of vitamin B12. This is almost three times the recommended dietary allowance of cobalamin. Lamb and other red meats are also excellent sources of vitamin B12.
Red meat also contains vitamins B3 and B6, protein and fat. Additionally, red meat provides significant amounts of iron and other minerals like selenium and zinc. To access even more benefits, choose pasture raised meat. Pasture raised meat is a good source of omega 3 fatty acids which provide anti-inflammatory support to the body.

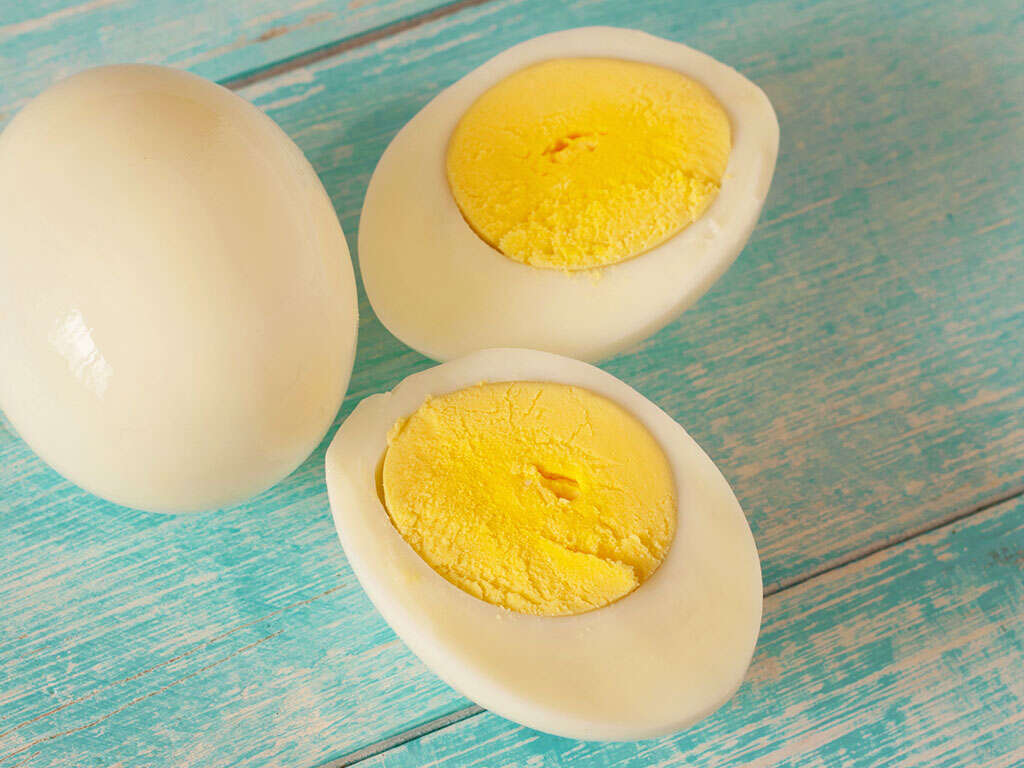
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #6: Eggs
Chicken, duck, goose and quail eggs are a source of many readily digestible nutrients. They are also a rich source of vitamin B12. One goose egg contains 7.3 micrograms of vitamin B12, one duck egg contains 3.8 micrograms while one large chicken egg contains 0.45 micrograms and one quail egg has 0.1 micrograms of cobalamin. Most of the vitamin B12 in eggs is found in the yolk.
Eggs also provide a nutrient called choline which the liver requires for proper functioning. Additionally, eggs contain vitamins B2, B6, D, E, K protein, fat and minerals like iron, calcium, selenium and zinc and antioxidants like carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin.

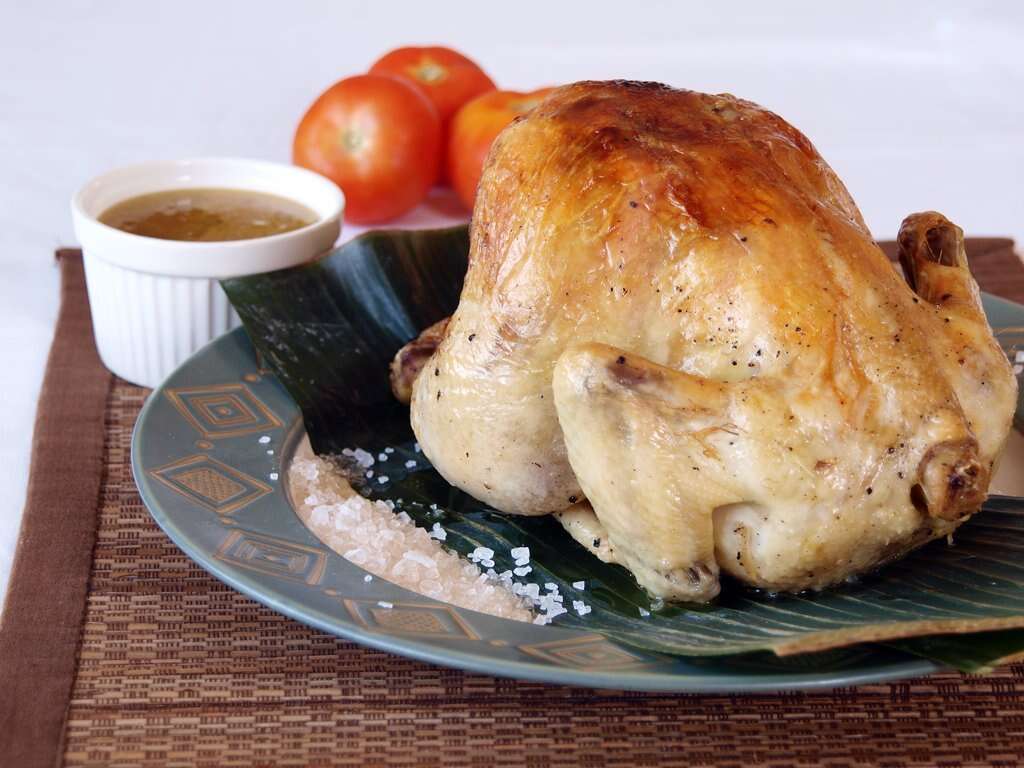
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #7: Poultry
Chicken, turkey and other poultry meats are an excellent alternative to red meats for protein and other nutrients. Poultry is white meat, and without skin contains minimal amounts of fat. It also contains significant amounts of vitamin B12, besides vitamins A, C, B6, niacin, riboflavin, thiamin, folate and pantothenic acid. A 3 ounce serving of roasted chicken breast with skin contains 0.31 micrograms of vitamin B12. Turkey has a similar amount of cobalamin. Because this is almost one eight of the RDA of vitamin B12, use it in combination with other richer sources.
Poultry is also a good source of minerals such as iron, selenium, manganese, copper, zinc and phosphorus.

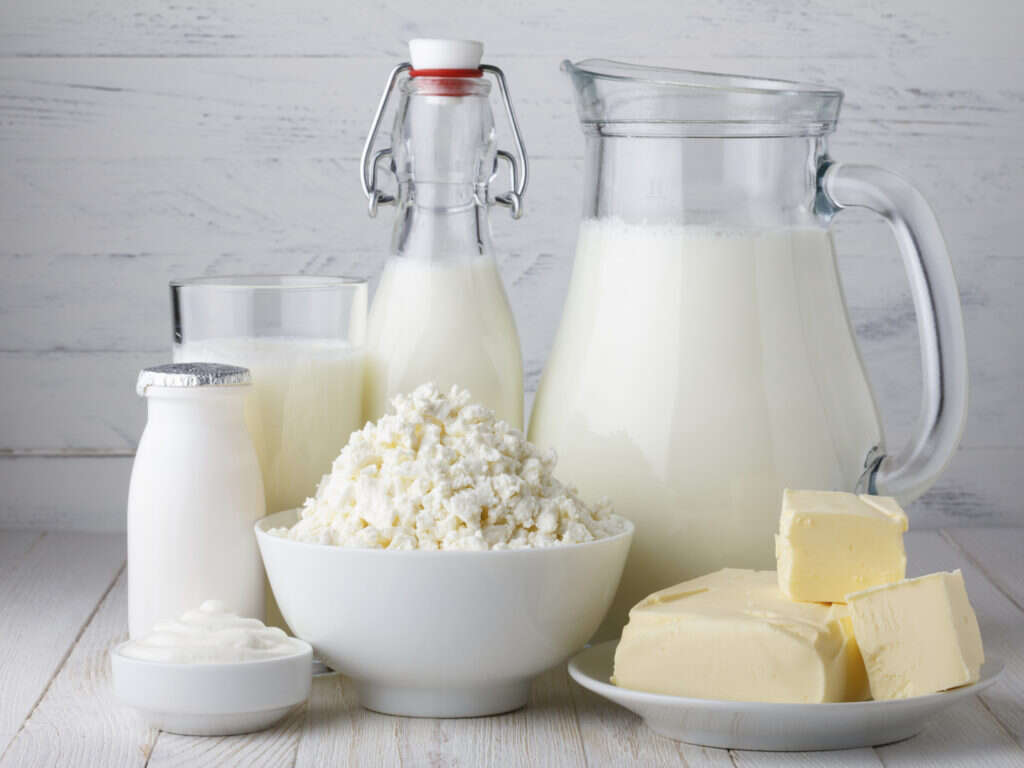
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #8: Milk and Milk Products
One cup of unfortified, whole or skimmed milk contains 4.16 micrograms of vitamin B12. This means that by drinking one cup of milk, you get enough cobalamin for the day. Yoghurt and cheese contain similar amounts. Vitamin B12 from dairy is more readily absorbed into the body. According to some studies, your body accesses vitamin B12 from milk and other dairy products better than from sources like beef, eggs and fish. In addition to cobalamin, milk contains other vitamins including A, B1, B2, D and choline.
Other nutrients in milk and yoghurt include protein, calcium, potassium, phosphorus and magnesium. Milk from pasture-fed animals is also a good source of vitamin K2.

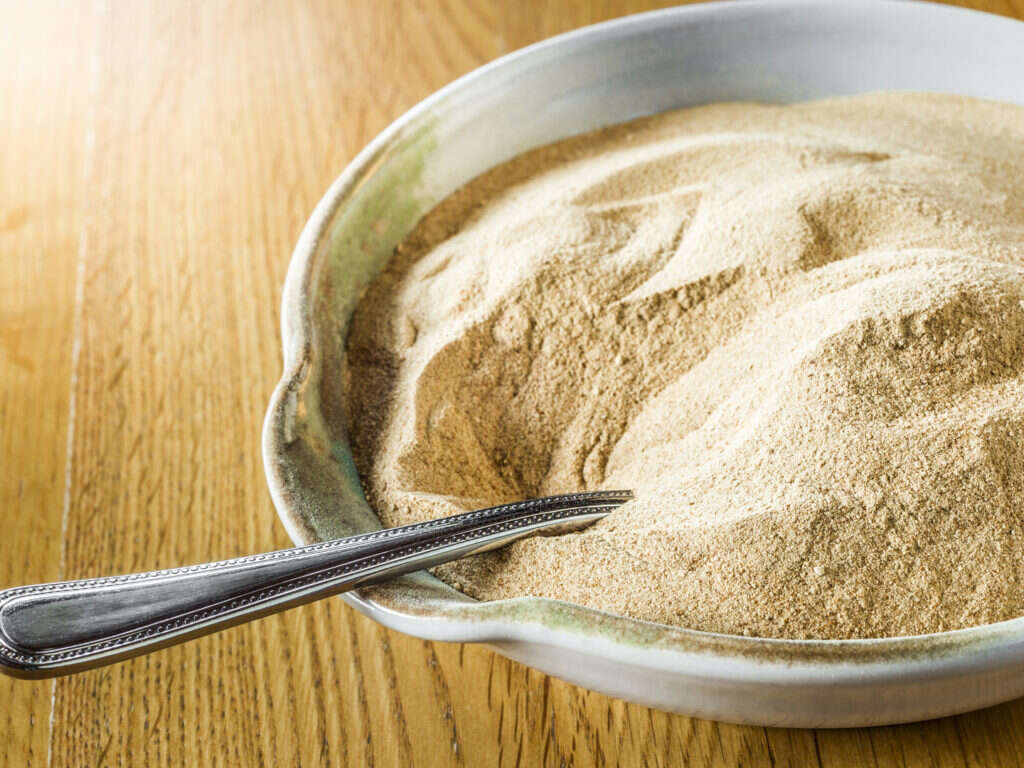
Vitamin B12 Rich Food #9: Nutritional Yeast
While nutritional yeast is not a natural source of vitamin B12, fortification makes it an important source of cobalamin. This is especially useful for vegetarians and vegans. Because only foods of animal origin contain significant amounts of vitamin B12, vegetarians and vegans are at a high risk of cobalamin deficiency. The requirement for fortification of foods is intended to mitigate deficiencies of B12 besides other vitamins and minerals. Two tablespoons of nutritional yeast contain 7.8 micrograms of cobalamin.
Vegetarians and vegans should include fortified foods like nutritional yeast in their diet to mitigate vitamin B12 deficiency. Nutritional yeast is also a good source of protein.

Vitamin B12 Rich Food #10: Fortified Cereals
Many cereals are typically fortified with vitamins and minerals to address deficiencies. In the case of vitamin B12, vegans and vegetarians with lactose intolerance may not get the recommended 2.7 mcg of the vitamin from their normal diet. However, they can get adequate vitamin B12 by including cereals in their diet. One ounce of high fiber bran flakes provides 7.9 micrograms of B12. This is more than three times the recommended dietary allowance.
Form the habit of reading the label when buying cereals and other foods. This way, you will ensure that you are getting the RDA of B12 and other micronutrients, always. Besides the added vitamins and minerals and their high carbohydrate content, cereals also contain fiber and some protein.