What Causes Gout?
With as many as 8.3 million people living with gout in the United States, the condition has become more common as obesity rates continue to rise. Gout can cause extreme pain and discomfort, with frequent attacks that can lead to serious impairment and even permanent damage to the joints and other parts of the body.
Fortunately, with the right medication and lifestyle changes, living with gout can be more bearable. Read about this condition to learn what causes gout, how it can be treated, and which prevention methods are the most effective.
1. What Is Gout?
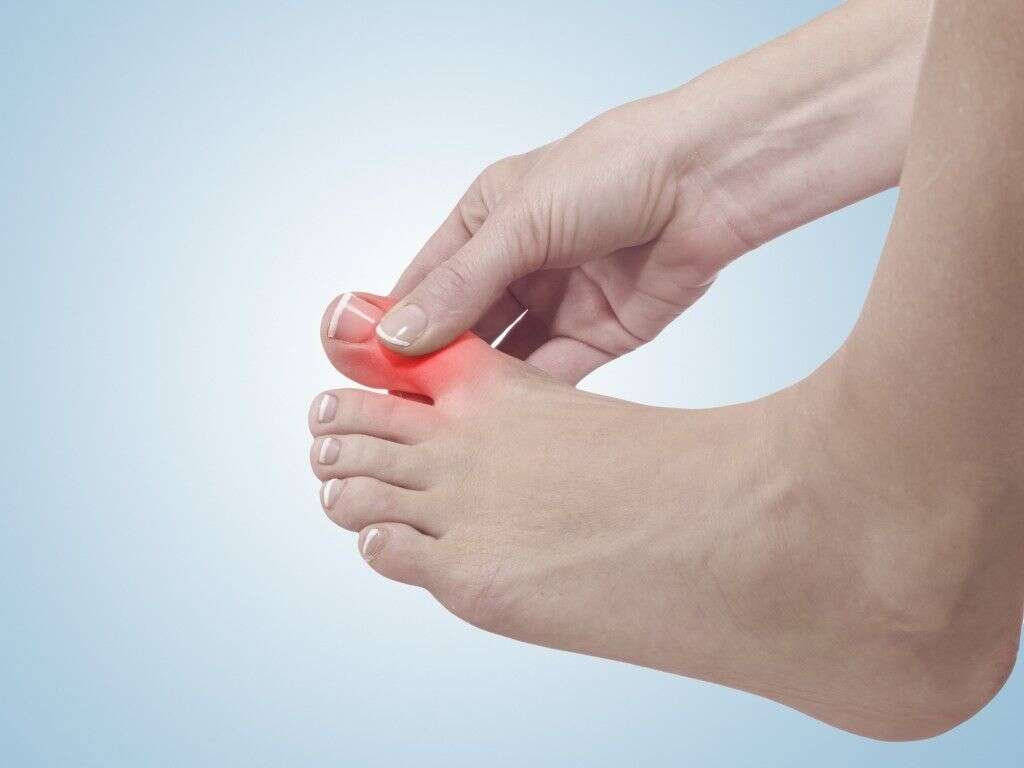
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that can affect any joint in the body but most often occurs in the big toe. It is also common for people to experience gout in the knees, ankles, fingers, wrists, elbows, and heels. The condition only affects one joint at a time and typically happens in flares, with periods of no symptoms followed by times where symptoms are severe.
For people who get frequent flare-ups, gout can eventually turn into a more severe, chronic position called gouty arthritis. Recurrent attacks make it difficult for people to perform everyday activities as it may be too painful to do so or the actual joint may be too damaged to function.
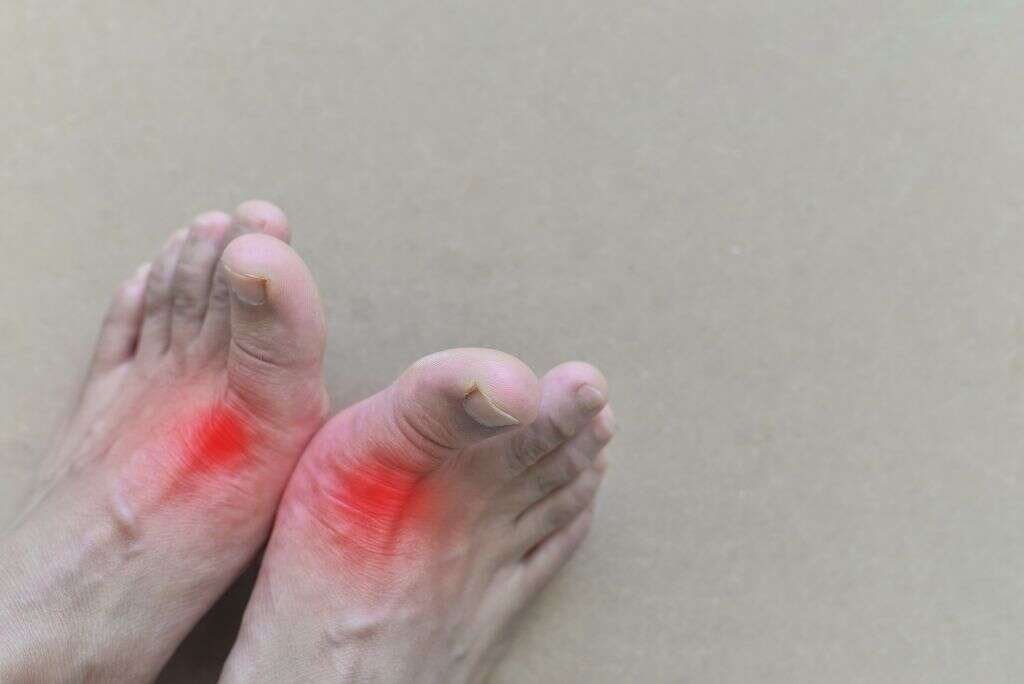
2. What Causes Gout?
The main cause of gout is an excess of uric acid in the body, which crystallizes and builds up in the joints. This buildup of acid causes inflammation of the affected joint, leading to intense pain in the areas when the acid accumulates.
Food or certain medical conditions affecting the kidney are often to blame for the overproduction of uric acid. Certain foods and beverages, such as red meat, seafood, fructose, and alcohol, have high levels of uric acid, which the kidneys may struggle to process and eliminate from the body.

3. What Are the Symptoms of Gout?
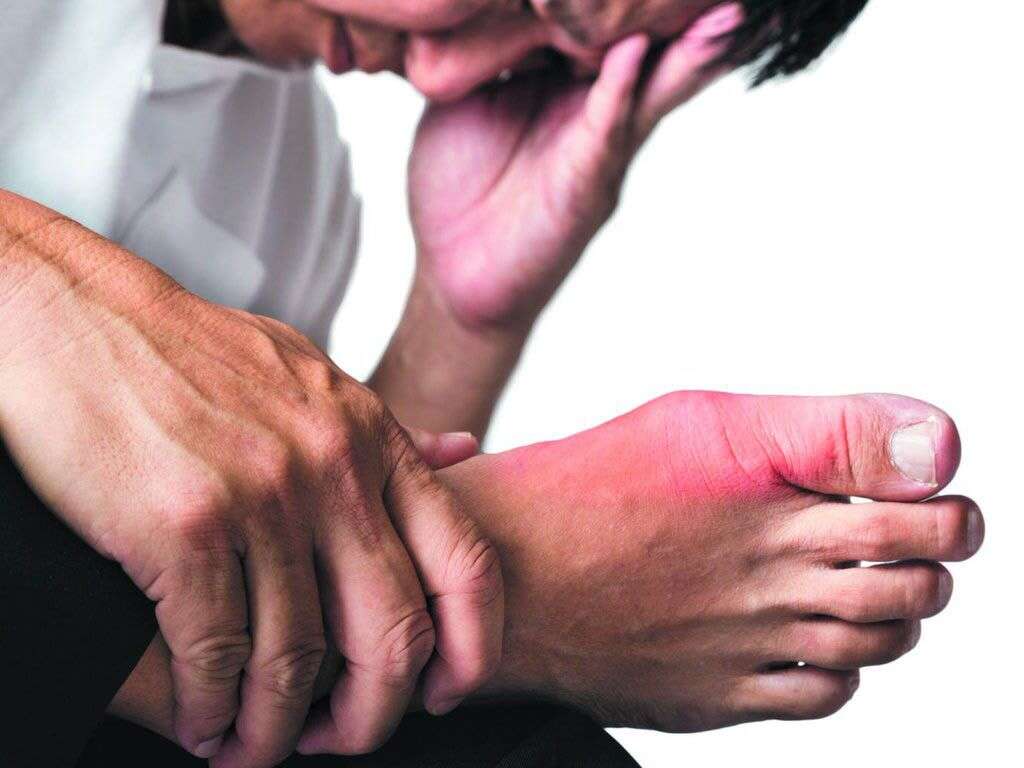
The main symptom of gout is intense pain in a joint that comes and goes in episodes. This pain is often felt like heat in a very localized area. For some people, the pain is so intense they believe that the area is experiencing a joint infection.
Gout can physically alter the appearance of the joint as well, making it appear very red and swollen. Large bumps called tophi may be visible, which are swollen nodules containing the accumulation of uric acid crystals.

4. How Is Gout Different From Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is another type of arthritis that can cause inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joints. However, unlike gout, it can affect multiple joints at once and is more common in the hands, wrists, and feet. The pain may be milder but cannot be cured.
Additionally, while gout has a clear cause, there is little known about why a person develops rheumatoid arthritis. Some researchers believe that there is a strong genetic factor that comes into play when certain environmental factors are met.
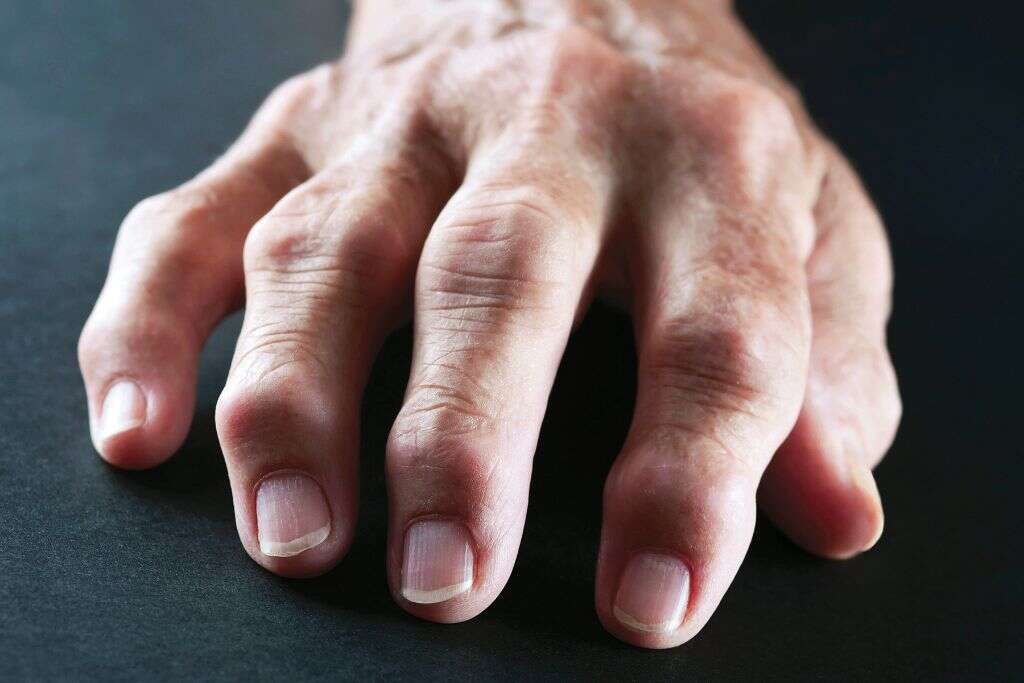
5. How Is Gout Diagnosed?
The first step to getting a gout diagnosis and receiving a treatment plan is to be examined by a doctor. This can involve discussing symptoms with the doctor and having the area looked at for any signs of swelling, heat, or tophi.
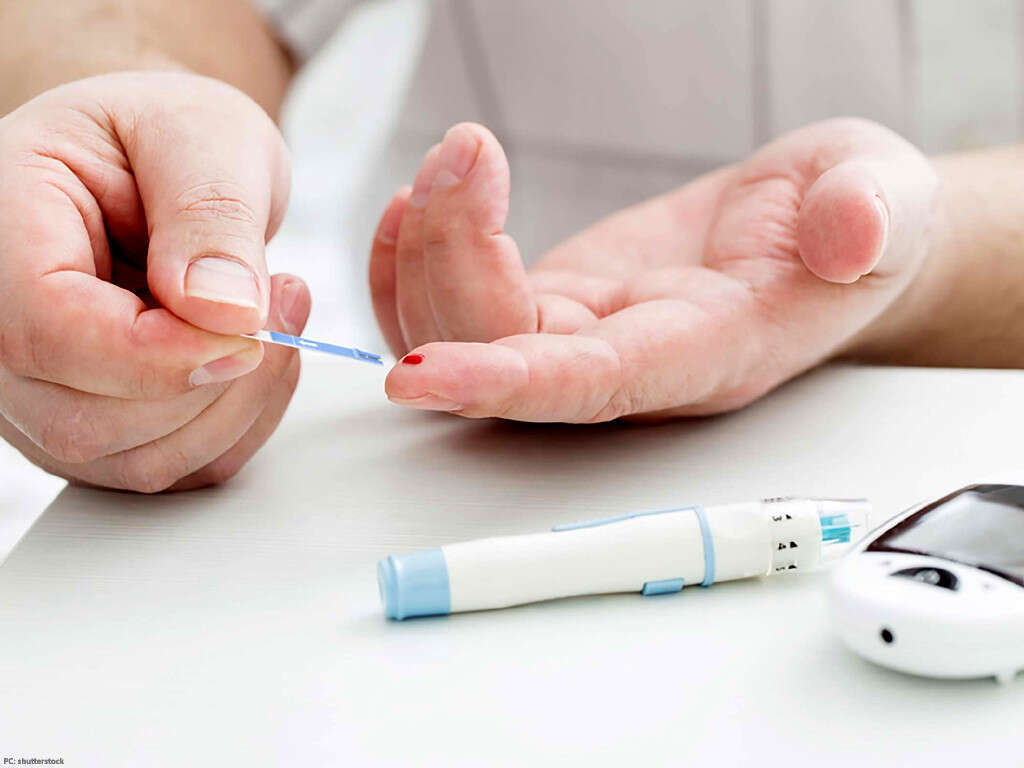
To confirm that it is in fact gout causing the pain and not another condition, joint fluid analysis is required to test for uric acid crystals. However, this sample can only be accurately taken during a flare-up. A blood test for measuring how much uric acid is in the blood may also be required.

6. Can Gout Cause Joint Damage?
Not only can untreated gout cause the individual immense pain, but it can also eventually lead to extensive joint damage as the attacks grow in severity. If tophi are present underneath the skin, they can grow very large and cause the deterioration of the joint and even damage the surrounding skin.
Additionally, gout typically gets more severe with time, leading to longer, more frequent attacks. The amount of inflammation experienced by the joint can result in erosion of the bones and cartilage surrounding the joint until it completely deformed.
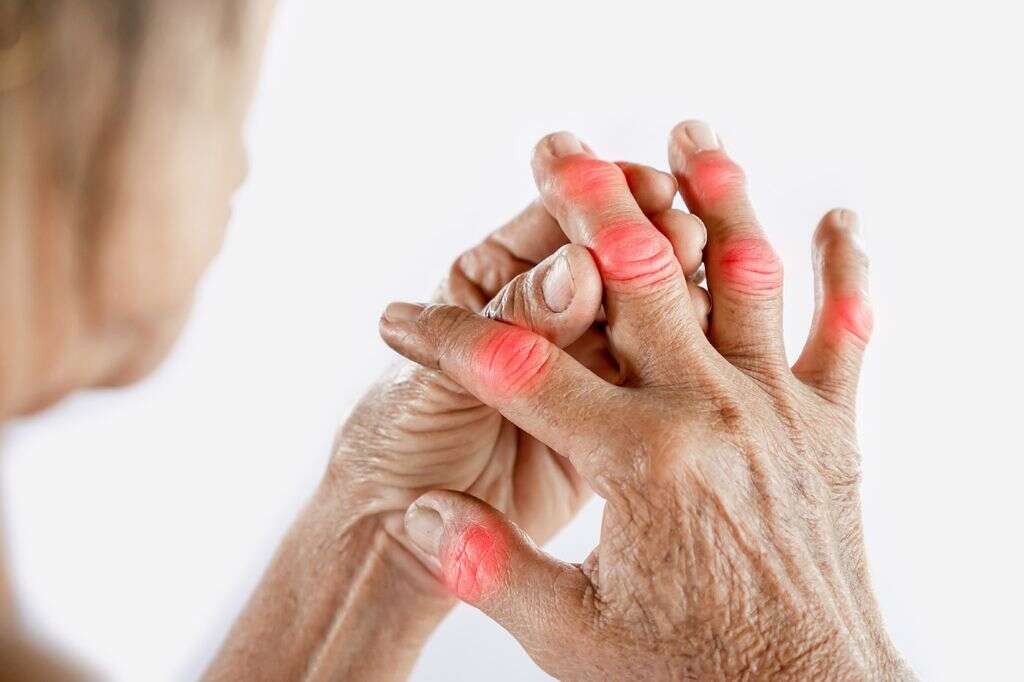
7. What Other Complication Can Gout Cause?
In addition to causing physical harm to the joints where flare-ups occur, there is a strong connection between gout and kidney stones and kidney disease. Often, people with high concentrations of uric acid will also develop crystals in the actual kidney and may experience decreased function.
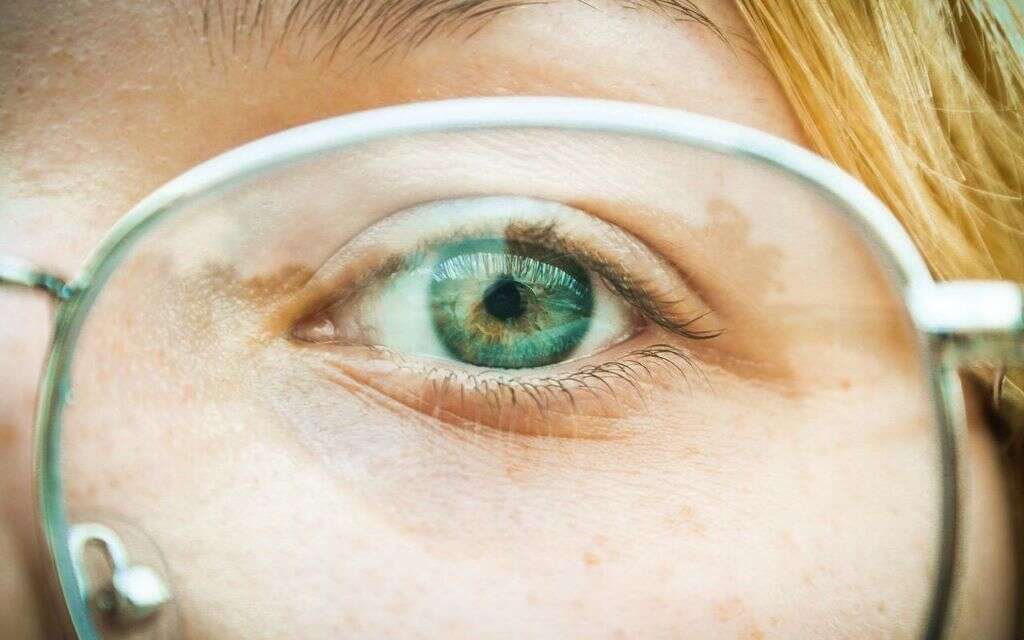
Other conditions that can be due to excess uric acid in relation to gout include dry eye syndrome and cataracts, which can cause the person to have clouded vision. While rarer, some people may have uric acid crystals form in the lungs, which can even lead to tophi developing inside.

8. What Are the Risk Factors for Gout?
There are a wide variety of factors that can contribute to someone developing gout. For one, the condition is much more common among men and often worsens with age. Obesity and a diet high in certain purine-rich food are major risk factors for this type of arthritis.
Heavy alcohol consumption and the use of certain types of medications can also make the risk of gout go up. Gout often occurs with several other health conditions, including problems with the kidneys, diabetes, high blood pressure, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and congestive heart failure.

9. Does Gout Ever Go Away?
While gout never fully goes away, there are several treatment options that can make it less likely that an individual will experience an attack in the future. Working with a doctor to manage pain and identify habits or foods that cause flare-ups is an essential part of this process. If alcohol or medication is thought to be the cause, cessation of these substances may be necessary.
There are several drugs that can be prescribed to help with gout. Medications such as febuxostat, pegloticase, and allopurinol can all be used to help lower uric levels to more normal levels. To help combat pain inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help make the condition more manageable. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen and aspirin.

10. How Can You Prevent Gout?
Understanding the risk factors that cause gout can help people come up with strategies to lengthen the time between attacks or to avoid developing the condition to begin with. This can include limiting the consumption of alcohol, seafood, and red meat protein products.
Additionally, people, if obese, should try to lower their body weight in a healthy manner. Losing weight too quickly can actually cause uric acid levels to rise, potentially causing an attack. Substituting sugary drinks that contain fructose with plenty of water can also help people better manage gout.