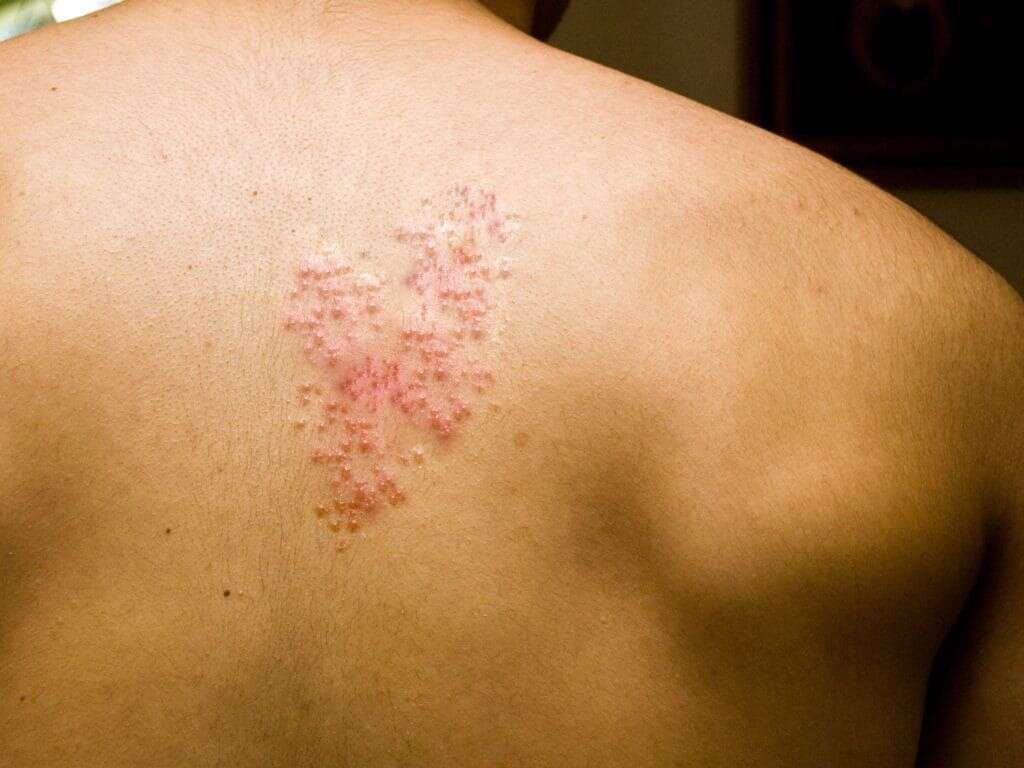
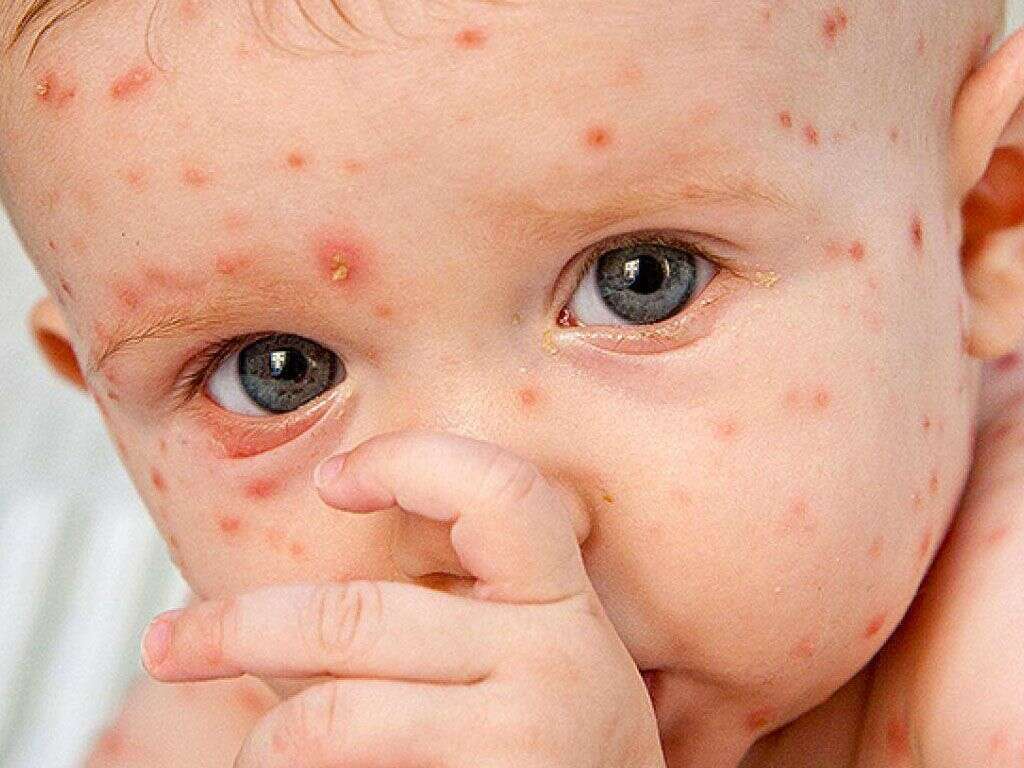
What Causes Shingles?
3. Signs and Symptoms - Face
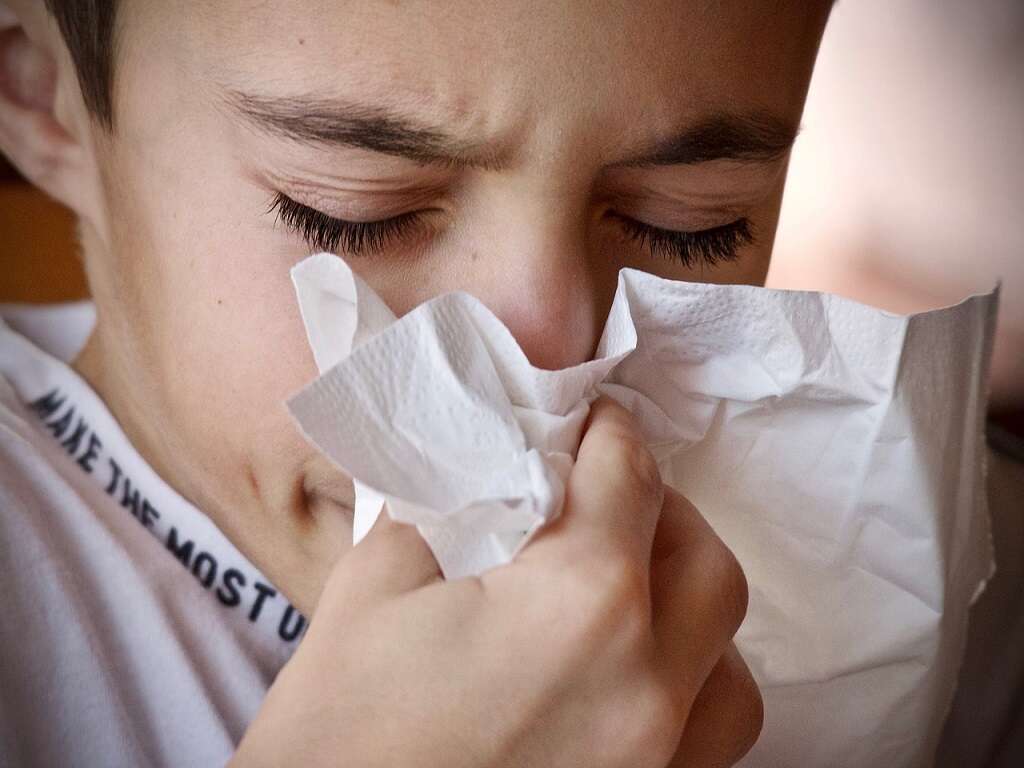
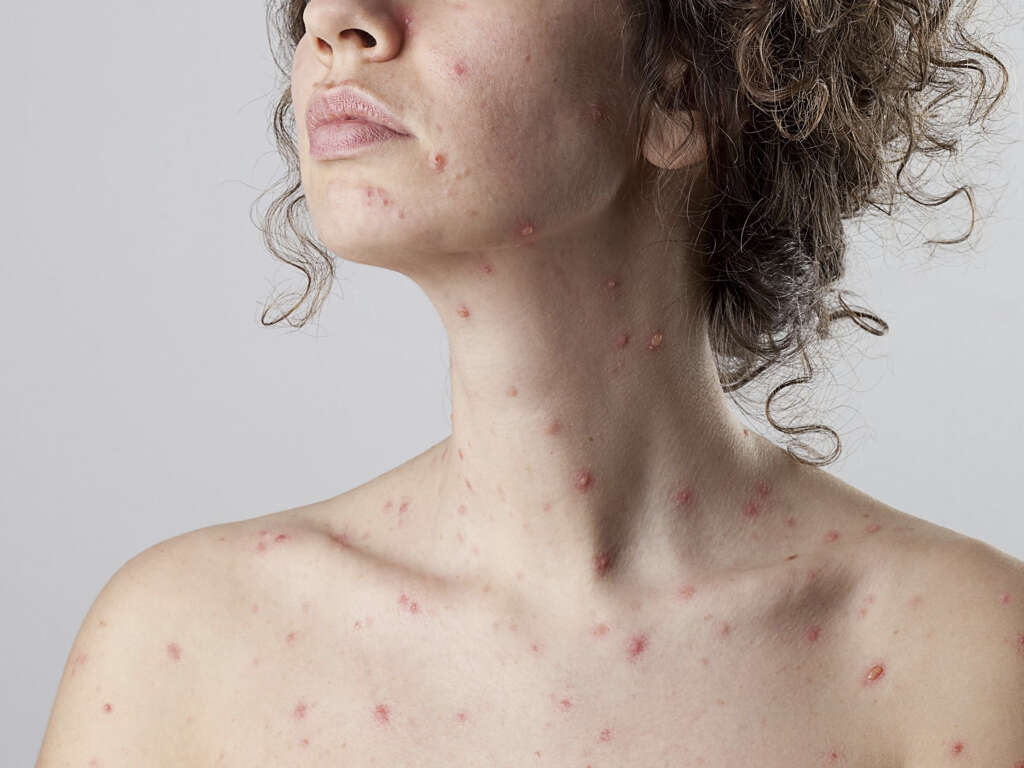
When shingles affects the face, it most commonly affects the trigeminal nerve. In the trigeminal nerve, it usually affects the ophthalmic branch causing the skin of the forehead and around the eyes to be affected. Ten percent to 25% of patients with shingles experience this and may have symptoms such as uveitis, keratitis, and conjunctivitis that leads to vision loss and inflammation in the eye.
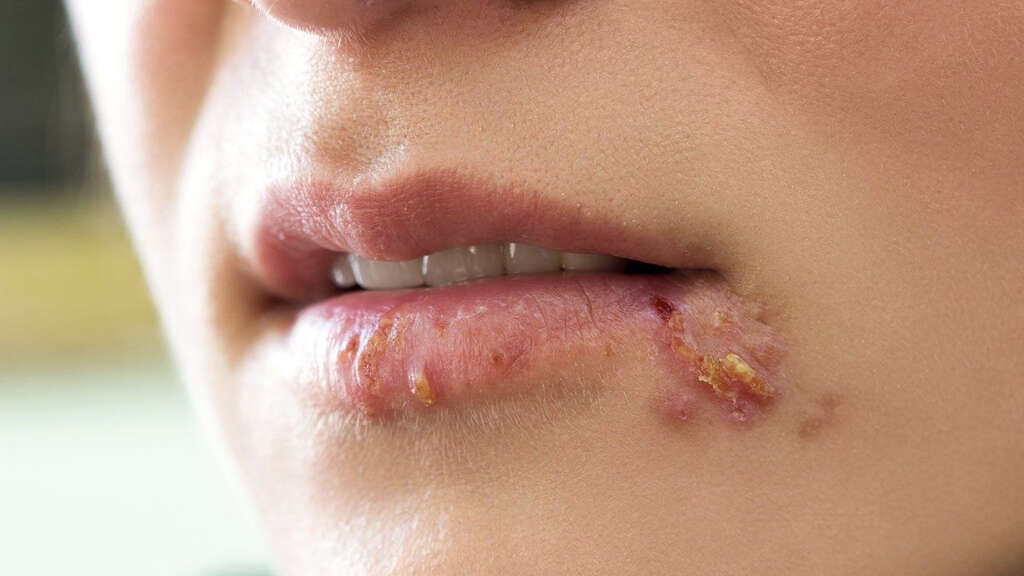
When it affects the ear, it is known as herpes zoster oticus or Ramsay Hunt syndrome type II. Other cranial nerves may also be involved which can cause further signs and symptoms. A vesicular rash may appear on the ear. Since it affects the facial nerve, shingles can also cause patients to lose taste sensation in the anterior two thirds of the tongue.
Advertisement