Health Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Pumpkin Seeds Pack a Healthy Punch.' heart.org, www.heart.org/en/news/2018/10/25/pumpkin-seeds-pack-a-healthy-punch.
- 2. 'Fluorescence screening of antioxidant capacity in pumpkin seed oils and other natural oils.' European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.200390055.
- 3. 'Antioxidants, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease.' World Journal of Cardiology, Baishideng Publishing Group Inc, 26 June 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4072837.
- 4. 'Effect of Pumpkin-Seed Oil on the Level of Free Radical Scavengers Induced during Adjuvant-Arthritis in Rats.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7784309.
- 5. 'Antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activities of pumpkin seed extracts.' Europe PMC, europepmc.org/article/agr/ind44207266.
- 6. 'The Association between Dietary Lignans, Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods, and Fiber Intake and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk: a German Case-Control Study.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22591208.
- 7. 'Effects of Phytoestrogen Extracts Isolated from Pumpkin Seeds on Estradiol Production and ER/PR Expression in Breast Cancer and Trophoblast Tumor Cells.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859042.
- 8. 'Seeds and Oil of the Styrian Oil Pumpkin: Components and Biological Activities.' European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.200700105.
- 9. 'Effects of Pumpkin Seed Oil and Saw Palmetto Oil in Korean Men with Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.' Nutrition Research and Practice, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2809240.
- 10. 'What We Eat in America.' U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, www.ars.usda.gov/SP2UserFiles/Place/80400530/pdf/0506/usual/nutrient/intake/vitD/ca/phos/mg/2005-06.pdf
- 11. 'Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Coronary Heart Disease.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15330276.
- 12. 'Efficacy of Simvastatin and Pumpkin-Seed Oil in the Management of Dietary-Induced Hypercholesterolemia.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9299202.
- 13. 'Improvement in HDL Cholesterol in Postmenopausal Women Supplemented with Pumpkin Seed Oil: Pilot Study.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21545273.
- 14. 'Antihypertensive and Cardioprotective Effects of Pumpkin Seed Oil.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22082068.
- 15. 'Zinc Levels in Seminal Plasma Are Associated with Sperm Quality in Fertile and Infertile Men.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19285597/.
- 16. 'A Review on Pharmacological Activities and Utilization Technologies of Pumpkin.' PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16758316.
- 17. 'Zinc Is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization.' Journal of Reproduction & Infertility, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6010824.
- 18. 'Protective Effect of Pumpkin Seed Oil against Genotoxicity Induced by Azathioprine.' The Journal of Basic & Applied Zoology, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090989612000422.
- 19. 'Sleep in Elite Athletes and Nutritional Interventions to Enhance Sleep.' Sports Medicine, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4008810.
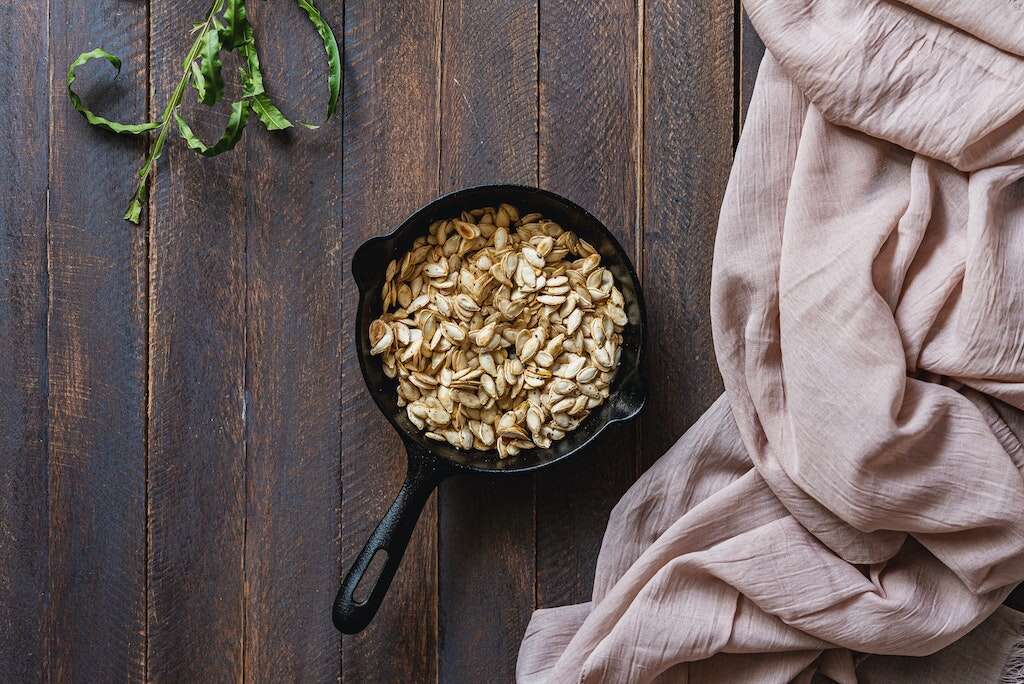
Small as they seem, pumpkin seeds are a powerhouse of nutrients. Just a few seeds can provide a healthy dose of zinc, magnesium and healthy fats. Pumpkin seeds provide many other health benefits as well, and they're easy to incorporate into a healthy diet.
The most common way of preparing pumpkin seeds for consumption is to roast them and enjoy them as a healthful snack. Pumpkin seeds are also seen frequently in Mexican cuisine, where the seeds are often referred to as pepitas, which means little seed of squash in Spanish.

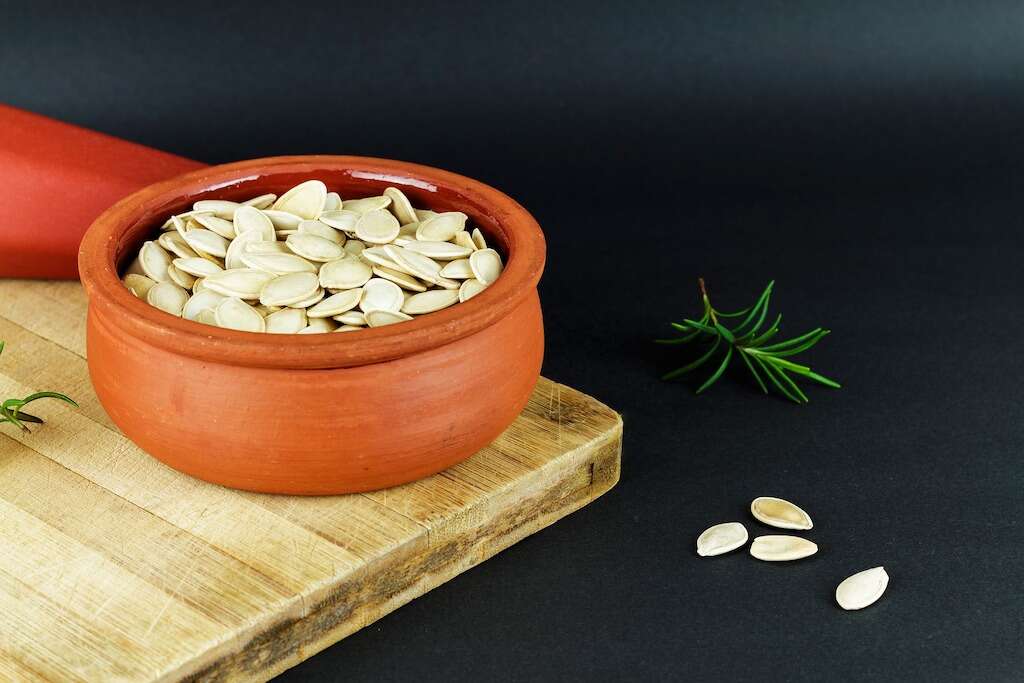
1. They’re Rich in Nutrients
Every ounce, or 28 grams, of pumpkin seeds contains about 151 calories, most of which are protein and fat. This quantity also contains 5 grams of carbs; 13 grams of fat, six of which are omega-6s; 1.7 grams of fiber; 23% of the recommended dietary intake, or RDI, of iron; 42% of the RDI of manganese; 37% of the RDI of magnesium and 7 grams of protein.
Pumpkin seeds also contain many other beneficial properties, including plenty of antioxidants, and a significant amount of potassium, polyunsaturated fatty acids, riboflavin and folate.1‘Pumpkin Seeds Pack a Healthy Punch.’ heart.org, www.heart.org/en/news/2018/10/25/pumpkin-seeds-pack-a-healthy-punch.

2. They’re High in Antioxidants
Pumpkin seeds contain vitamin E, carotenoids and other antioxidants.2‘Fluorescence screening of antioxidant capacity in pumpkin seed oils and other natural oils.’ European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.200390055. Antioxidants are compounds that minimize inflammation and prevent harmful free radicals from damaging cells, and eating foods that contain enough antioxidants may provide protection from many diseases.3‘Antioxidants, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease.’ World Journal of Cardiology, Baishideng Publishing Group Inc, 26 June 2014, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4072837.
Nutritionists believe some of the positive health effects of pumpkin seeds are partly due to their high levels of antioxidants. One study found pumpkin seed oil reduced inflammation of rats with arthritis, without any side effects.4‘Effect of Pumpkin-Seed Oil on the Level of Free Radical Scavengers Induced during Adjuvant-Arthritis in Rats.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7784309.

3. They May Reduce the Risk of Certain Cancers
Diets that include pumpkin seeds are linked to a reduced risk of colon, prostate, lung, breast and stomach cancer.5‘Antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activities of pumpkin seed extracts.’ Europe PMC, europepmc.org/article/agr/ind44207266. Results from one large observational study suggested that eating pumpkin seeds may reduce the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women.6‘The Association between Dietary Lignans, Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods, and Fiber Intake and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk: a German Case-Control Study.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22591208.
Other studies have shown that the lignans found in pumpkin seeds may help prevent and manage breast cancer.7‘Effects of Phytoestrogen Extracts Isolated from Pumpkin Seeds on Estradiol Production and ER/PR Expression in Breast Cancer and Trophoblast Tumor Cells.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859042. However, more research is needed to confirm the anti-cancer qualities of pumpkin seeds. Adding these seeds to a healthy diet can reap many health benefits.

4. They May Improve Prostate and Bladder Health
According to several studies that have been carried out on humans, eating pumpkin seeds may help reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH, symptoms.8‘Seeds and Oil of the Styrian Oil Pumpkin: Components and Biological Activities.’ European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.200700105. BPH is a condition that can cause enlargement of the prostate gland.8‘Seeds and Oil of the Styrian Oil Pumpkin: Components and Biological Activities.’ European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejlt.200700105.
The results of a one-year study of more than 1,400 men with BPH indicated that the consumption of pumpkin seeds reduced the symptoms of the condition and improved their quality of life.9‘Effects of Pumpkin Seed Oil and Saw Palmetto Oil in Korean Men with Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.’ Nutrition Research and Practice, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2809240.

5. They’re High in Magnesium
Pumpkin seeds are among the richest sources of magnesium. The diets of many people in Western countries lack this mineral. For example, the diets of approximately 79 percent of people in the United States don't include the daily recommended amount of magnesium.10‘What We Eat in America.’ U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, www.ars.usda.gov/SP2UserFiles/Place/80400530/pdf/0506/usual/nutrient/intake/vitD/ca/phos/mg/2005-06.pdf
Over 600 chemical reactions in the human body rely on magnesium. These reactions include blood pressure regulation, reducing the risk of heart disease, formation and maintenance of healthy bones and blood sugar level regulation.

6. They May Have Cardiac Benefits
Pumpkin seeds contain compounds, such as magnesium and antioxidants, that can improve heart health.11‘Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Coronary Heart Disease.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15330276. Some animal studies show that these seeds may reduce the risk of high cholesterol levels and high blood pressure.12‘Efficacy of Simvastatin and Pumpkin-Seed Oil in the Management of Dietary-Induced Hypercholesterolemia.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9299202.
Another study revealed that consuming pumpkin seed supplements increased good HDL cholesterol and reduced diastolic blood pressure.13‘Improvement in HDL Cholesterol in Postmenopausal Women Supplemented with Pumpkin Seed Oil: Pilot Study.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21545273. Other studies have found that the seeds may increase nitric oxide production in the body and improve heart health.14‘Antihypertensive and Cardioprotective Effects of Pumpkin Seed Oil.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22082068.
7. They May Help Lower Blood Sugar
Animal studies suggest a link between lower blood sugar levels and eating pumpkin seeds.15‘Zinc Levels in Seminal Plasma Are Associated with Sperm Quality in Fertile and Infertile Men.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19285597/. People with diabetes could benefit from eating these seeds because they may be able to help control blood sugar levels.
Other studies show that pumpkin seed powder and pumpkin juice may reduce blood sugar levels in individuals with Type 2 diabetes.16‘A Review on Pharmacological Activities and Utilization Technologies of Pumpkin.’ PubMed, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16758316. The high levels of magnesium in pumpkin seeds may play a role in their positive health effects in people with diabetes.

8. They May Improve Sperm Quality
A high risk of male infertility and a reduction of sperm quality are associated with low levels of zinc.17‘Zinc Is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization.’ Journal of Reproduction & Infertility, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6010824. Pumpkin seeds are a good source of zinc and may help improve the quality of sperm.
One study of mice revealed that pumpkin seeds may protect sperm from the damage that autoimmune diseases and chemotherapy cause.18‘Protective Effect of Pumpkin Seed Oil against Genotoxicity Induced by Azathioprine.’ The Journal of Basic & Applied Zoology, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090989612000422. Pumpkin seeds are also a rich source of several compounds that play a role in having healthy levels of testosterone and overall good health.
9. They May Help With Sleep
Eating pumpkin seeds before sleeping can help with poor sleep. The seeds contain tryptophan, a sleep-promoting amino acid. It's believed that eating 1 gram of tryptophan every day can help with sleep.19‘Sleep in Elite Athletes and Nutritional Interventions to Enhance Sleep.’ Sports Medicine, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4008810.
However, to ingest the required amount of tryptophan, an individual needs to consume about 7 ounces, or 200 grams, of pumpkin seeds. The zinc in pumpkin seeds may also be helpful in the conversion of tryptophan to serotonin, which in turn converts to melatonin, the sleep-regulation hormone.

10. They're Part of Healthy Diet
Pumpkin seeds are a popular snack in many cultures and can be easily incorporated into a healthy diet. They can be eaten raw or roasted, with or without salt, and added to fruit salads, Greek yogurt and smoothies, depending on an individual's dietary preferences.
As with other nuts and seeds, it's advisable to sprout or roast pumpkin seeds to reduce their levels of phytic acid, which reduces consumed minerals' bioavailability.











