10 Copper Deficiency Symptoms
Copper is an important mineral that is involved in the formation of adenosine triphosphate, also referred to as ATP. ATP is the body’s main source of energy for its many functions. Aside from ATP production, copper is involved in healthy metabolism and in the maintenance of a healthy nervous system and strong, healthy bones.
Copper deficiency, although rare, occurs when intake of the mineral into the body is inadequate. This, in turn, has various effects that negatively impact the health status of the affected people.
Copper deficiency leads to hormonal imbalances due to the accumulation of iron within the endocrine system. It can also cause irregular heartbeats, bone fractures, and a low white and red blood cell count. Here are 10 copper deficiency symptoms to watch out for.

Symptom #1: Fatigue
One of the main roles of copper is the production of energy. Copper is an essential component of ATP, the organic chemical from which energy is produced in the body. Copper is also responsible for the absorption of iron from the gut.
When copper levels are too low, less iron is absorbed into the body. This minimal absorption of iron can lead to iron deficiency anemia, a condition in which the body is unable to deliver adequate oxygen to its tissues. This lack of oxygen is responsible for feeling weak, tired, or fatigued as a consequence of copper deficiency.

Symptom #2: Anemia
Anemia is the condition in which blood does not have enough healthy red blood cells. In order to make hemoglobin, the compound in red blood cells that gives blood its red color, your bone marrow requires iron. This means that in the absence of adequate iron, your body is unable to produce the required amount of hemoglobin for the red blood cells.
Copper is responsible for the transportation of iron to the bone marrow for use in the production of hemoglobin. When copper levels are low, iron accumulates in one area instead of being taken to where it is required. Consequently, fewer red blood cells are produced, which leads to anemia. Characteristics of anemia include pale skin and fatigue.
Symptom #3: Sensitivity to Low Temperature
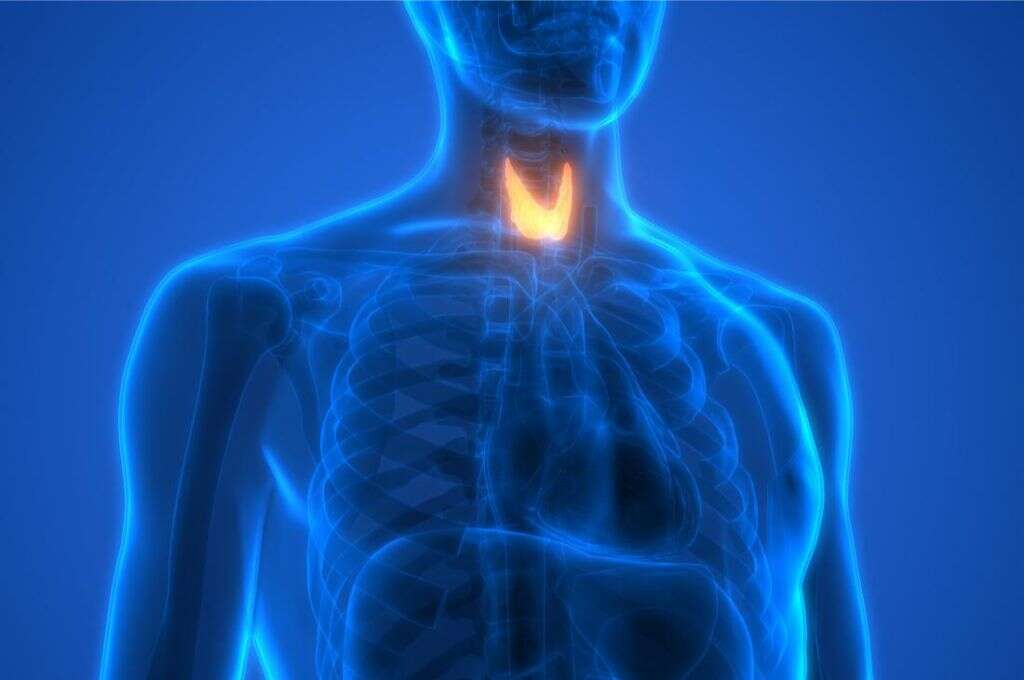
Most individuals with copper deficiency may tend to be more sensitive to lower temperatures. This is because copper has a role in the working of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a small gland in the neck that produces thyroid hormones. These hormones are essential for the regulation of body heat, heart rate, metabolism, and blood pressure.
Research shows that T3 and T4 thyroid hormones are associated with the levels of copper in the body. The thyroid hormone levels fall when the levels of copper are low. This negatively affects the thyroid gland function. Because the thyroid gland helps to regulate heat production and metabolism, the low levels of thyroid hormone can contribute to increasing your sensitivity to cold.
Symptom #4: Bone Abnormalities
Copper is a component in the process of forming collagen, an essential building block of connective tissues and bones. The collagen in bones and connective tissues ensures that bones are strong and healthy.
Studies have established that osteoporosis, a condition associated with weak bones, is in parts a result of copper deficiency in the body. Additionally, copper has an important role in the development of osteoblasts. These are cells that help strengthen and reshape bone tissues. Inadequate copper ingestion leads to decreased energy available for the process of linking bones with connective tissues. This leads to deformities in bones. If you notice some deformities in your bones, you probably need to increase your copper intake.
Symptom #5: Mental Issues
Copper is vital for the development and functioning of the brain, including thought and cognitive processes. It is a component of some enzymes that are responsible for supply of energy to the brain. It also plays a part in signals to the body besides assisting in the brain’s defense system.
These functions will be negatively affected in case of copper deficiency, leading to mental difficulties. Some studies have linked Alzheimer’s disease, a condition in which memory deteriorates, with copper deficit within the body and specifically the brain. By ensuring that your diet includes foods containing copper, you can boost your brain function and prevent its premature deterioration.

Symptom #6: Skin Paleness
Copper is necessary in the process of producing melanin, the pigment that determines skin color. Copper also plays a part in determining skin texture. A reduction in the amount of copper in the body can limit the melanin produced, which in turn leads to paleness of skin.
As mentioned earlier, copper is also involved in the production of collagen. Collagen has a key role in ensuring that skin maintains its elasticity and youthfulness. Copper deficiency can limit the production of an enzyme known as tyrosinase, which is also required for the production of melanin. A deficit in copper levels, therefore, can lead to the skin appearing pale.

Symptom #7: Premature Gray Hair
The pigment melanin is also responsible for the coloring of the hair. As mentioned above, copper has a vital role in the production development of melanin. Copper deficiency may lead to a condition known as copper deficiency gray hair.
Some studies have been carried out to measure the levels of copper in the blood of individuals under the age of 20 years with gray hair. In conclusion, the investigations revealed that copper deficiency was at least partly responsible for the development of premature gray hair among the subjects. Further studies are, however, necessary to determine how copper deficiency and gray hair are associated.

Symptom #8: Vision Loss
Vision is very important in our day-to-day activities. But it can suffer due to low levels of copper in the body. As mentioned elsewhere, copper plays an important part in maintaining good health of the nervous system, besides the rest of the body.
While you may not be aware, your eyes depend on the nervous system so you can discern what you are looking at. It follows that inadequate intake of copper can lead to vision loss. Some surgeries may also lead to the loss of vision. This happens when the surgery makes it difficult for the body to absorb copper from the food you eat. The culprit surgeries include gastric bypass surgery.

Symptom #9: Poor Immunity
The immune system is the body’s main defense mechanism, which is responsible for combating all manner of infections and diseases that may otherwise degrade your health status. It does this with the help of white blood cells. White blood cells are the body’s first line of defense. Copper, in addition to its other roles, is an important component necessary for the production of the white blood cells or neutrophils.
A reduction in the copper levels will make it difficult for the body to produce the cells necessary to provide defense against infections and disease. When this occurs, the human body gets easily attacked by infections. If you tend to easily fall ill, it is probably because your body does not contain inadequate copper levels.

Symptom #10: Impaired Growth
Lack of copper can lead to stunted growth and poor development in children. Copper, together with iron, assists the body to produce red blood cells as previously stated. In addition to this, copper plays an important role in bone development and maintenance of healthy blood vessels, the nervous system, and the immune system. These roles are necessary for a strong and healthy body.
It follows that inadequate amounts of copper in the body will end up adversely affecting growth, development, and healthy maintenance of the body. It is noteworthy that copper deficiency can especially impair growth in children. Deficiency should, therefore, be addressed as soon as it is suspected to ensure that children get sufficient amounts of copper.