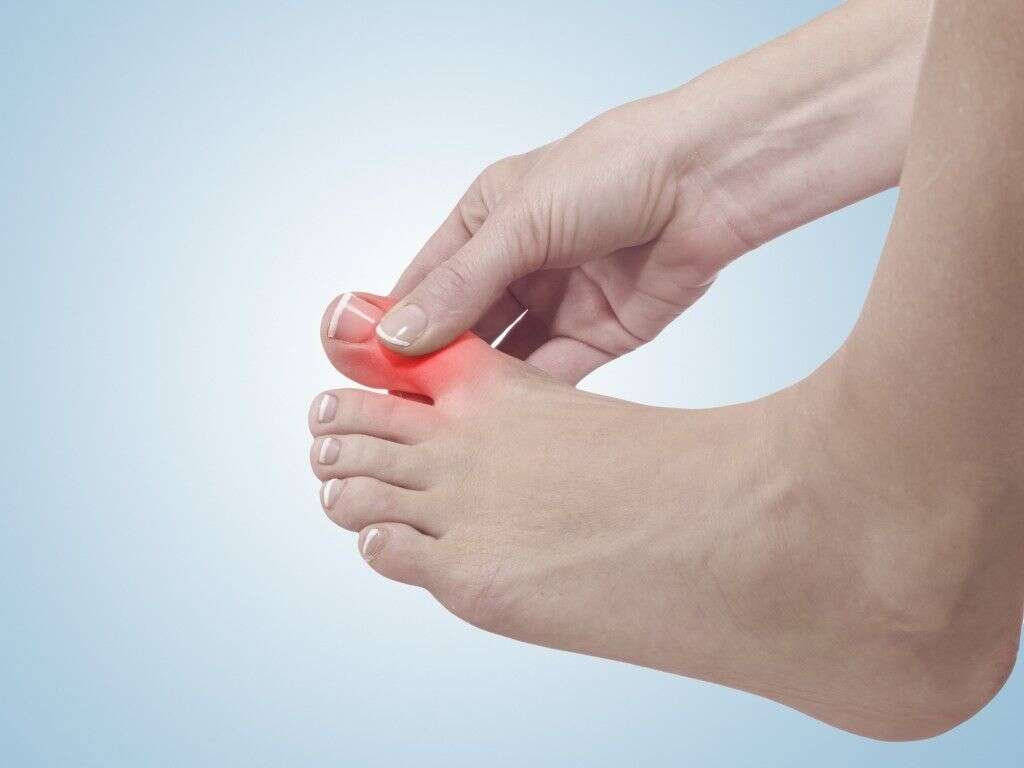
What Is Gout?
5. Complications of Gout
If gout remains unmanaged, it will cause damage and deformity of the joints as a result of gout-induced arthritis. This phenomenon causes bone erosion and loss of cartilage, which in turn leads to loss of mobility and compromised range of motion.
In the longer term, bone loss and deposits of chalky lumps under the skin referred to as tophi may occur. Kidney stones may also develop as a result of crystallization of uric acid. This can interfere with normal functions of the kidney, and hence, lead to chronic kidney disease, which may lead to kidney failure.
Advertisement