What is Diverticulitis?
A healthy digestive system is very important to us. It is very closely linked to our overall physical health, and also to our mental health. Unfortunately, there are numerous things that can go wrong with our digestive system, and they can make us quite ill.
One potential problem is diverticulitis. It is a potential complication of a fairly common condition that many people will have, although most will never be aware. It is not usually dangerous but it will develop into something potentially serious in a small number of cases. The condition is also treatable, and treating the milder cases is usually straightforward.
1. Diverticulitis
Our digestive system is lined with specialized tissues that help to protect it from the caustic nature of our digestive juices. Diverticulosis is a condition where the patient has developed bulges known as diverticula on the walls of their digestive system. They are a common condition, and they are also unlikely to cause any symptoms for the patient. These pouches are most likely to be located on the colon.
Although the condition usually causes no symptoms, problems will arise in some cases. The pouches will sometimes become inflamed, which is likely to be troublesome. This is a condition known as diverticulitis, which can become severe, but it is treatable.

2. Causes
Some parts of the walls of the intestines are weaker than others and these can sometimes give way and be pushed outwards when there is too much pressure placed on them. This can then result in the small pouches that are known as diverticula, and they are usually around the same size as a marble.
These pouches can sometimes tear, and this can result in the inflammation that results in diverticulitis. In addition to inflammation, these tears will also sometimes allow infections to develop in the walls of the digestive system. This will, in turn, result in a number of unwelcome symptoms.
3. Pain
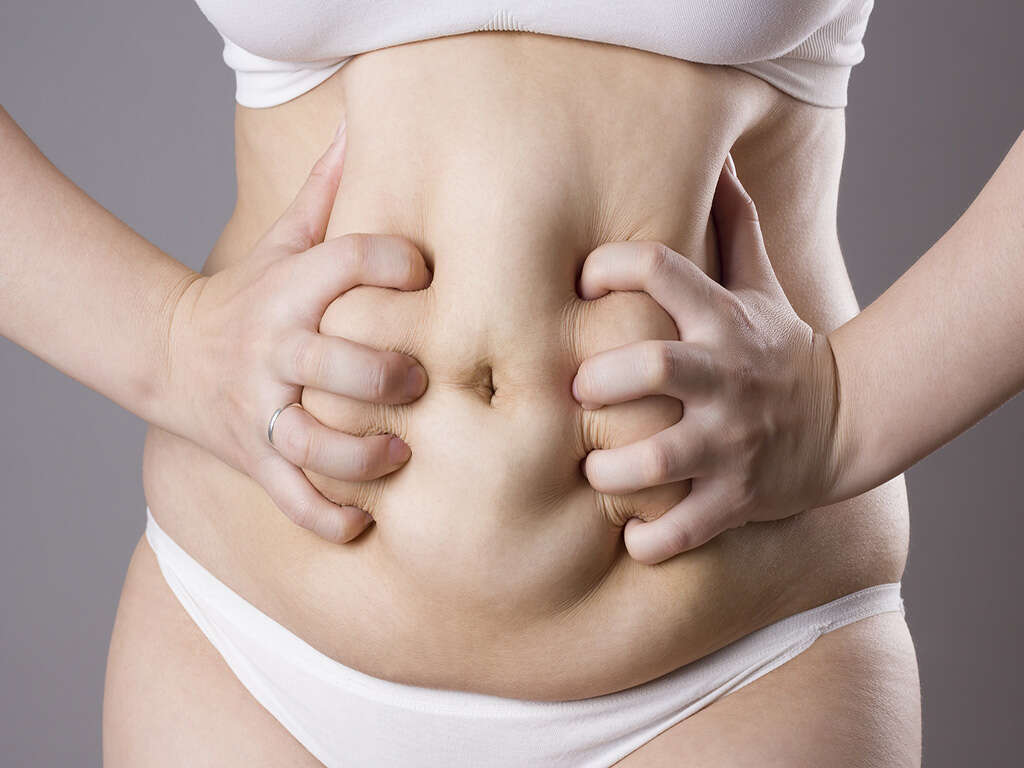
Perhaps the most common symptom of diverticulitis is pain. It is typically located on the left side of the abdomen, but there will sometimes be more pain on the right side. The latter tends to be the case in people that are from Asian heritage. Regardless, the pain is likely to last for days, and it will also likely be constant.
If an infection occurs, then the patient can also experience a fever. Constipation is another potential symptom, whereas a smaller number of people with diverticulitis will develop diarrhea. These symptoms should encourage you to make an appointment with your doctor as soon as you are able to.

4. Complications
In addition to the symptoms already mentioned, around one quarter of all people with diverticulitis will develop further complications. This includes pus accumulating in the diverticula to form abscesses. These abscesses can burst, potentially releasing a large volume of toxins into the patient’s body.
The lining of the digestive system can also become scarred, and this can result in food becoming blocked. A fistula can also develop, which is the medical term for an abnormal passageway between different parts of the body. These are complications that should be treated as soon as they have been detected because they might otherwise cause serious problems.

5. Peritonitis
The peritoneum is the name of the protective membrane that lines the internal wall of the abdomen. The membrane surrounds much of the digestive system, with some of our most important organs contained within. Peritonitis is the name of the condition where this membrane has become inflamed.
There are numerous reasons why this inflammation might happen, one of which is diverticulitis. Some cases of diverticulitis can result in the contents of the intestines passing through ruptured diverticula, leaving the contents in the abdominal cavity where it can do a lot of damage. Peritonitis is potentially very dangerous and should be treated as a medical emergency.

6. Risk Factors
Just about anybody can develop diverticulitis, but some people are more prone to the condition than others are. This includes people who are obese, while it is also more likely to occur as people get older. People that don’t exercise enough are also at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Other potential factors include smoking, with non-smokers less likely to develop diverticulitis. Some medications will also increase risk, including some NSAIDs such as ibuprofen. Your diet can also have an impact, and people that eat a lot of animal fats and little fiber are more likely to develop diverticulitis.

7. Prevention
Diverticulitis can happen to anybody, but there are some ways to help make it less likely you will develop the condition. This largely involves living a healthy lifestyle, and quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to help prevent a wide range of health conditions.
You should also try and get a lot of fiber in your diet, and this means lots of fruits and vegetables. You should also try and avoid fatty foods. Drinking plenty of fluids will also help as it can aid with your digestion. Exercising can also help with the functioning of your bowels, as well as helping to overcome obesity.

8. Diagnosis
The symptoms caused by diverticulitis can also be caused by a wide range of other medical conditions, so tests will likely need to be performed to help reach a diagnosis. However, a brief physical exam may also be performed to help look for signs of other medical conditions.
Other tests can involve a stool test to help rule out infections. A pregnancy test may also be performed, while urine and blood samples may also be taken to be analyzed. A liver enzyme test may also be performed, and a CT scan can help experts to look for signs of diverticula.

9. Medication
How diverticulitis is treated will depend largely on how severe the condition is. Treatment will often involve antibiotics, but they are not always deemed necessary. Instead, the patient is often advised to eat a liquid diet to try and give the condition an opportunity to heal on its own.
If the condition is more severe, then stronger antibiotics are likely to be used, and they may be administered intravenously. This is likely to mean having the patient stay in hospital so the antibiotics can be delivered through a saline drip. Medication is all that is needed in the majority of cases.

10. Surgery
In some cases, it may be necessary to drain any abscesses, and this is usually done by inserting a tube. Other surgical procedures may also be performed if medication is not working, or if the patient has medical conditions that can cause other complications. Perforations and fistulas may also need to be repaired.
A primary bowel resection may be performed, which involves removing the parts that are badly infected and/or damaged. Another potential treatment is a bowel resection with colostomy, which involves attaching a bag for waste to pass into. The bag will often be removed when the condition has improved.