10 Side Effects of Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is an over the counter (OTC) drug commonly used to relieve pain (analgesic) and fever (antipyretic). Also known as paracetamol (outside the US and Canada), it is a widely used medication both in the adult and pediatric populations. It comes in a wide array of formulas and dosages and it can be found mixed with many other drugs as well.
The exact mechanism of action of acetaminophen is still unclear, but it is thought to act centrally in the central nervous system with very little effect (if any) at blocking the production of pro-inflammatory products like prostaglandins. It has a good safety profile if administered properly and this is one of the reasons it has become one of the most popular OTC drugs in the market. Nevertheless, it shouldn’t be used indiscriminately. Acetaminophen toxicity is one of the leading causes of acute liver failure in the US.
1. Dizziness
Dizziness is defined as the loss of balance and/or the feeling of being lightheaded. It is a subjective sensation that can show up suddenly and may cause a person to feel ill. It is important to try to sit down as soon as possible to prevent falls that could result in serious complications.
Due to its good safety profile, it is not common to see many side effects related to acetaminophen, but this is a fairly common one to find. It usually resolves quickly and without the need to do anything other than to sit down for a while. If the dizziness persists, you should seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.

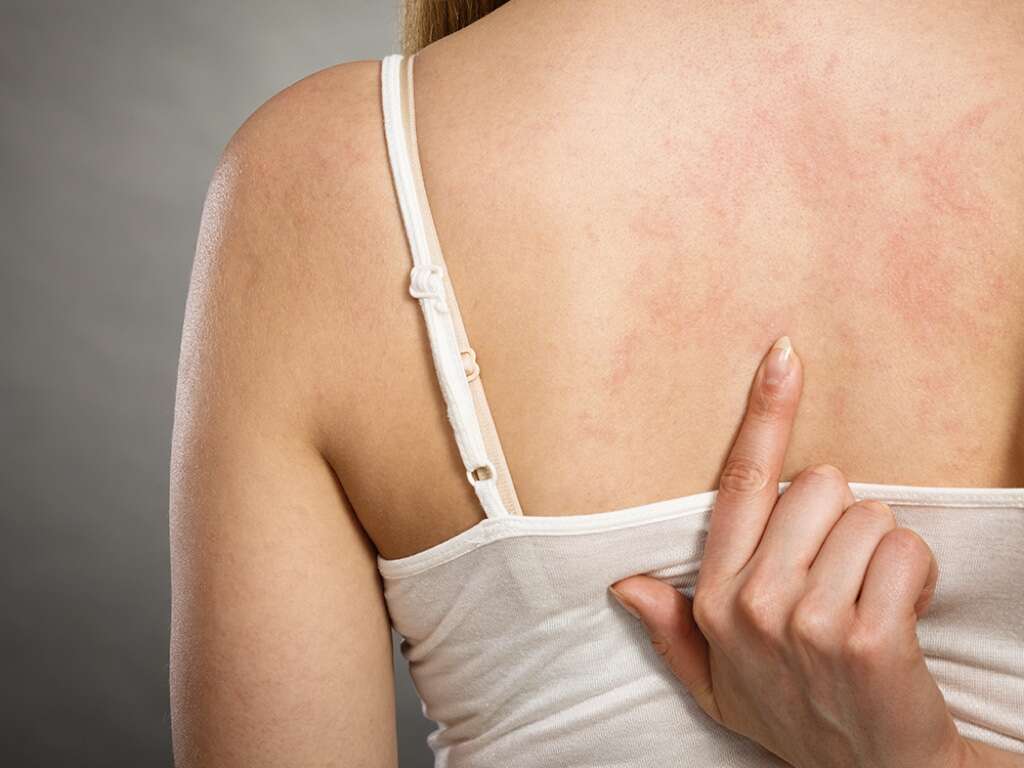
2. Rash
A rash is a disturbance in the normal structure of the skin, usually involving changes in the skin color and texture. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in many conditions. Usually, a rash can cause itchiness in the affected area, but this is not always the case.
When a skin rash appears shortly after the administration of a drug like acetaminophen, it is important to look for other signs of an allergic or hypersensitivity reaction. These signs include increased heartbeat, difficulty breathing, dizziness, and sweating. If you suspect that you might have an allergic reaction, seek medical attention as soon as possible to prevent further complications.

3. Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is the medical term used to describe a low platelet count. Platelets are blood cells that help the blood clot. This is vital to avoid losing too much blood due to wounds and other injuries. When the platelet levels are too low, we may find it harder to form a clot and bleeding becomes a problem.
Even though acetaminophen is less likely to cause this side effect than a regular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), it is still possible. This is particularly important if the patient has liver or kidney problems that could interfere with acetaminophen’s metabolism or excretion from the body.
4. Kidney Toxicity
Nephrotoxicity is the medical term used to describe a chemical process that alters the proper functioning of the kidneys. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity is associated with many drugs such as aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, and Cisplatin to name a few, but other drugs may cause damage to the kidneys as well.
Acetaminophen may cause nephrotoxicity, especially in patients with an underlying renal disease. This is not a common side effect associated with this drug but it is important to know that even it is considered to have a good safety profile, this does not mean that it is risk-free.
5. Liver Toxicity
Hepatotoxicity is the medical term used to describe a chemical process that causes damage to the liver. Drug-induced liver damage is a common form of hepatotoxicity and it can be severe enough to permanently scar the liver to a point that a transplant is required.
Acetaminophen may cause hepatotoxicity at higher doses. Therefore, it is important not to exceed the recommended dose prescribed by your doctor. If the dosage is not corrected, eventually this may lead to acetaminophen toxicity which can cause the patient to experience acute liver failure.
6. Neutropenia
Neutropenia is defined as a low count of neutrophils in the bloodstream. Neutrophils are a unique kind of white cell that helps us fight infections, especially the ones that are caused by bacteria. Neutropenia can be caused by many conditions like infections (both bacterial and viral infections), congenital diseases, and many drugs are linked with the appearance of neutropenia.
The chronic use of acetaminophen has been linked with this side effect. It is not a very common side effect and usually, it causes no symptoms, therefore it is oftentimes overlooked or discovered unintendedly.
7. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is a type of hypersensitivity reaction that usually involves the skin and mucous membranes. It can be caused by infectious diseases, drugs, and it can be associated with certain malignancies as well. The early stages of this disease are associated with mild headaches and malaise. Eventually, the characteristic rash appears with the usual target-like appearance. The rash can be seen anywhere in the body but the palms, soles, and the dorsum of the hands are most commonly affected.
Antibiotics are the most common culprit of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, followed by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other analgesics like acetaminophen. This is a rare side effect associated with acetaminophen but it can be seen, especially in patients with underlying liver disease.

8. Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) is considered to be a more severe form of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. It can be caused by infections and malignancies but most commonly it is associated with certain drugs like antibiotics, anticonvulsants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), acetaminophen, and many others. Symptoms include fever, headaches, and anorexia during the early stages of the disease. As the condition progresses, the characteristic painful red spots appear in the torso and face, sparing the scalp.
TEN is a life-threatening condition that can also affect the mucous membranes. It is not a common side effect related to acetaminophen but it has been described. Therefore, it is important not to abuse this over the counter drug.

9. Acute Liver Failure
Acute Liver failure is defined as a rapid decline in liver functions. It can be caused by viral and autoimmune hepatitis, but the most common cause is due to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Patients with acute liver failure often present with yellow-coloring of the skin (also known as jaundice) and right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness.
Given the fact that the number one cause of acute liver failure is related to acetaminophen ingestion, it is important to avoid self-medication and only use this over the counter drug as the doctor prescribes.
10. Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia is defined as elevated levels of ammonia in the blood. Ammonia is a normal component of the fluids in our bodies. When it accumulates in the blood, it can go into the brain, causing most of the symptoms associated with this condition. The most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, irritability, sleep disturbances, and gait problems.
Hyperammonemia is a rare side effect linked with acetaminophen ingestion. It is important to remember that overall, acetaminophen has a very good safety profile, but this does not mean that it is safe to overuse it. If you are experiencing symptoms related to Hyperammonemia, you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.