Chills, No Fever: Causes, Remedies & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Glucose). Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Glucose)' | ADA, www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/blood-glucose-testing-and-control/hypoglycemia.
- 2. 'University Health Service. Anxiety Disorders and Panic Attacks' | University Health Service, uhs.umich.edu/anxietypanic#what.
- 3. 'Drug-Induced Tremor: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000765.htm.
- 4. 'Heat Exhaustion.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 10 Nov. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/symptoms-causes/syc-20373250.
- 5. Person, et al. 'Signs You Might Have a Thyroid Problem.' Intermountainhealthcare.org, 24 Oct. 2019, intermountainhealthcare.org/blogs/topics/live-well/2019/09/signs-you-might-have-a-thyroid-problem/.
- 6. 'Malnutrition.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/malnutrition.
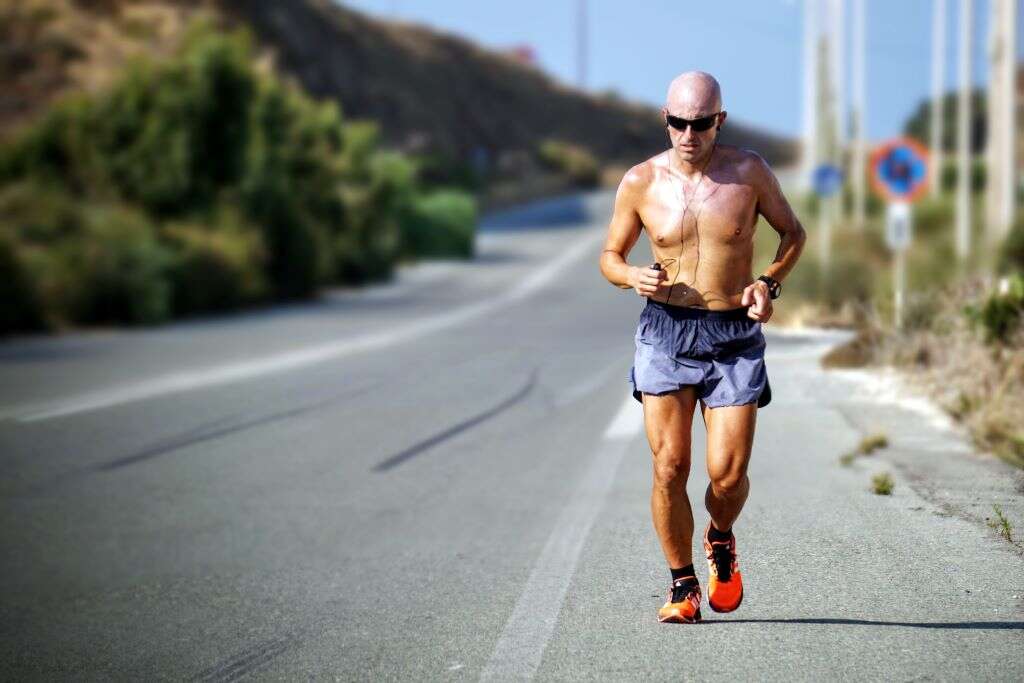
4. Heat Exhaustion
Heat exhaustion occurs when someone's body overheats. It's most common when there's high humidity in the air, but a person may also develop it from strenuous activity or from being outside in the heat for a prolonged period.
This issue may cause a person to feel faint or tired. Their pulse may become either weak or rapid, and muscle cramps and nausea can occur. Moreover, it's possible that a person will get chills as their body tries to cool itself.4‘Heat Exhaustion.’ Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 10 Nov. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heat-exhaustion/symptoms-causes/syc-20373250.
Advertisement