10 Mouth Cancer Symptoms
The term cancer refers to the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in one part of the body, that can end up damaging other cells of surrounding tissues and organs. Mouth cancer is any cancer that affects the oral cavity and other tissues within it. It includes cancers of the mouth itself, the tongue, the gums, the lips, cheeks, palates, and the pharynx.
Close to 50,000 cases of mouth cancer are diagnosed in the United States annually. It is more common in people older than 40 years with two-thirds of the cases occurring in men compared to women. Studies indicate that most oral cancer cases result from the use of tobacco and alcohol, and due to infection with human papilloma virus, also referred to as HPV. The following are mouth cancer symptoms, some of which may also be present in other conditions.
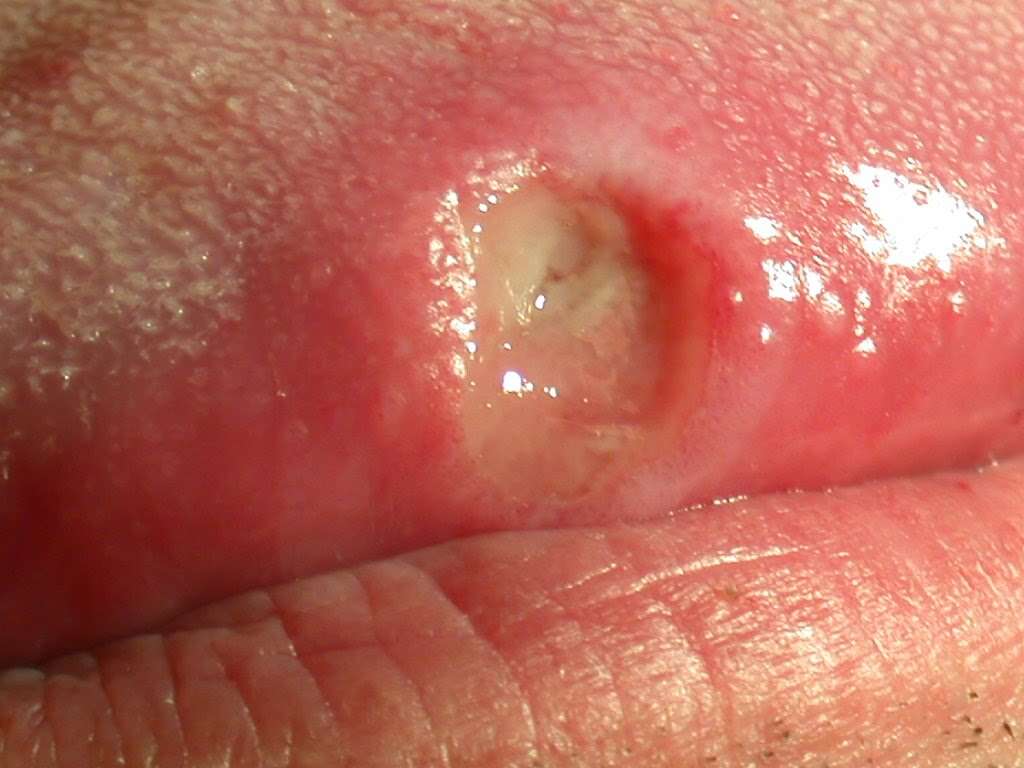
Symptom #1: Ulcer That Does Not Heal
An ulcer that occurs anywhere within the mouth and does not easily heal may be a sign of oral cancer. This is a common mouth cancer symptom that is present in about 8 of every 10 cases. While other mouth diseases may also be accompanied with oral sores, these tend to heal rapidly with proper treatment. However, mouth sores associated with mouth cancer remain unhealed for more than three weeks.
Another differentiating factor is that while non-cancerous sores are normally soft and do not usually bleed, cancerous sores are hard, red, thick and will usually bleed.
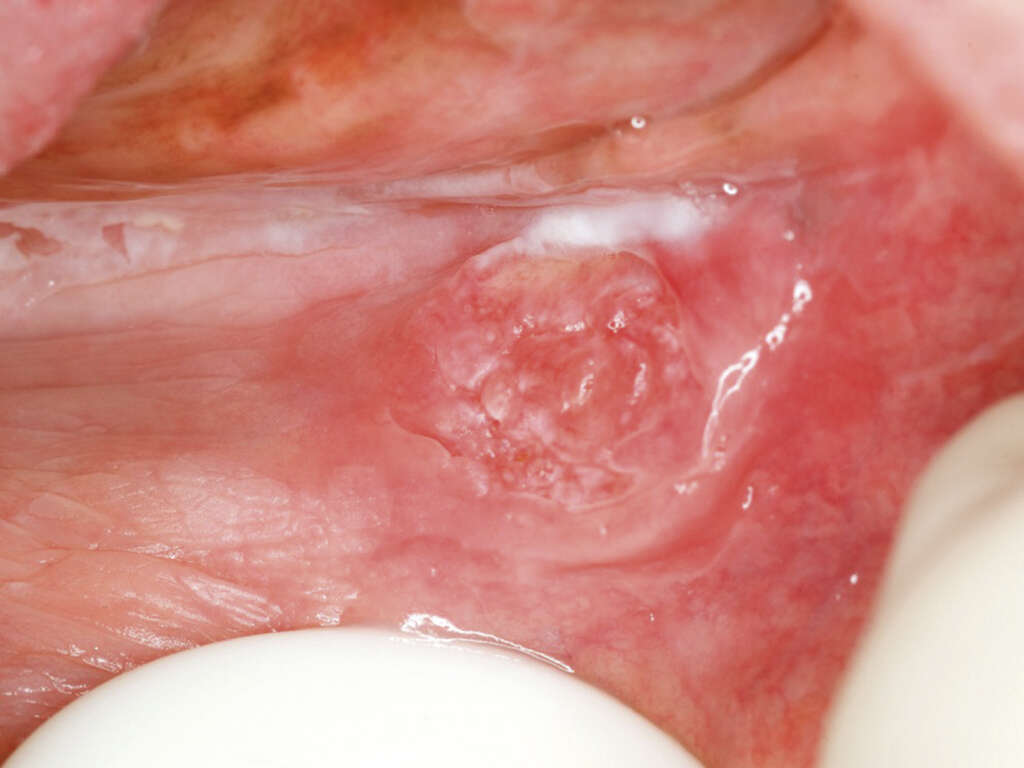
Symptom #2: White Patches
Sometimes, white patches on the tongue, gums, floor or roof of the mouth, the inside surface of the cheeks or any other parts of the mouth can be considered premalignant lesions of oral cancer. The condition, known as leukoplakia is usually caused by smoking or other irritants.
The thick, flat, white patches are normally painless, and can’t be scrapped off. Other premalignant lesions can be red (erythroplakia), red and white (erythroleukoplakia), or verrucous (verrucous leukoplakia). However, not all cases of leukoplakia transform into cancer.
Symptom #3: Bad Breath
Bad breath, also called halitosis can be an oral cancer symptom. It can occur as a result of infections of existing mouth ulcers by bacteria. Because oral cancer sores continue growing without healing, they are exposed to bacteria and other microorganisms in the mouth. Additionally, the painful sores can make it difficult to swallow, which would otherwise reduce the numbers of bacteria in the mouth. This leads to a foul breath that does not improve even after brushing your teeth or washing your mouth.
It is always prudent to consult your doctor or dentist in case of bad breath that doesn’t go away after you brush your teeth.

Symptom #4: Loose Teeth
Loose teeth can be a sign of mouth cancer that can result from tumors present on the gums. The condition may affect one or several teeth depending on the size of the tumor.
Because gums provide anchorage for teeth, tumors that grow on them can displace the teeth and cause them to loosen or even fall off. However, not all cases of loose teeth are symptoms of mouth cancer. Other dental health conditions may have similar signs. Therefore, in case you have some loose teeth, visit a dentist for treatment. A biopsy of the gum tissue may be required for testing to determine the cause of the condition.
Symptom #5: Lump In The Neck
Mouth cancer symptoms normally appear in the oral cavity and in tissues within it. However, if it spreads (metastasis), cancer cells can end up in the lymphatic system and cause the regional lymph nodes to swell (i.e. cervical lymph nodes). The enlargement of cervical lymph nodes, especially if hardness (in consistency) and fixation to adjacent tissues are present, can be a sign of oropharyngeal cancers.
At presentation, from 30 to 80 percent of patients with oral cancer have metastases in the cervical lymph nodes. Note, however, that swollen cervical lymph nodes can also be a sign of many other benign or malignant conditions.

Symptom #6: Weight Loss
In patients with oral cancer, malnutrition and weight loss are most commonly a result of insufficient calorie intake. The most important cause is usually a functional impairment of facial muscles, tongue, and temporomandibular joint (jaw). As a consequence, patients can experience chewing and swallowing problems.
Furthermore, radiotherapy can be used as a treatment for certain types of cancers. However, it can also have a negative impact on weight. It can influence the sense of taste, and cause dryness and swelling of the mouth. Moreover, patients who have compromised gums or have lost several teeth can also experience difficulty chewing and swallowing.

Symptom #7: Hoarseness
Hoarseness can be present in certain types of head and neck cancers. Laryngeal cancers often cause hoarseness or a change in the voice at very early stage. However, for cancers that don’t start on the vocal cords, hoarseness occurs only at a very late stage or when they have spread to the vocal cords.
More commonly, patients with oral cancer may experience difficulty articulating words (i.e. tongue cancer).

Symptom #8: Jaw Pain
Jaw pain can be another symptom of oral cancer. The pain can worsen when there is movement of the jaw joint (i.e. opening of the mouth).
Jaw pain may occur once oral cancer has metastasized or spread to the jaw. Less commonly, it can also occur due to a primary tumor growing on the jawbone. Besides jaw pain, oral cancer that affects the jaw may exhibit other signs. These include swelling of the jaw, presence of lumps (i.e. roof of the mouth or gumline), as well as increased tooth mobility.

Symptom #9: Difficulty Swallowing
Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing is a common symptom of head and neck cancer, but can also be a sequela of its treatment. It is a disruption in the swallowing process of bolus transport from the mouth to the stomach. As mentioned before, patients with oral cancer can experience functional impairment for chewing and swallowing. The severity of the swallowing deficit will be dependent on the size and location of the lesion. Also, patients can experience pain and discomfort due to oral lesions that can impair these processes.
Surgical resection of the lesion, the nature of the reconstruction, and the side effects of antineoplastic agents (radiation and/or chemotherapy) are also important factors that can impair swallowing.

Symptom #10: Ear Ache On One Side
A persistent earache that only affects one ear can be a symptom of oral cancer. The pain can be experienced in the ear because the nerves serving different parts of the oral cavity carry nociceptive or pain information to the same spinal nucleus. Thus, pain may be perceived in any of these areas, although the painful area may not be directly affected.
Note that there are many other causes of ear pain in adults. Consult with your physician if you experience persistent ear pain.