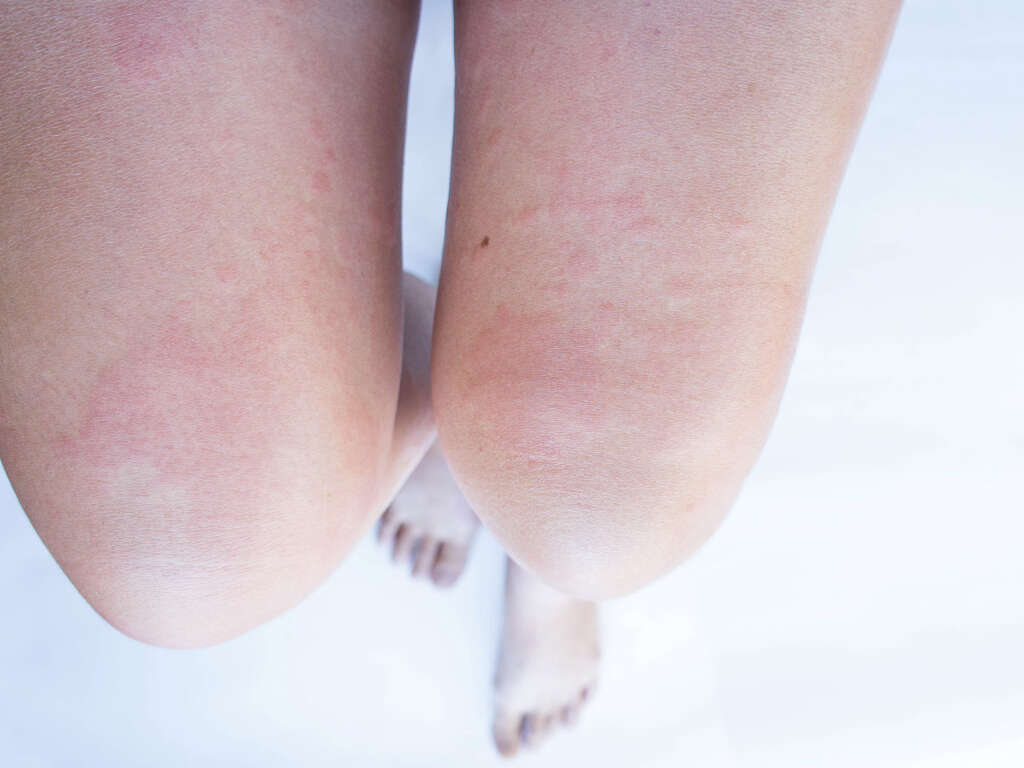
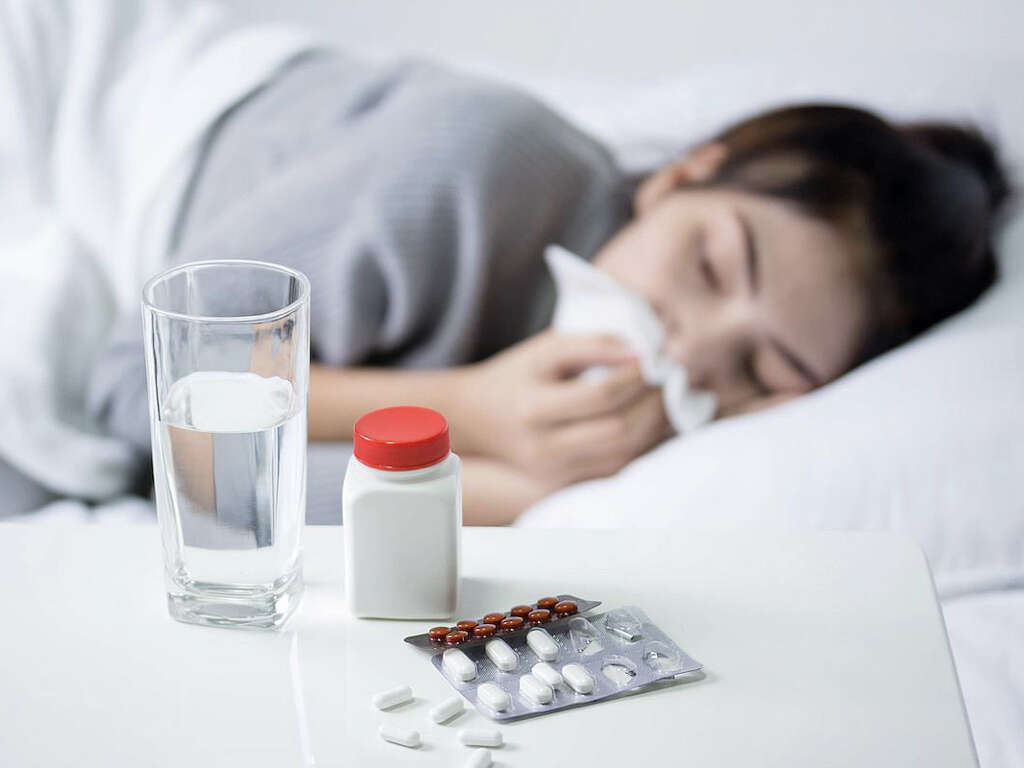
What Is Lymphangitis?
For many people who suffer from lymphangitis, it seems like a nightmare manifested in real life. The sores and the brightly colored lines in the skin point to an obvious, serious problem that cannot be ignored.
This can inspire panic, especially when coupled with other symptoms of infection that can cause you to feel weak and disoriented. Here are the 10 main questions people ask about this condition and the answers so you know what to look for and how to handle the issue.
1. What Exactly Is Lymphangitis?
As the name implies, the condition involves an attack on the lymphatic system. This generally appears as a skin infection that may vary from mild to serious. Ironically, skin infections are also a common cause of the condition. How the body responds to infections can also further increase the risk.
When the body detects an infection, the lymphatic system sends lymph fluid containing antibodies to fight off the invading infection. Unfortunately, this infected fluid can cause contamination in the lymph vessels, which leads to lymphangitis.
2. What Are the Most Common Symptoms?
This condition affects each person differently, but there are some common symptoms to look out for. The first and most frequently reported is the appearance of colored streaks stretching out from the source of the injury or infection that caused the problem. In fact, streaks can appear even if you do not know you have an infection.
In addition to visible symptoms, people often experience lethargy, chills and a loss of appetite. Some people also experience swelling in the armpits, groin or near the injury. Other symptoms include fevers and headaches.

3. Which Organs Can Be Affected?
The skin is the largest organ of the body and is typically affected by lymphangitis. Also affected is the lymphatic system. If the condition is left unchecked, other organs may also suffer temporary or permanent damage. In some instances, lymphangitis can lead to organ failure.
The tonsils, thymus and spleen are the main organs of the lymphatic system. The tonsils are the fleshy lumps at the back of your throat. The thymus sits in the upper chest region and plays a crucial role in the development of white blood cells, while the spleen is located in your abdomen and helps to keep the blood clean.
4. What Causes Lymphangitis?
Infections are the root cause lymphangitis. Most of these begin in the skin. Many people may assume this means a pre-existing, chronic skin condition. However, there are some everyday conditions that can put you at risk.
For instance, an insect sting or bite may become infected. If you have a wound that required stitches and opted not to see a doctor or waited too long to do so, this can also lead to lymphangitis. Other common causes include cellulitis, infected surgical wounds and sporotrichosis.
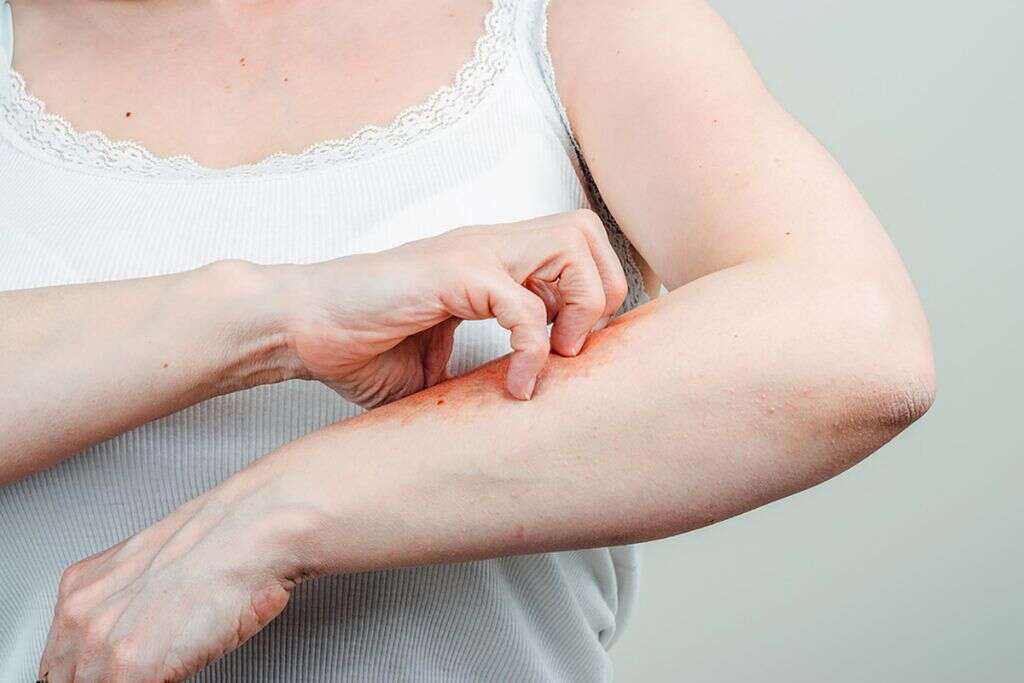

5. Do Any Health Conditions Increase the Risk?
Unfortunately, there are several health conditions that increase the likelihood of developing lymphangitis or that worsen the severity of the symptoms. People who suffer from HIV or diabetes have a higher chance of developing lymphangitis.
There are also several medical conditions that involve treatment to depress the immune system, such as cancer therapies. A depressed immune system not only becomes more vulnerable but can have a harder time overcoming this condition.
6. How Do Doctors Diagnose Lymphangitis?
If you are relying on telehealth services, you may wonder if a doctor can diagnose you without a physical in-person visit. Most often, the answer is yes. This condition is so unique in appearance that doctors are often able to diagnose it without the need for an appointment.
However, there are some instances where the doctor may request an in-person visit for a more thorough inspection. This is especially likely if the wound is painful, needs stitches or begins to ooze pus. A thorough exam also becomes necessary if there is no obvious source of the problem. The doctor must determine the cause to prescribe the proper treatment.
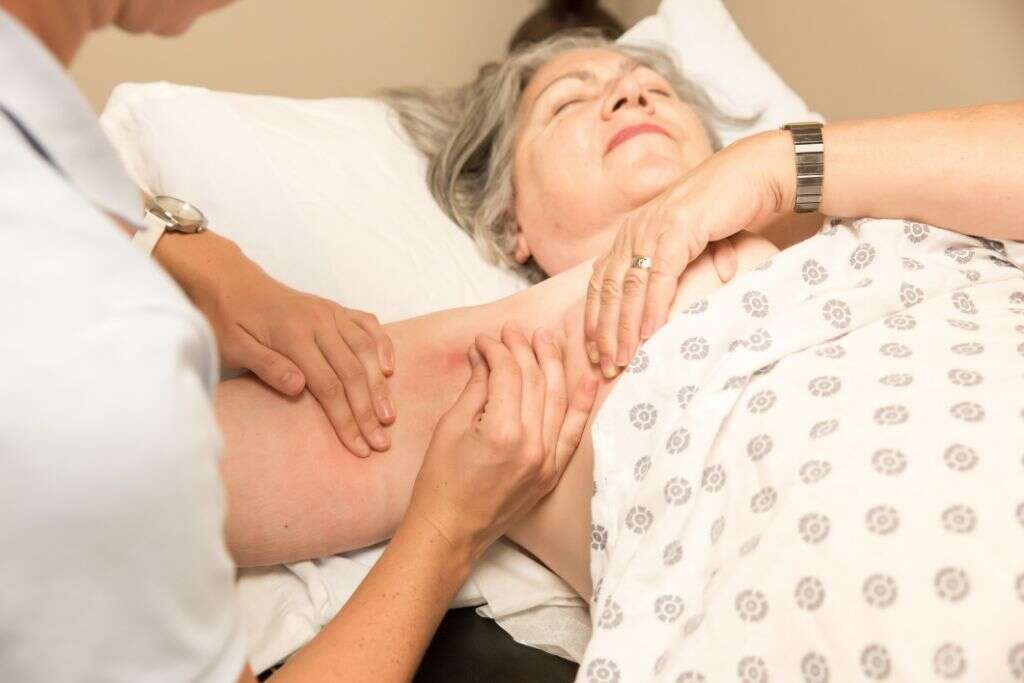
7. How Do Doctors Treat Lymphangitis?
The most common and effective treatment for most cases is antibiotics, which require a doctor’s prescription. In some instances, the doctor may determine you need fast and direct doses, so administer the medication intravenously rather than orally. While bacteria remains a common culprit, it is not the only one. If doctors determine a viral or fungal infection is at fault, they may prescribe antiviral or antifungal drugs instead.
You may also receive additional medication to treat specific symptoms, such as painkillers. In rare instances, the doctor may need to perform surgery to remove tissue that is affected beyond recovery.
8. What Can I Do To Protect Myself?
After experiencing lymphangitis for the first time, no one wants to experience this problem again. Thankfully, there are many things you can do to protect yourself. The best and most proactive approach is to practice consistent, good hygiene. Extend this to not just human family members but your pets as well.
Clean any bites or wounds you may suffer, no matter how small. If the wounds are large and may require medical attention, do not delay this. You should also think twice about swimming in lakes, ponds, or rivers if you have cuts or sores.

9. Will I Make a Full Recovery?
Most people make a full recovery from lymphangitis, but that depends on how urgently they treated the problem once discovered. This holds true even for people with underlying conditions. How healthy you were before the infection occurred also plays a role. The recovery time generally ranges from days to several months.
Unfortunately, with people who delayed treatment or were not healthy when the infection started, they may not recover. When lymphangitis goes untreated for too long, it can lead to sepsis. This is an infection that affects the whole body and can have life-threatening consequences.
10. Can I Get It More Than Once?
Like certain other infections, it is possible to suffer from lymphangitis more than once. The body does not develop an immunity to the condition. It may, however, develop immunity against specific bacteria or viruses that lead to lymphangitis. Some people suffer from recurring lymphangitis, which heals with proper treatment but tends to return later on. This is considered a chronic illness that can affect the individual for a lifetime.
For most people, lymphangitis ultimately looks more serious than it really is. This does not mean you do not require medical attention. What it does mean is that a swift and full recovery is likely if you receive treatment as soon as possible. When it comes to wound infections, it is always better to err on the side of caution, no matter how mild your symptoms may initially seem compared.