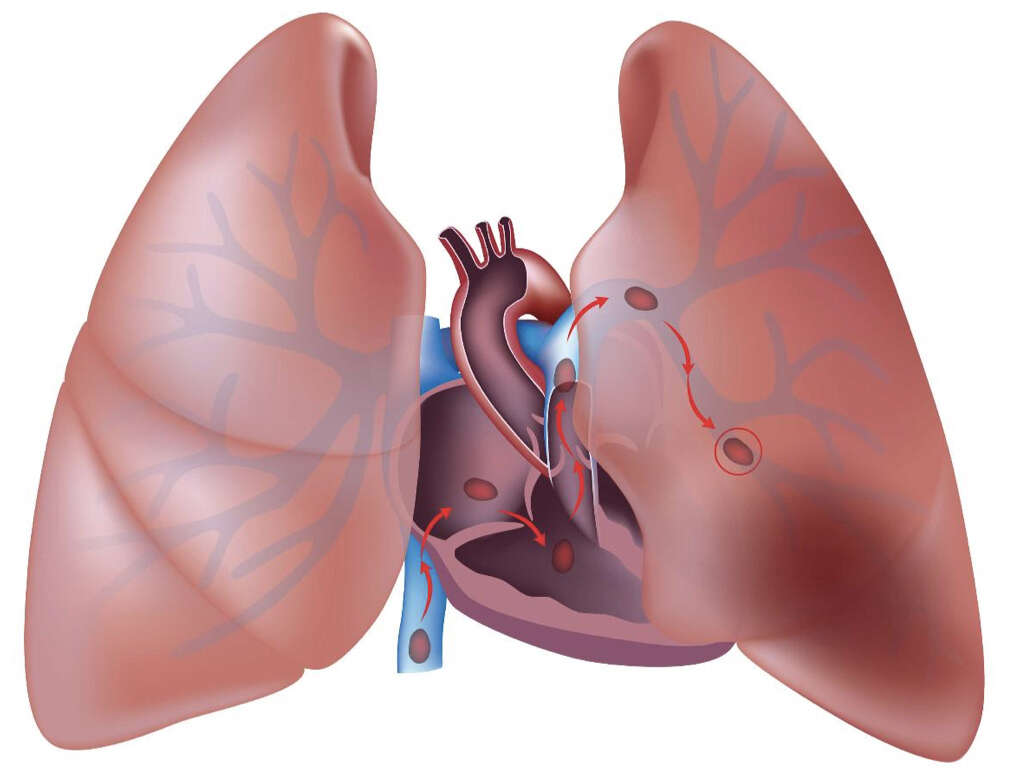
What Is Embolic Stroke?
Learn the signs, symptoms and prevention strategies of an embolic stroke today. Compare this diagnosis with other types of strokes and explore possible treatment options, complications and other features of this issue.
There are many causes of strokes. Depending on the area that is affected, the symptoms can also be varied. While it may be difficult to see signs of an oncoming stroke, there are certain risk factors that can be avoided to reduce the chance of a stroke occurring. If you or someone you love suffers from an embolic stroke, find out how prompt diagnosis and treatment options can help.
1. What Does Embolic Stroke Mean?
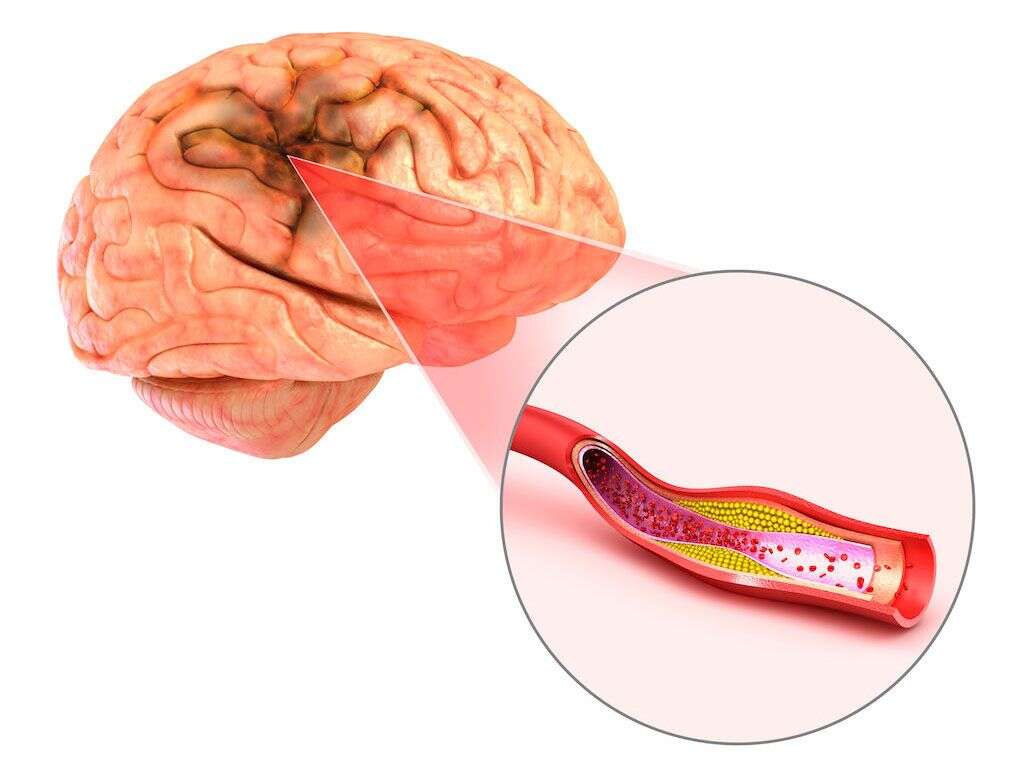
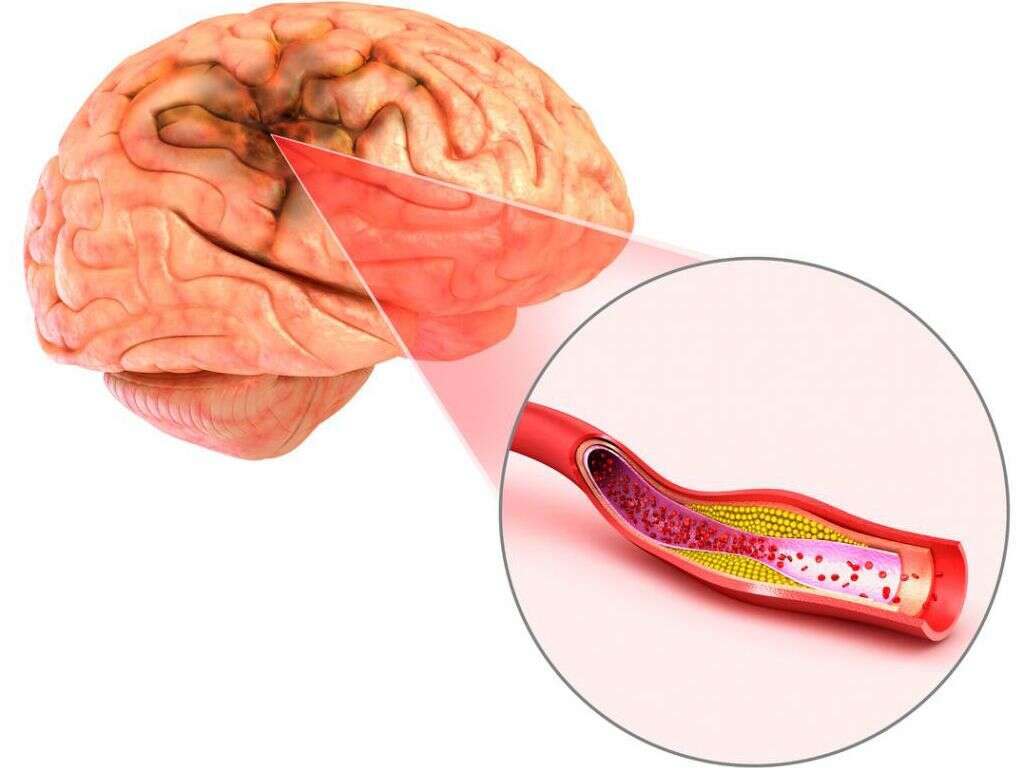
This type of stroke is caused by an emboli, which is a blockage of blood flow to the brain. As a type of ischemic stroke, an embolic stroke drastically affects brain blood flow. If the blockage continues for more than a few minutes, then brain cells begin to die.
The symptoms, seriousness and treatment options vary on the location and severity of the blockage. Learn more about the causes and symptoms and don’t hesitate to contact a doctor if you or someone you know has one or more symptoms of an embolic stroke.
2. What Are Common Causes?
A number of issues can create an emboli. The most common causes are cholesterol plaque or a blood clot. When any of these migrate toward the brain, they can become stuck in an artery and create a blockage.
There are other, less common causes of an embolic stroke. Air in the bloodstream, a leg blood clot, infectious clot or dislodged heart tumor can all cause a stroke. The cause and location of the blockage affects the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options, so it’s essential for a medical professional to determine the cause and location of the blockage.
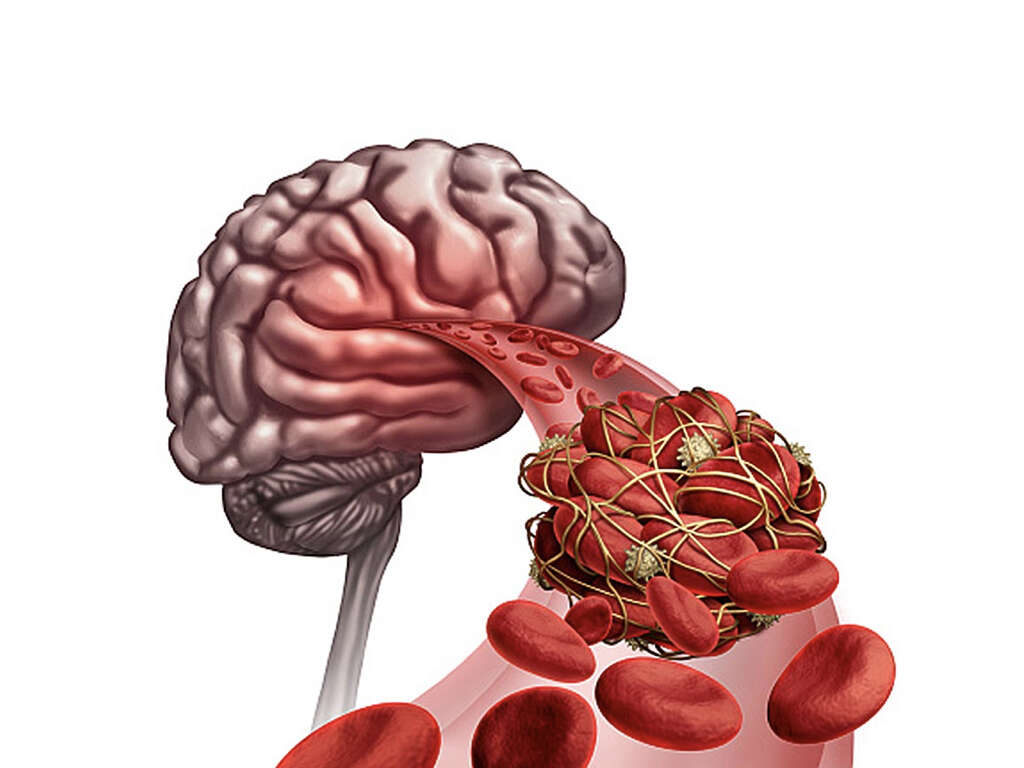
3. What Are Typical Symptoms of Embolic Stroke?
Because a stroke causes brain damage, the symptoms can vary. Typically, individuals experience difficulty walking, speaking and/or understanding words. Some individuals experience numbness in either side of their face or in their limbs. In some cases an embolic stroke can cause temporary paralysis of limbs or face.
Other symptoms can include slurred speech, dizziness, lethargy, faint feelings and sleepiness. Any of these symptoms can occur without warning and in combination with others. They are categorized as muscular, cognitive and other symptoms. While some appear more extreme than others, it’s important in all cases to contact local emergency services immediately if you suspect that you or someone you know is experiencing a stroke.
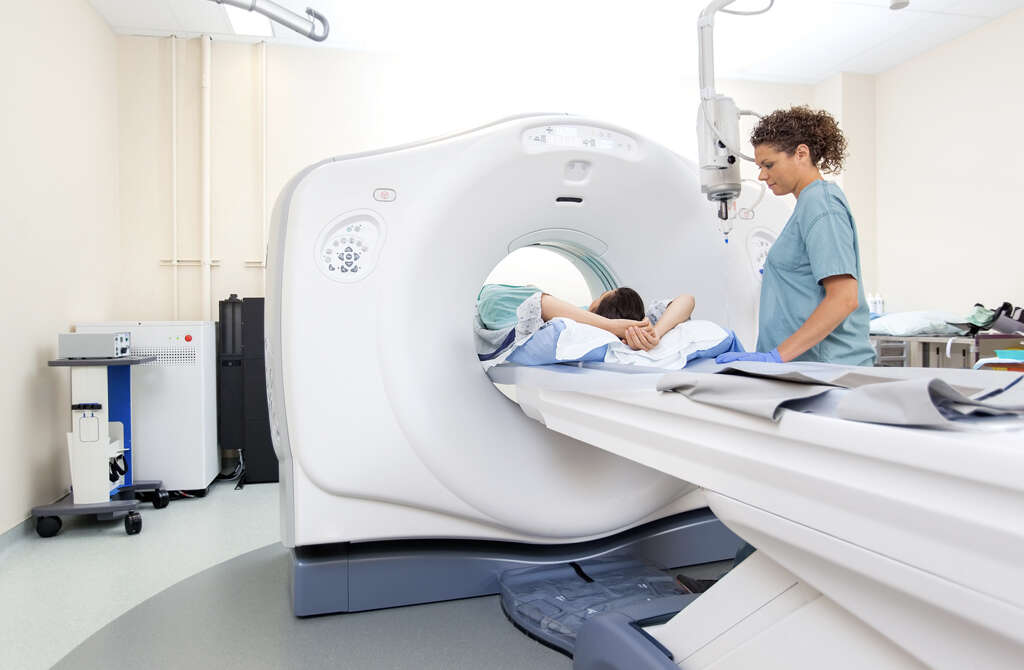
4. How Is It Diagnosed?
There are a number of tests that doctors can perform to diagnose a stroke. These are used to establish the cause of the symptoms as well as determine the location of the blockage. Common tests include a CT scan and MRI.
In some cases, a doctor may also perform a blood test, echocardiogram, carotid ultrasound or cerebral angiogram. These tests determine the location and type of block that is present. These tests may be performed before a treatment option or after a clot-busting medication is taken.
5. What Steps Should You Take If Someone Is Having a Stroke?
It’s critical that you take the necessary steps to identify and respond to a stroke. The most important step you can take to assist an individual experiencing a stroke is to look for the following symptoms and to contact an emergency service immediately.
The most apparent symptoms often include slurred or strange speech, a limp or paralyzed arm and visible face droop. Any combination of these symptoms should be treated seriously and local emergency services contacted. A quick response can mean the difference between serious complications and a full recovery.
6. Are There Treatment Options?
A doctor may recommend an intravenous or oral clot-busting medication. If taken promptly, this medication can prevent serious brain damage caused by an embolic stroke. Every second can mean additional brain damage due to the blockage, so it’s essential to receive the medication as quickly as possible if it’s recommended by a doctor.
Another common treatment option is a mechanical clot removal. This procedure is known as a mechanical thrombectomy and is typically used within the first 24 hours of the first stroke symptoms.

7. Who Is at Risk of Embolic Stroke?
There are a few key factors that can help predict the risk of a stroke. Women are more likely to experience a stroke than men, and African-Americans are more likely than Caucasians. Family history plays a large part in increasing the risk as well, particularly if an immediate family member has had a stroke. A history of high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol is also a risk factor.
Other predictors include a personal history of heart attack, stroke or other similar issues. An individual who has previously experienced a stroke is significantly more likely to have a major stroke, as is someone who has experienced a heart attack. Finally, the risk of a stroke doubles with every decade after the age of 55.
8. What Are Prevention Strategies?
Many of the prevention strategies are aimed at reducing the level of risk. Ask your doctor about ways to manage high cholesterol, diabetes or other risk factors. Moderating drinking, engaging in regular exercise and managing your diet are common prevention strategies.
Some risk factors are associated with obesity, so your doctor may also recommend maintaining a healthy weight as part of your prevention strategy. While an embolic stroke can affect anyone, the risk is higher for individuals 55 years and older.

9. What Are Other Types of Strokes?
Strokes can be categorized as ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes include embolic and thrombotic types. They are caused by blockage in veins and blood vessels in or leading to the brain. While a thrombotic stroke occurs from a clot that has traveled to the brain, embolic strokes are caused by any material within a vessel that has traveled to the brain.
Hemorrhagic strokes occur due to a rupture in a blood vessel. A rupture prevents blood flow to the brain and can create irritation and swelling in the affected area.
10. How Common Is Embolic Stroke?
There are about 140,000 deaths caused by strokes every year in the United States. Of these, approximately 87% are ischemic. This means that embolic and thrombotic strokes are the most common types of strokes in the United States, with hemorrhagic ones being less common.
Understanding the causes, signs and prevention strategies of strokes can help you and your loved ones reduce the risk of a stroke and serious complications related to a stroke. Carefully review the prevention strategies and symptoms and respond immediately to the first signs of a stroke.