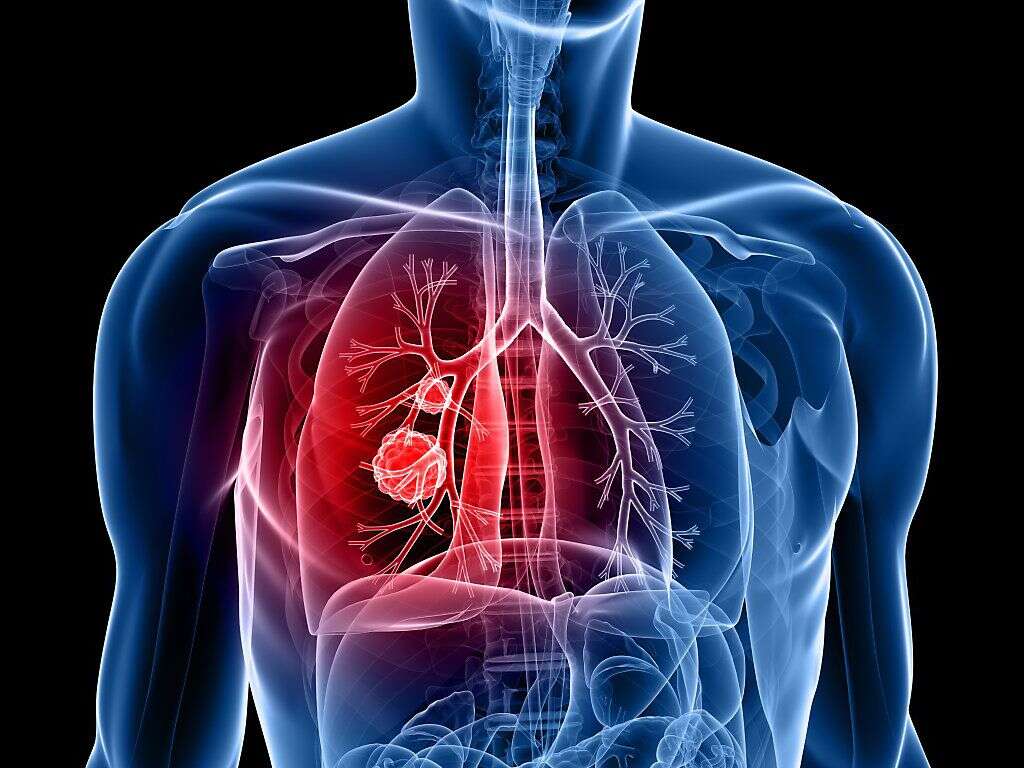
10 Lung Cancer Symptoms
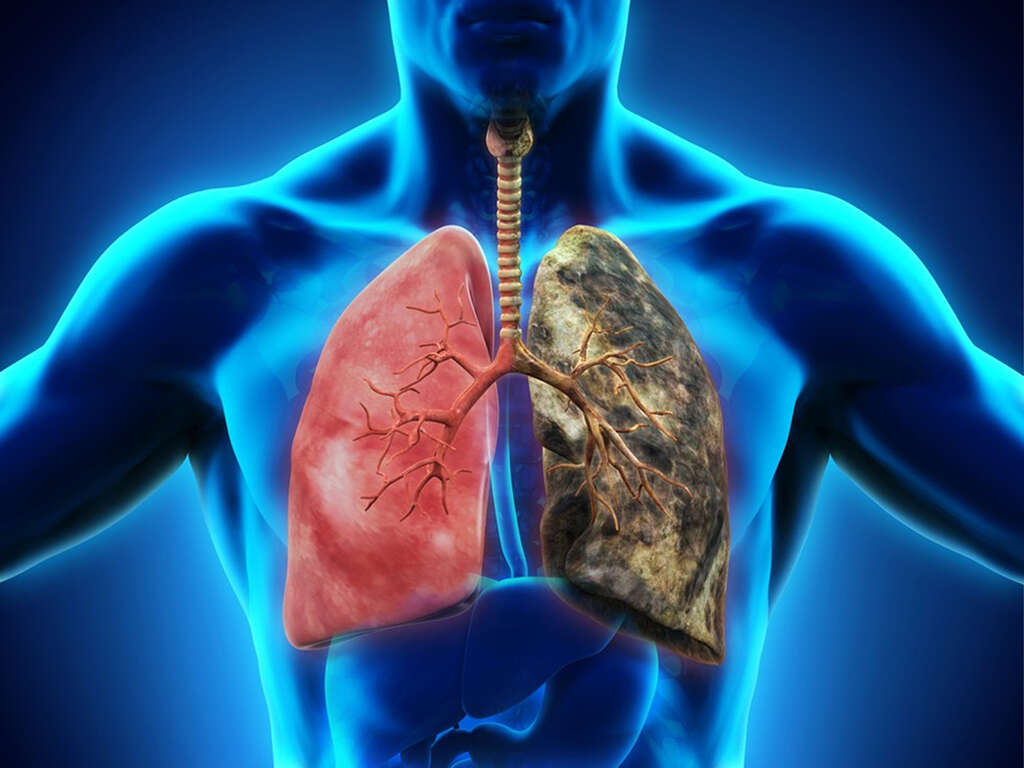
Lung cancer or lung carcinoma occurs when there is malignant cell growth in the tissues of the lung. This growth can spread via local invasion into adjacent structures or through blood and lymph channels to other parts of the body. This is known as the process of metastasis. There are two main types of lung cancer: small cell lung carcinoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma. Most cases of lung cancer are seen in patients who have smoked tobacco for a prolonged duration. 10 to 15 percent of cases occur in those who have never smoked. These cases may have occurred due to exposure to any form of air pollution along with genetic factors.
The diagnosis of lung cancer is confirmed through biopsy by bronchoscopy. It can also be seen on computed tomography scans or chest radiographs. The prognosis of lung cancer depends on the type of cancer, stage, and overall health of the patient. Treatment includes surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. In 2012, approximately 1.8 million individuals have lung cancer. It resulted in 1.6 million deaths. It is one of the commonest causes of cancer-related deaths in both men and women. In the United States, about 17.4 percent of individuals with lung cancer survive five years after diagnosis with lower outcome rates in developing countries.

Symptom #1: Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is a medical term that describes the coughing up of blood. Hemoptysis can occur in lung cancer, bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, injuries, and some cardiovascular conditions. In massive hemoptysis (300 ml or more), there is a risk of choking.
The treatment of hemoptysis depends on the underlying cause. It may include the use of iced saline, topical vasoconstrictors like vasopressin or adrenalin, endobronchial tamponade, selective bronchial intubation, laser photocoagulation, and many more.
Symptom #2: Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when there is reduction of the total body mass due to loss of muscle, fluid, adipose tissue, bone mineral deposits, or other connective tissue. Weight loss can occur intentionally or unintentionally. Intentional weight loss usually occurs when one is trying to improve their health or physical looks.
Unintentional weight loss can occur when there is malnutrition or disease. There are four mechanisms for weight loss: impaired intake of food, impaired absorption or digestion, excessive loss of nutrients, and altered requirements of the body.

Symptom #3: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea is a feeling when one is unable to breathe well. It can be assessed based on the degree of distress and the burden it has on daily routines. Patients may complain of requiring extra effort to breathe, air hunger, and chest tightness.
Besides lung cancer, it can also be seen in cardiac ischemia, pneumonia, asthma, interstitial lung disease, heart failure, panic disorder, anxiety, and more. In palliative cases (cancer and non-cancer), opioids may be beneficial in decreasing the shortness of breath in emergent cases. Physiotherapy and pulmonary rehabilitation may also be helpful.

Symptom #4: Chest Pain
Chest pain is pain that occurs in any area of the chest. It can be a symptom of several serious conditions and is considered to be a medical emergency. Chest pain can be categorized into non-heart related or heart related chest pain. Heart related chest pain is known as angina pectoris.
Some of the noncardiac causes of chest pain are issues with the lungs, musculoskeletal, or gastrointestinal. Causes of chest pain due to lung issues are bronchitis, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, hemothorax, pneumothorax, tuberculosis, pleurisy, and lung malignancy.

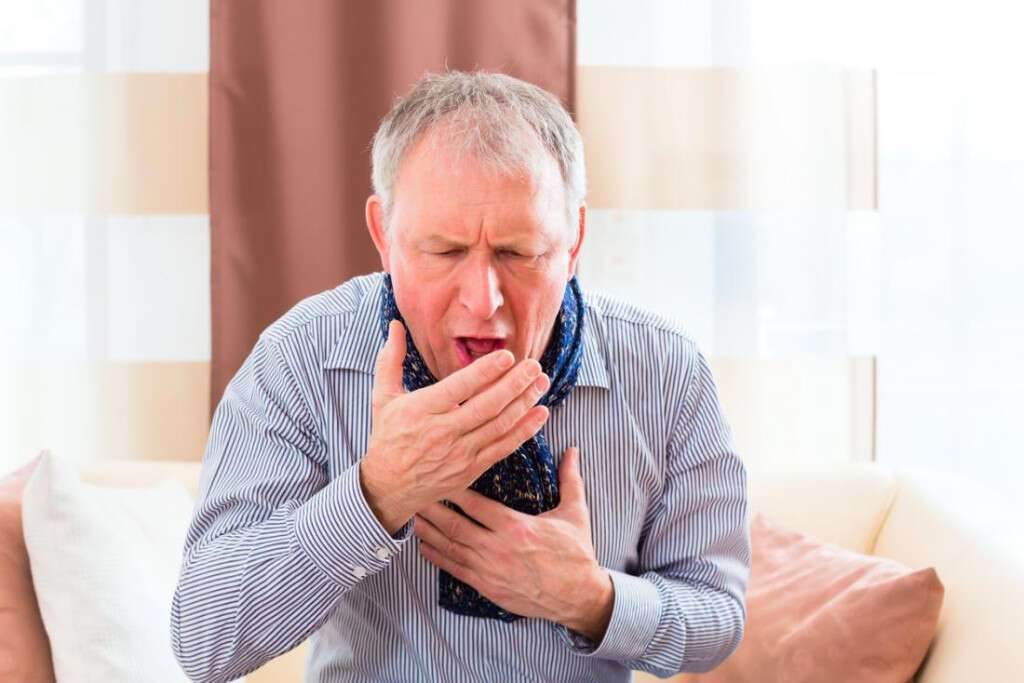
Symptom #5: Coughing
A cough is a repetitive and sudden reflex that helps to clear the breathing passages from irritants, microbes, fluids, and foreign particles. Coughing can be triggered by air pollution, choking, asthma, smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic bronchitis, post-nasal drip, heart failure, side effect of medication, lung tumors, and more.
The treatment of cough depends on the underlying cause. Cough suppressants can be prescribed but have been shown to have little effect.

Symptom #6: Weakness
Weakness is a common symptom seen in many different conditions. It can be divided into true and perceived muscle weakness. True weakness is seen in skeletal muscle diseases while perceived weakness occurs when a person feels that more effort is needed despite muscle strength being normal.
Examples of true muscle weakness are muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and inflammatory myopathy. A good example of perceived weakness is chronic fatigue syndrome.

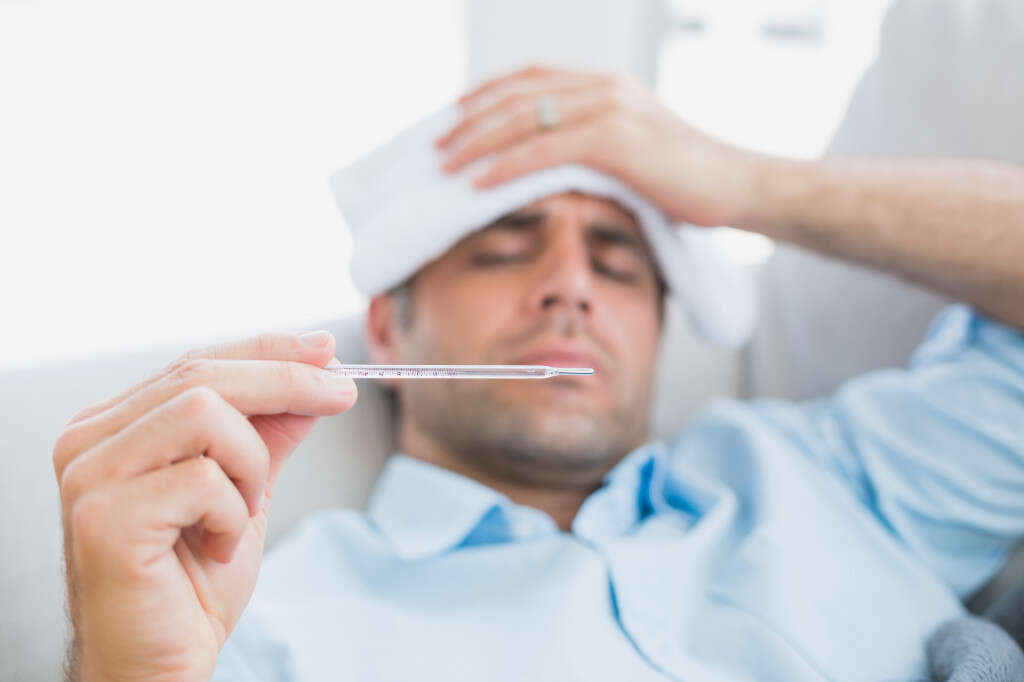
Symptom #7: Fever
Fever occurs when there is an increase in the set point of body temperature resulting in muscle contractions and a feeling of coldness. This causes the body to increase the production and conservation of heat.
There are many causes of fever such as infections (bacterial, viral, parasitic), appendicitis, vasculitis, side effect of medications, deep vein thrombosis, and cancer. Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and paracetamol (acetaminophen) can be beneficial to help lower temperature.

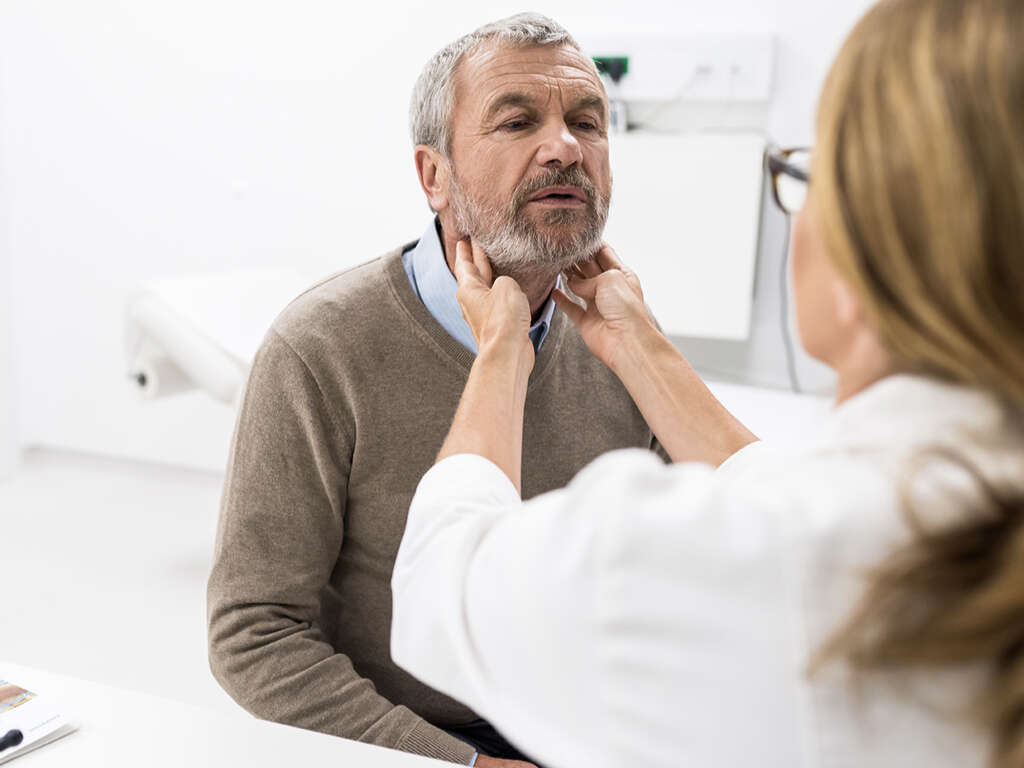
Symptom #8: Nail Clubbing
Nail clubbing or digital clubbing occurs when the nails of the fingers or toes are deformed (usually) due to diseases of the heart and lungs. It can be seen in lung cancer, interstitial lung disease, sarcoidosis, mesothelioma, cyanotic heart disease, tetralogy of Fallot, or any other disease where there is chronic hypoxia.
It has been theorized that nail clubbing occurs due to vasodilation, secretion of growth factors, and other mechanisms have been proposed.
Symptom #9: Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a term describing difficulty swallowing. However, some patients with dysphagia may be unaware of it. It can manifest as a sensation where one feels there is difficulty in the passage of solids or fluids from mouth to stomach.
It should be distinguished from odynophagia which is pain during swallowing. Patients with dysphagia have a higher risk of aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition, dehydration, and renal failure.

Symptom #10: Edema of the Face and Upper Limbs
Edema of the face and upper limbs can occur in lung cancer as the growing tumor compresses the vessel wall in the mediastinum. This is also known as superior vena cava syndrome. Non-malignant causes include aortic aneurysms, infections, benign tumors, and more.
Besides the characteristic edema seen in the face and arms, there can also be swollen collateral veins on the chest, shortness of breath, coughing, difficulty swallowing, headache, and stridor.