What Is an Endocrinologist?
Hormones play a larger part in our lives than you might think. For one thing, they have a huge impact on how we are feeling and they can even change our mood in just a matter of moments. In addition, they affect the functioning of our organs in a way that ensures everything is running just as it should be.
Things can go wrong with our hormone levels, and this can have a powerful impact on our lives. It can have a devastating effect on our mood and can also cause the misfunctioning of our essential organs. The good news is that if something does go wrong, endocrinologists are available that will help treat the condition the best they can.

1. Hormones
Hormones are naturally occurring chemicals that are produced by the body and have an impact on various functions of the body. Homo sapiens produce more than 50 types of hormones, with each one performing a different function. It is often the case that they are produced in very small amounts but still have a profound impact on our well-being. It is important that our hormones remain in balance to ensure everything is running smoothly. Otherwise, some of our organs would struggle to function, and we can also experience symptoms like depression and anxiety. Hormones also encourage growth, allow us to sense the world around us, and are also very important for reproduction.

2. The Endocrine System
As mentioned, it is very important that the body maintains the right balance of hormones in order to help ensure that everything is running smoothly. This is achieved with help from the endocrine system, which monitors, produces, and secretes these hormones into our body. Most hormones are released directly into the bloodstream.
They will then be transported in the blood to the various organs and other parts of the body where the hormones can do their job. Because our hormones are flowing through the blood, blood tests are often used to help medical professionals gauge hormone levels in the body.
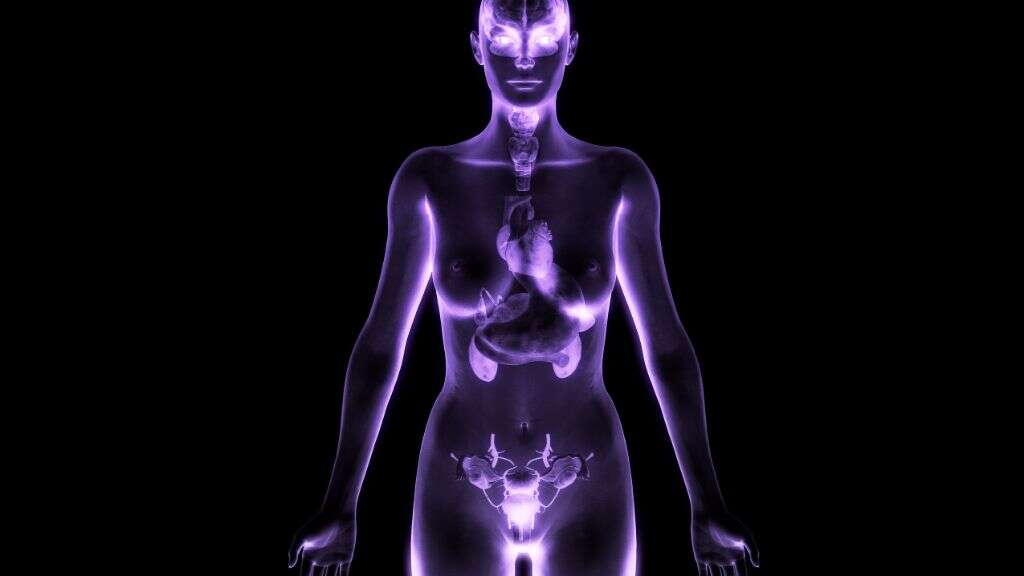
3. Endocrinologist
An endocrinologist is somebody that specializes in the field of endocrinology. Endocrinology is the study of hormones in the body, the endocrine system and, by extension, complications that occur as a result of issues with the endocrine system.
The endocrine system is quite large, and there are numerous medical conditions that can result from a patient that has hormonal imbalance problems. As such, an endocrinologist will often have a considerably varied role to perform. Depending on the symptoms, they will need to perform thorough physical examinations on their patients while also undertaking tests to see what the cause of the problem is.

4. Adrenal
The human body has a number of hormone-releasing glands, one of which is the adrenal gland. The glands are located on top of the kidneys and they are largely responsible for producing hormones that affect our stress levels and our sexuality. The adrenal glands produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones, although women do also have certain levels of androgens in their body.
If women have too many of these hormones then they can begin to develop some typically male characteristics. Other hormones released here include catecholamines and corticosteroids, which have an effect on how we respond to stressful situations.
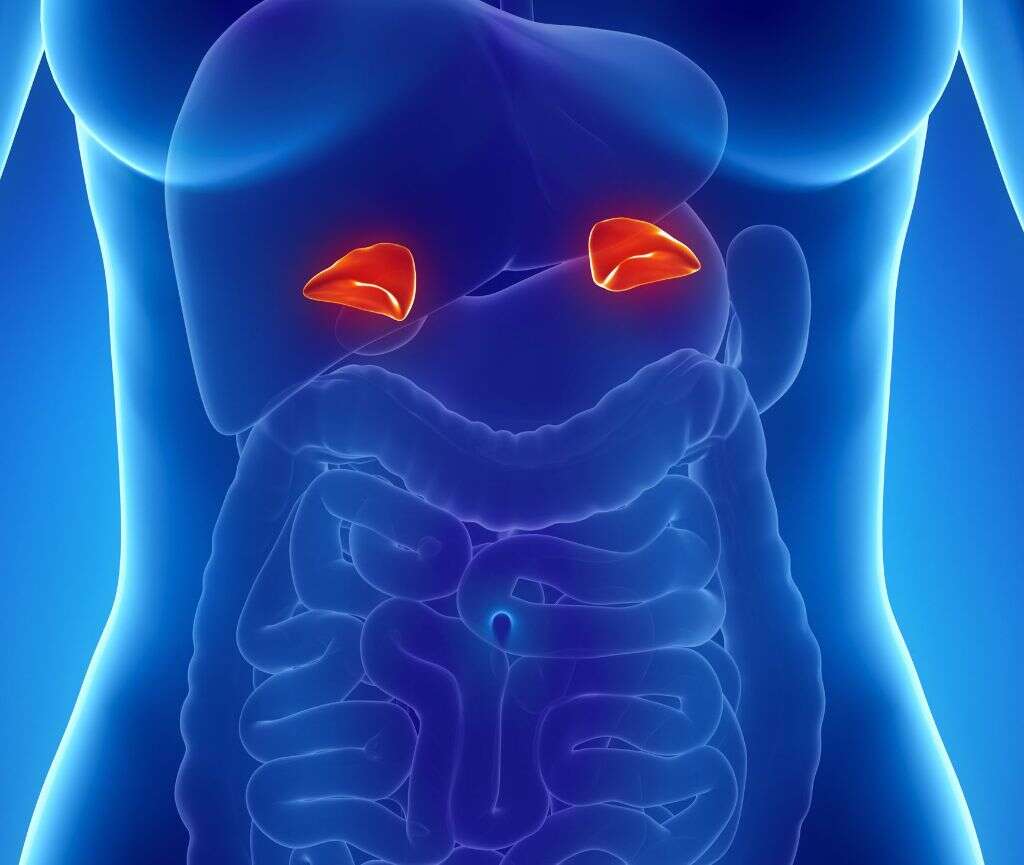
5. Testicles and Ovaries
The testicles and ovaries are essential elements of the human reproductive system. The ovaries produce ova (eggs), while the testicles produce sperm. In addition, they also produce and secrete hormones. The ovaries produce the female hormones progesterone and estrogen, and these influence processes like menstruation and sexual development.
The testicles mostly produce testosterone, a hormone which affects the production of sperm, sexual development, and libido. Both men and women have a certain amount of all of these hormones, although they are present at different levels in each sex. Problems with the production of these hormones can have a profound impact on how the patient develops and their fertility.

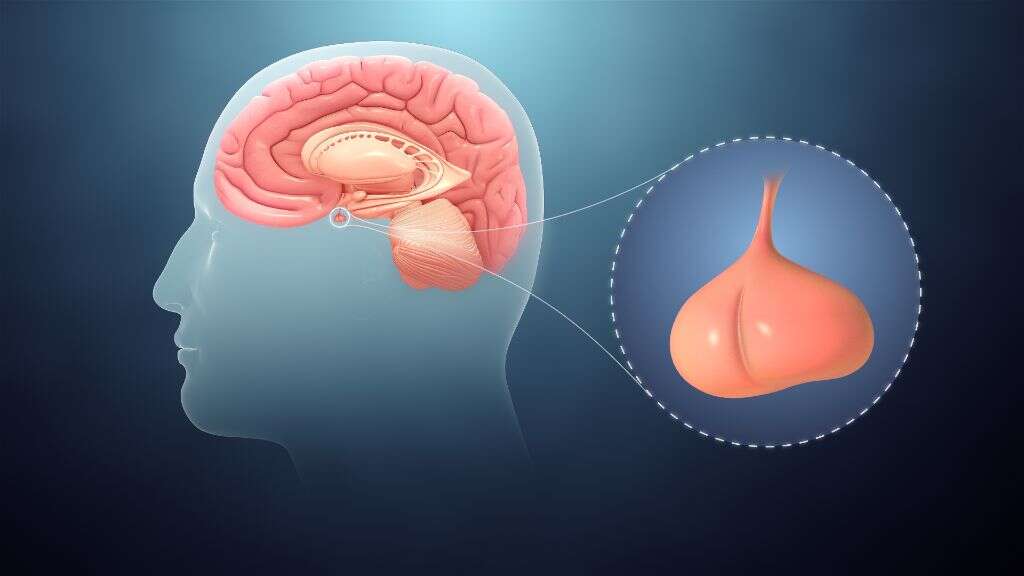
6. Hypothalamus and the Pituitary Gland
The hypothalamus is a gland that is found at the top of the brain stem, just below the thalamus. It is responsible for helping to control important processes such as breathing, heart rate, appetite, and sleeping. At the base of the hypothalamus is the pituitary gland, another hormone-releasing gland.
The pituitary gland produces and secretes hormones that help to regulate other glands. In addition, it secretes hormones that help to regulate growth and sexual development. The pituitary gland is also sometimes referred to as the master gland because of the influence it has over the other glands in the body.
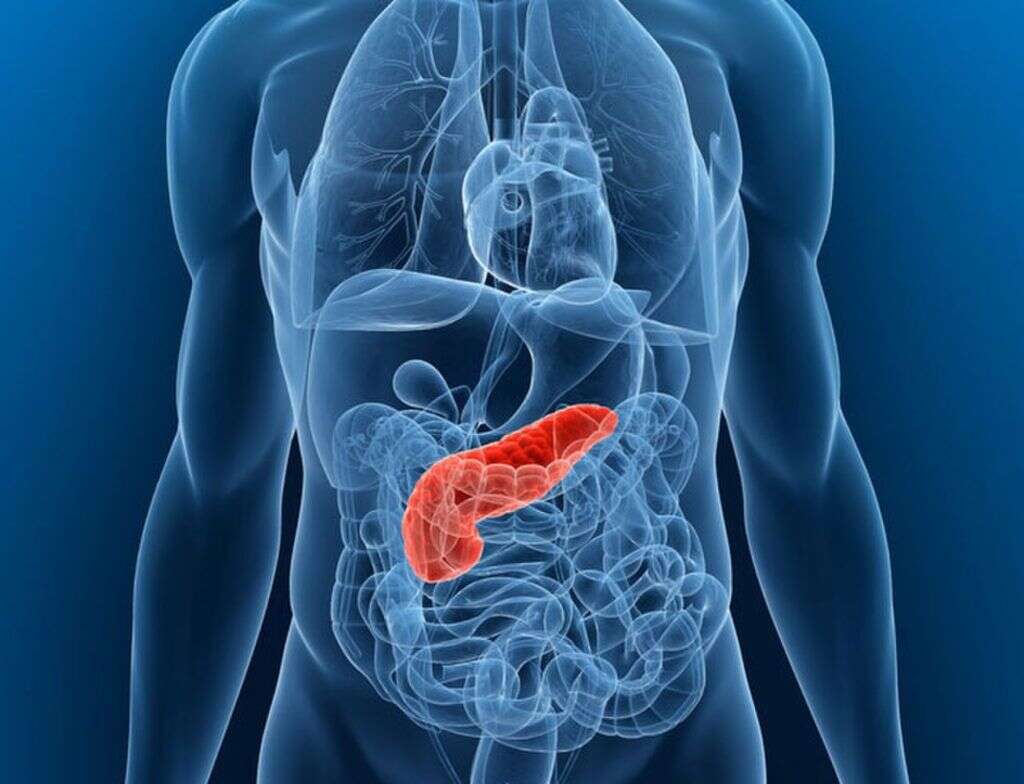
7. Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ that is found in the abdomen area and plays an important role in the functioning of the digestive system. It is just around 6 inches long in adults and is located just behind the stomach. One of the functions of the pancreas is the production and release of insulin.
This is a hormone that helps the body to process sugar and regulate the levels of sugar that are flowing through the body. As such, issues with this gland mean that the patient might struggle to regulate their blood sugar levels, resulting in the well-known condition called diabetes.
8. Parathyroid Glands
The parathyroid glands are also located near the thyroid at the area of the throat. One of its functions is to help regulate the body’s level of calcium and phosphate.
These are very important for us because they help ensure messages can be sent around the body, including to and from the brain. The balance needs to be right otherwise the patient could begin experiencing some very unwelcome symptoms. The pineal gland is located in the brain. It has the role of producing and releasing melatonin, which is a hormone that helps to regulate our sleeping patterns as well as helping to regulate our sex hormones.

9. Thymus Gland
The thymus is a gland that is found deep to the sternum, otherwise known as the breastbone, and it plays an important part in the immune system. This gland will often stretch from the sternum to the thyroid gland in children, but it will begin to shrink in people who have reached puberty.
The thymus gland is where T lymphocytes, or T-cells, develop. These cells, also known as killer cells, play a very important part in helping to keep the body safe because they are able to directly attack and kill pathogens. In adults, T-cells are also found in the lymphatic system, meaning that the thymus gland becomes less important.
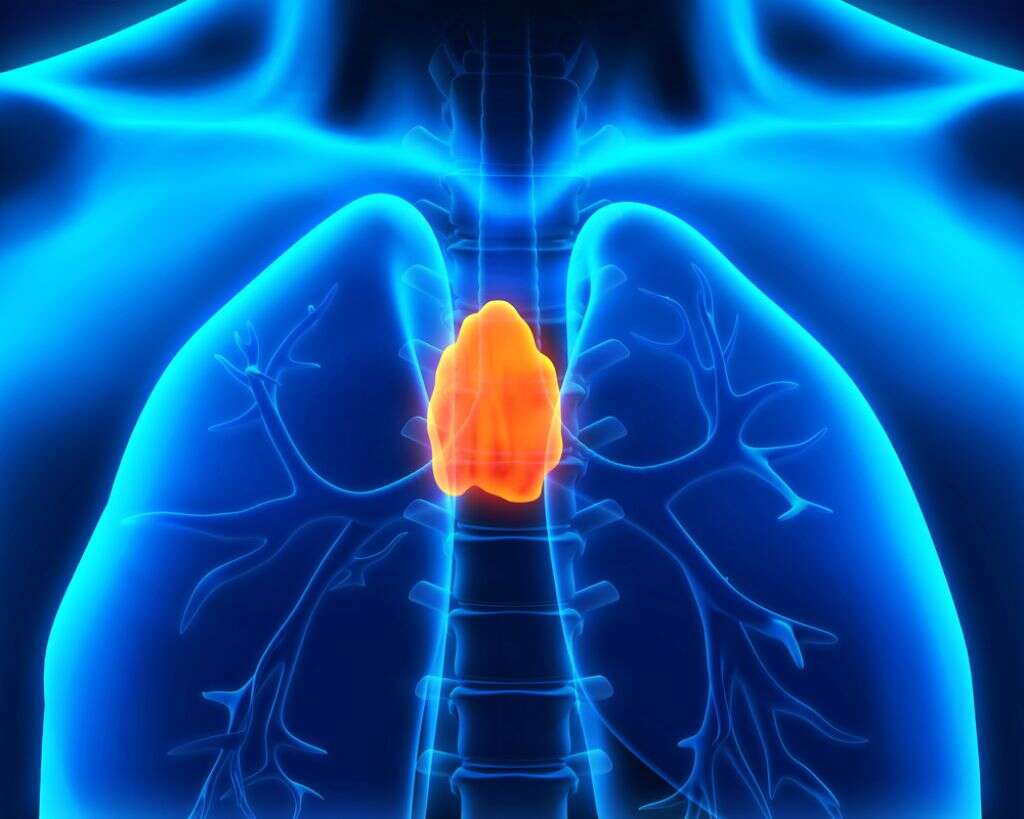
10. Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is located in the neck and has evolved to be butterfly shaped. This gland produces triiodothyronine and thyroxine, both of which are very important for regulating bodily functions. The thyroid gland is responsible for the regulation of functions such as the heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, and metabolism.
Problems with this gland can have effects such as making people depressed, too anxious, and/or causing them to lose or gain weight. The gland can sometimes become swollen, causing the neck to also become swollen, creating what is known as a goiter. In cases of an overactive thyroid gland, radioactive iodine treatment may be necessary.