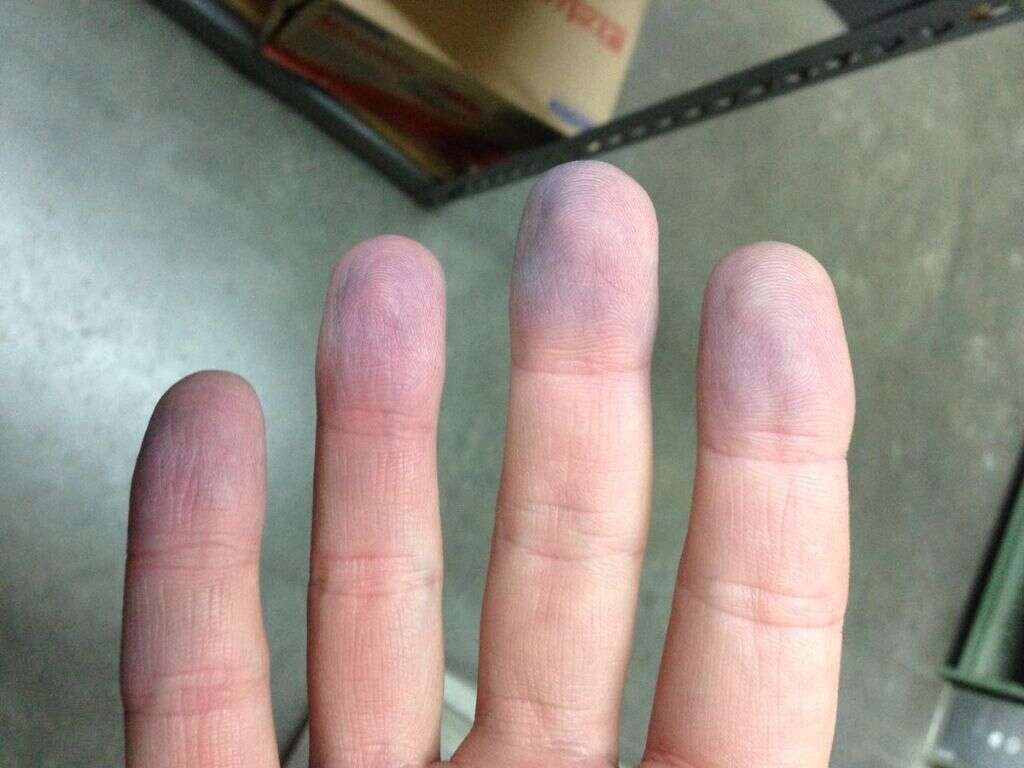
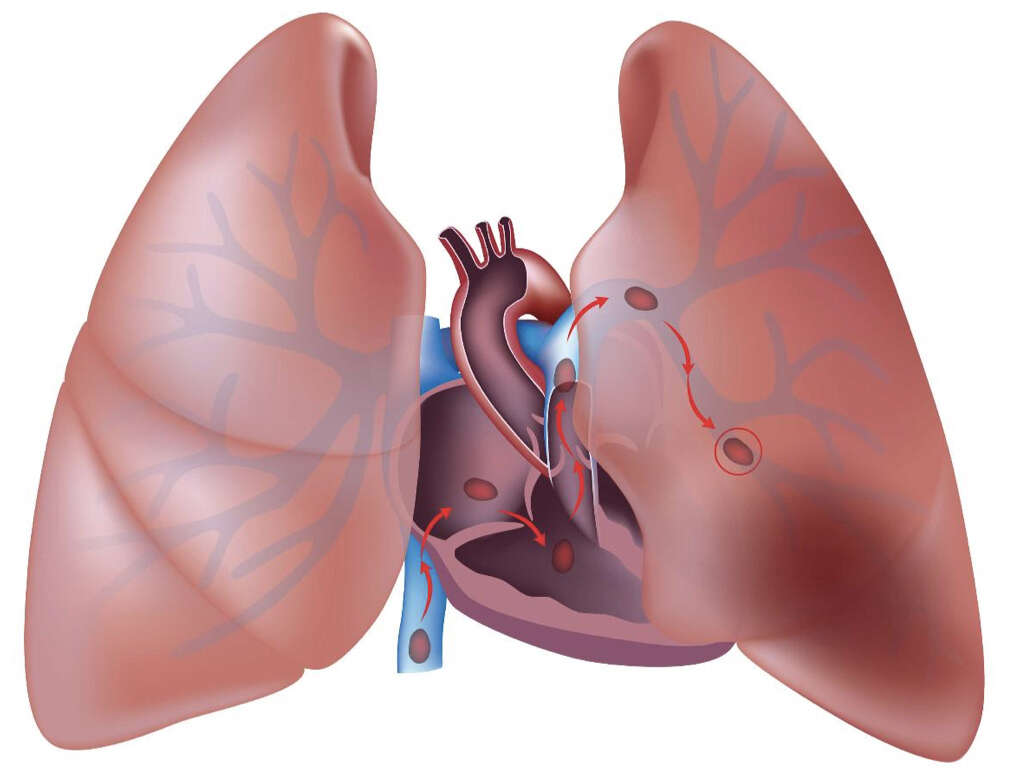
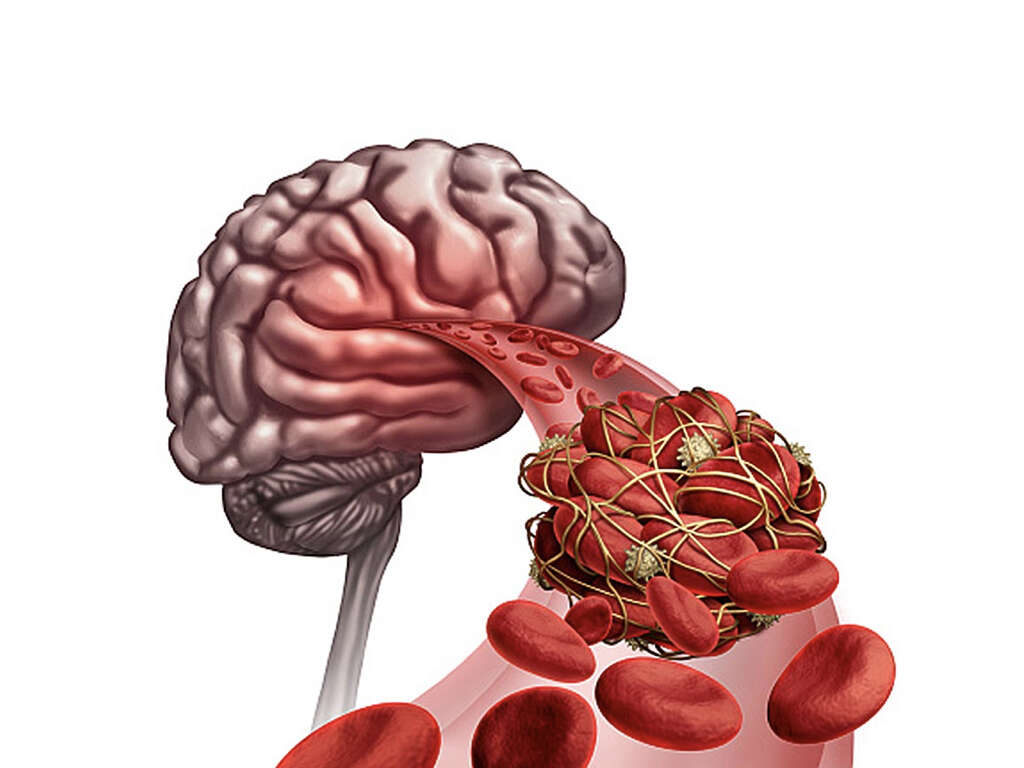
What Is a Pulmonary Embolism?
8. Approach to Treatment
Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis can still occur in patients who receive anticoagulants. In children, the treatment of choice is anticoagulants. There is very little evidence regarding the use of low molecular weight heparin in children who have thromboembolic disease. In adults, anticoagulants are the mainstay of treatment.
In acute cases, supportive treatments such as analgesia and oxygen can also be important. Patients given warfarin may remain in the hospital until they reach therapeutic levels. Low-risk cases can be managed at home. Thrombolysis can be used in patients who have acute pulmonary embolism, hypotension, and low risk of bleeding. Thrombolysis in this group should not be delayed as it can result in irreversible cardiogenic shock. Other treatment options include embolectomy and the insertion of a vena cava filter.
Advertisement