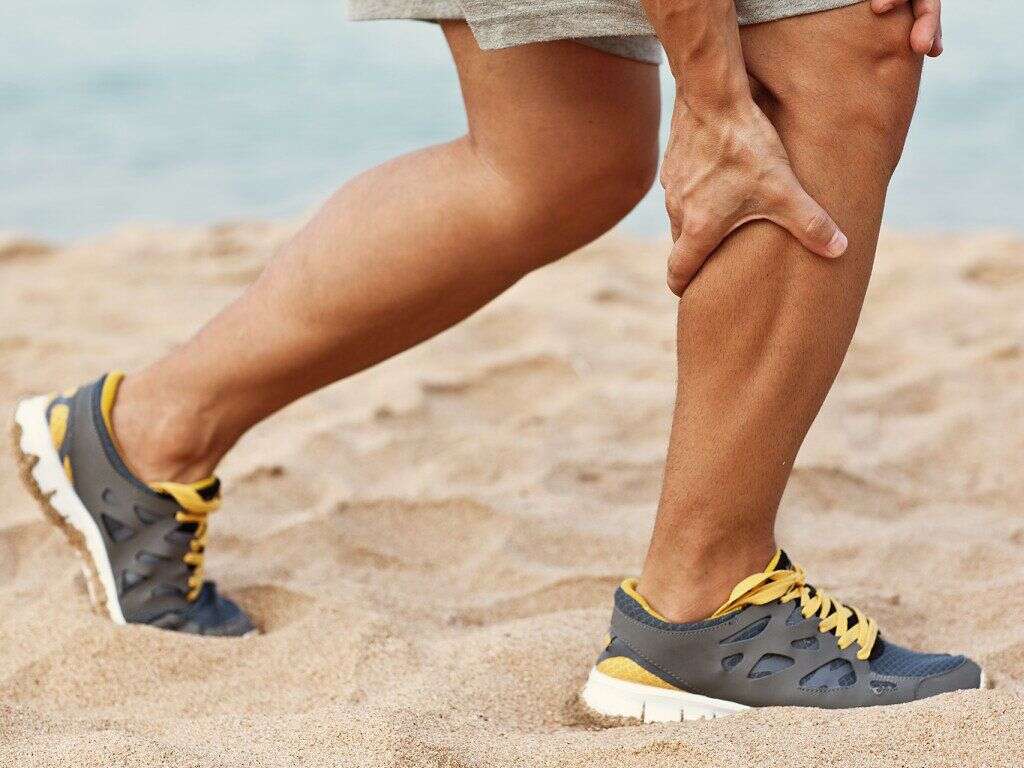
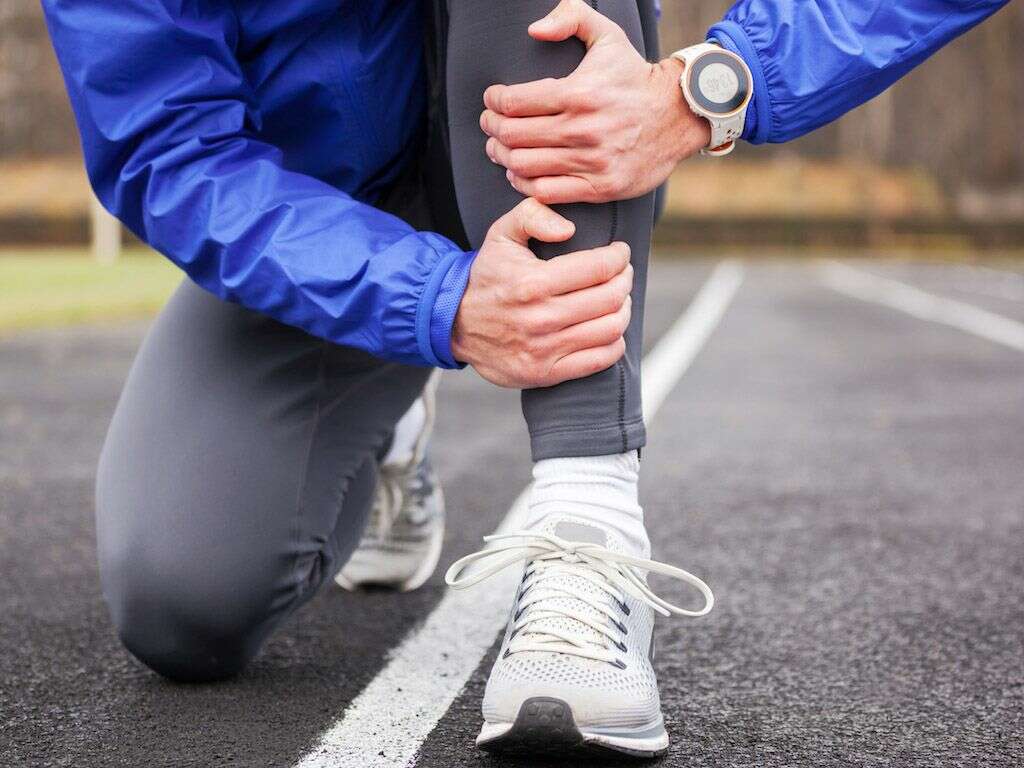
Shin Splints Causes And Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. McClure, Charles J. 'Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome.', U.S. National Library of Medicine, 10 Aug. 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538479/.
- 2. 'Shin Splints - OrthoInfo - AAOS.' _OrthoInfo_, orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/shin-splints.
- 3. A;, Nilsson J;Thorstensson. 'Ground Reaction Forces at Different Speeds of Human Walking and Running.' _Acta Physiologica Scandinavica_, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2782094/.
- 4. 'Are Feet at Fault for Back, Hip, and Knee Woes?'_Are Feet at Fault for Back, Hip, and Knee Woes? - Health Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center_, www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=1&ContentID=1158.
8. Shin Splint Pain Treatment
The initial treatment for shin splint pain centers around applying ice and resting. Low temperatures help reduce inflammation. If safe, anti-inflammatory medicine such as ibuprofen can also aid recovery.
While it can be frustrating, it’s essential to stop activity temporarily and rest. Walking is usually fine, and alternative cross-training with no impact such as swimming or cycling can be a good idea. Remember that time out for injury is an inevitable part of exercising.
Advertisement