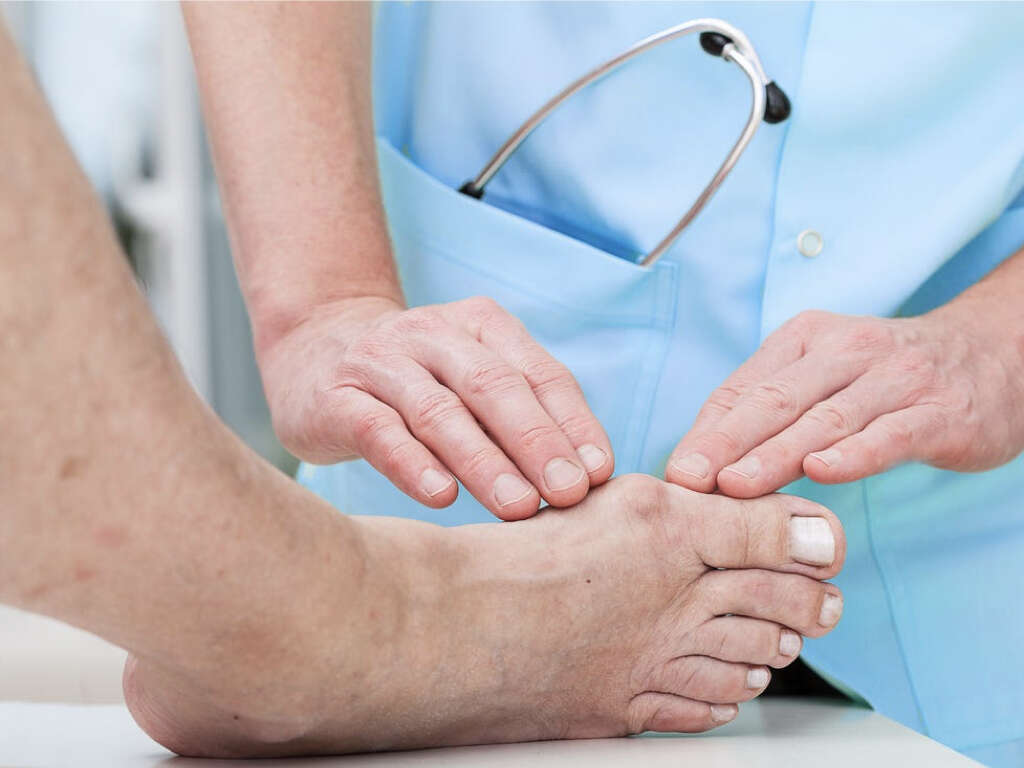
10 Causes of Gout
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis where the affected joint is swollen, painful, red, warm, and tender. The pain often begins rapidly, reaching a maximal intensity within 12 hours. In about 50 percent of cases, the joint at the base of the big toe is affected. Gout can also result in kidney stones, tophi, and urate nephropathy.
Gout occurs when the levels of uric acid in the blood is persistently elevated. This can be due to a combination of existing health conditions, diet, and genetic factors. When the uric acid levels are high, uric acid crystallizes and deposits in the tendons, tissues, and joints, resulting in a gout attack. Diagnosis can be achieved by confirming the presence of crystals in the joint fluid. Treatment includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and steroids.
Once the acute attack resolves, future episodes should be prevented through lifestyle changes and medication such as allopurinol and probenecid. Gout is estimated to affect about 1 to 2 percent of the Western population and is becoming increasingly common.
Cause #1: Food
While food is an essential part of life, there are certain foods that increase the risk or likelihood of gout. Meat and seafood have been strongly associated with gout as these are foods that are richest in purines, leading to a high yield of uric acid. Examples include shrimp, dried anchovies, dried mushrooms, organ meat (offal), and seaweed. Potatoes and chicken have also been implicated.
Individuals with a risk of gout are advised to cut back on saturated fats that are most often found in fatty poultry, high-fat dairy products, and red meat. They should focus on consuming lean meat and low-fat dairy. While seafood is generally higher in purines, the overall health benefits of eating fish potentially outweighs the risk of gout. Therefore, moderate portions of fish are still recommended.
Cause #2: Obesity
Obesity is a condition where there is accumulation of excessive body fat to the point where it has a negative effect on health. Individuals who are obese have a high body mass index [BMI = weight (kg) / height (m) x height (m)]. Obesity is defined as having a BMI of more than 30kg/m2. It is important to note that Asians have a lower threshold for being classified as overweight or obese as they have been found to have a higher percentage of body fat.
Obesity has been linked to various diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, obstructive sleep apnea, depression, osteoarthritis, and gout.

Cause #3: Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics are a type of medication that can be used in the treatment of hypertension and edema (due to liver failure, kidney failure, and heart failure). Diuretics also increases the risk of gout as diuretics increase urination and decrease the amount of fluid in the body. Once the remaining fluid in the body becomes more concentrated, it increases the risk of the development of urate crystals that cause gout.
Besides thiazides, there are also other types of diuretics that reduce the excretion of urate from the kidneys. Individuals who suffer from gout can speak to their doctor regarding changing their medication from thiazides to other substitutes to decrease the likelihood of having an attack of gout.
Cause #4: Aspirin
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is a type of medication used in the treatment of fever, pain, and inflammation. Aspirin is also required in the treatment of pericarditis, Kawasaki disease, and rheumatic fever. It can also be given after a heart attack to decrease the risk of death.
Low dose aspirin is often prescribed long term as it helps to decrease the likelihood of ischemic strokes, heart attacks, and blood clots. Some studies have also found it may decrease the risk of colorectal cancer. However, like all other medications, it can have side effects or adverse effects such as an upset stomach, stomach ulcers, and worsening asthma. It also increases the risk of gout. This is due to aspirin elevating uric acid levels as aspirin impairs the excretion of uric acid from the kidneys. However, patients should not stop taking aspirin unless it is recommended by their doctor as the benefits of aspirin may outweigh the risks of developing gout.

Cause #5: Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders where there is a prolonged duration of high blood sugar levels. Symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, and increased hunger. It can lead to various complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, and even death. It has also been associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, stroke, damage to the eyes, and gout.
While experts are still unsure on how diabetes and gout are related, it is believed to be due to the role of inflammation. Individuals with type 2 diabetes have also been observed to have higher levels of uric acid in their blood potentially due to the presence of extra fat. The presence of more insulin in type 2 diabetes also makes it harder for the kidneys to excrete uric acid, increasing the risk of gout.
Cause #6: Nonmodifiable Factors
Risk factors are conditions that increase the likelihood of developing a disease. They can be divided into modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors. This means that modifiable risk factors can be changed while nonmodifiable risk factors cannot be changed. For example, modifiable risk factors include diet, alcohol consumption, and exercise routine. These factors can be improved by the affected individual. Examples of nonmodifiable risk factors include age, race, and family history, which cannot be changed.
In gout, the nonmodifiable risk factors are age, gender, and family history. Men who are between the ages of 40 to 50, post-menopausal women, and those with a positive family history are more likely to develop gout.

Cause #7: Recent Surgery or Trauma
Patients who have recently undergone surgery or suffered an injury are also more likely to develop gout. This is thought to be due to injury and inflammation. For example, injury to some joints, especially the big toe, may trigger an attack as injury causing inflammation attracts more uric acid crystals to the joint.
Surgery also puts the body in a state of inflammation, which is necessary through the healing process, thus increasing the likelihood of developing a gout attack.
Cause #8: Alcohol
Alcohol is a source of purine, which produces uric acid once it is broken down by the body. The consumption of alcohol also increases the metabolism of nucleotides, which is another source of purine that could potentially be converted into uric acid. Another contributing factor would be the effect of alcohol on the rate at which uric acid is excreted, therefore increasing the levels of uric acid in the blood.
It should be noted that not all alcohol has an equal effect on the risk of gout. Regular beer has the highest purine content while spirits have the lowest purine content. Research has found that beer plays a more significant role in the development of gout.

Cause #9: Thyroid Disease
Common thyroid issues such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism have been associated with the development of gout. Studies have reported that high uric acid levels in the blood was found in patients who are hypothyroid. This was also seen in hyperthyroid patients.
However, the mechanism causing the increase of uric acid levels in the blood differs between both conditions. In hypothyroidism, high uric acid in the blood is due to decreased renal plasma flow and impaired glomerular filtration (in the kidney). In hyperthyroidism, hyperuricemia occurs due to increased urate production.
Cause #10: Kidney Disease
While kidney disease has been thought to cause gout, conversely, gout can also cause kidney disease. Uric acid is filtered through the kidneys. It has been observed that approximately 10 percent of individuals with chronic kidney disease have gout while a higher percentage of individuals with gout have kidney disease.
Individuals with kidney disease often have uncontrolled gout, which worsens the kidney disease. In kidney disease, the kidneys do not function normally and no longer filter out uric acid as well as causing a buildup leading to gout. Since most individuals with early kidney disease are unaware, gout can also be a warning sign of early stages of kidney disease.