10 Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
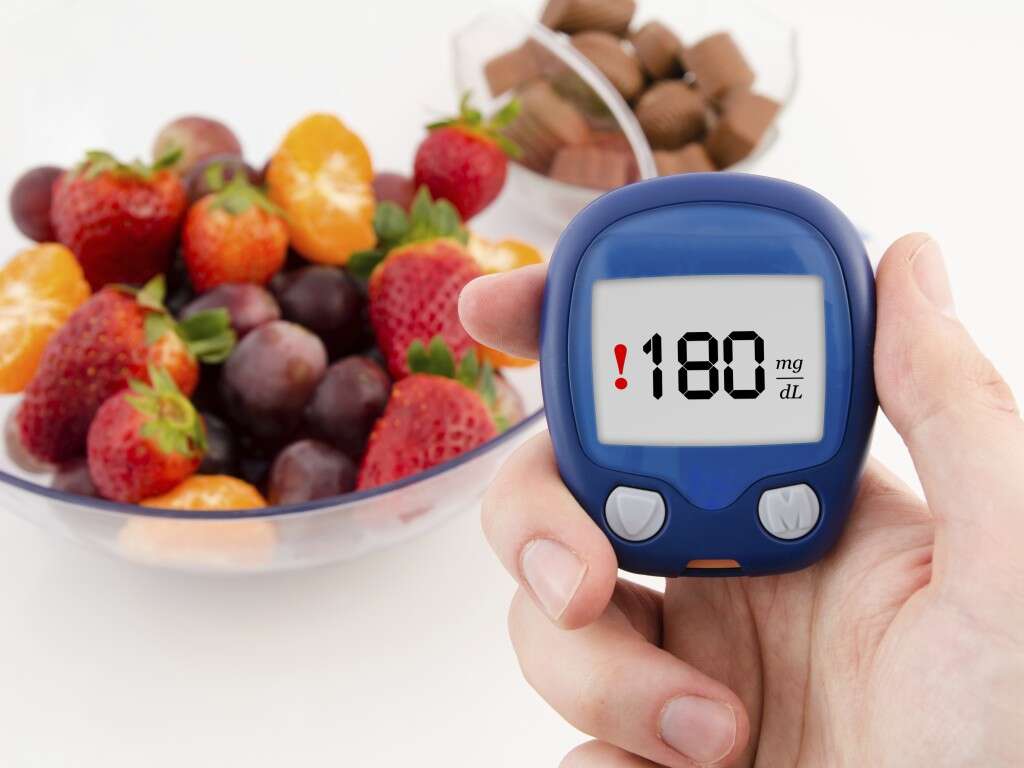
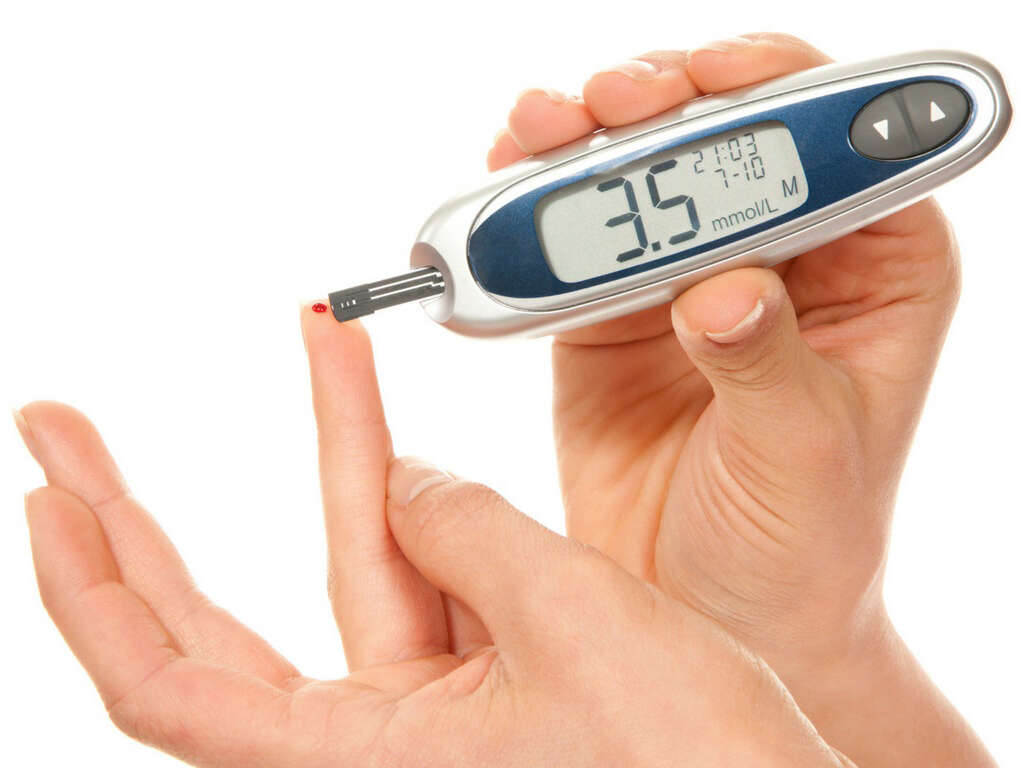
Low blood sugar is also known as hypoglycemia. It occurs when blood sugar levels drop below normal levels. However, the blood sugar level defining hypoglycemia can be variable. Patients usually experience hypoglycemia symptoms when their blood glucose level drops below 50 mg/dl.
The commonest cause of low blood sugar is the medications used to treat diabetes mellitus. The risk increases among diabetics who take the medications and eat less, exercise more, or consume alcohol. To prevent low blood sugar among diabetics, the dosage of their medications can be matched with their diet, exercise routines, and lifestyle habits. Diabetics also test their glucose levels if they suspect that they are low.
Other causes of hypoglycemia include certain tumors like insulinoma, kidney failure, hypothyroidism, liver disease, starvation, reactive hypoglycemia, severe infections, and drugs. Hypoglycemia can be treated by consuming foods that contain high amounts of simple sugars or by taking dextrose.
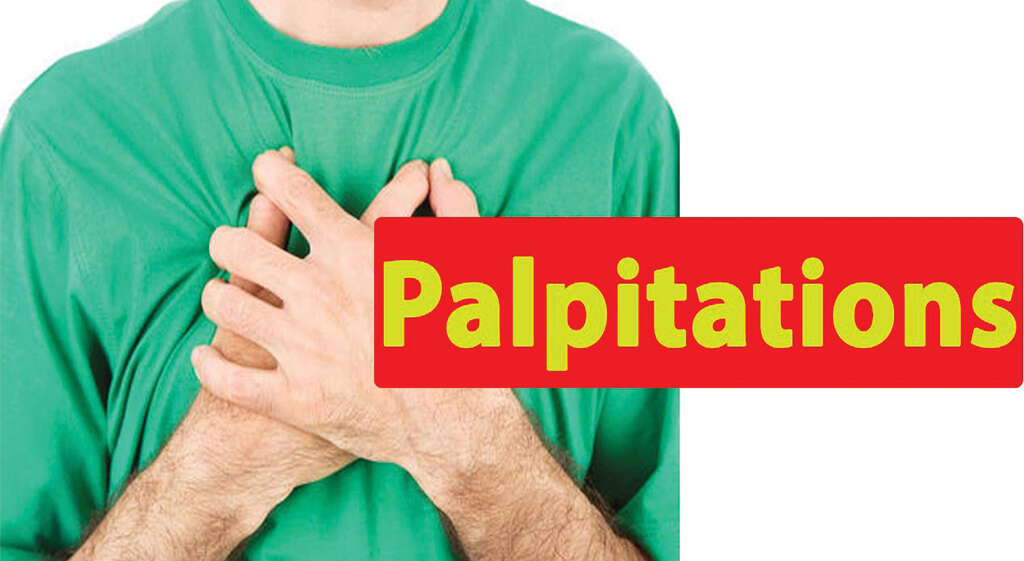
Symptom #1: Palpitations or Tachycardia
Palpitations refer to an abnormally hard, fast, or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations can occur during times of exertion and are observed in many conditions, such as anxiety, hyperthyroidism, and coronary heart disease. Tachycardia is the medical term for an abnormally fast heartbeat.
Some associated symptoms of palpitations and tachycardia include breathlessness, sweating, dizziness, headaches, and chest pain.
Symptom #2: Pallor and Coldness
Pallor is a paleness of the skin that can be caused by stress, emotional shock, illness, stimulant use, and anemia. It should be distinguished from hypopigmentation (a fair complexion). Pallor occurs when the blood has a lower amount of oxyhemoglobin, which is usually seen through the skin.
It is usually more apparent in the face and palms. One of its associated symptoms is coldness, where the skin feels cool or clammy. Cold sweats can also occur.
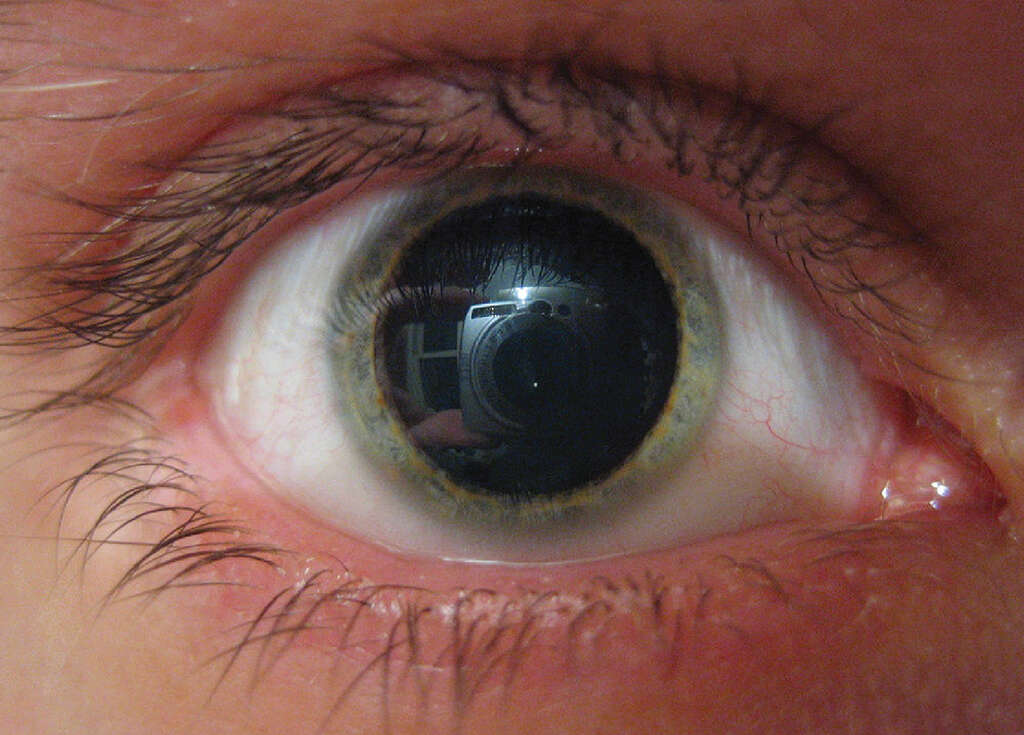
Symptom #3: Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupils in the eyes. The condition is also known as a blown pupil. In a normal physiological response, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in bright light to protect the retina from light damage. In mydriasis, the pupil remains dilated even in a bright environment.
Nonphysiological causes of mydriasis include trauma, drug use, and disease. It also can be a symptom of raised intracranial pressure.
Symptom #4: Anxiety and Shakiness
Anxiety is a feeling of excessive worry, uneasiness, turmoil, and dread about the future. It should be distinguished from fear, which is a feeling in response to a perceived immediate threat. Anxiety is often accompanied by nervous behaviors, such as somatic complaints, pacing back and forth, and rumination.
Patients with anxiety often experience associated symptoms, such as muscular tension, fatigue, and loss of concentration. Shakiness, where the affected person is nervous, trembling, and weak, is also a common sign of anxiety.

Symptom #5: Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort anywhere in the neck or head.
It is a common and nonspecific symptom seen in various conditions, such as dehydration, low blood sugar, stress, inadequate sleep, and high blood pressure.

Symptom #6: Hunger and Borborygmus
Hunger describes the physiological need to eat food. It is an unpleasant sensation that usually begins after a few hours without food. Borborygmus (also known as a stomach rumble, bowel sound, or peristaltic sound) is the rumbling, gurgling, or growling noise caused by the movements of gastrointestinal contents.
Borborygmus can occur when there is incomplete digestion or hunger. It can also occur in other conditions, such as celiac disease, colitis, diverticulitis, and irritable bowel syndrome.

Symptom #7: Difficulty Concentrating
If the brain doesn’t get enough energy, it will let us know one way or another. During episodes of hypoglycemia, our mental capacity and problem-solving skills will be considerably diminished.
If you are suffering from this symptom, you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Symptom #8: Profuse Sweating
When our blood glucose level drops significantly, our body enters an emergency state of alarm. The sympathetic nervous system becomes activated, releasing hormones to mediate the “fight or flight response”.
As a result, patients may experience excessive sweating like the response seen in panic attacks and generalized anxiety.

Symptom #9: Light-headedness and Confusion
Light-headedness is a sensation of dizziness that may cause someone to faint. The condition may be short term, chronic, or recurring. Causes of light-headedness include a shortage of blood or oxygen to the brain, low blood pressure, dehydration, low blood sugar, panic attacks, hyperventilation, and coronary heart disease.
Patients with low blood sugar may also suffer from confusion since the drop in blood sugar causes the body and brain to not function normally.

Symptom #10: Altered State Of Consciousness
Hypoglycemia is a very serious condition and if the glucose level drops considerably (especially in diabetic patients), the mental status can deteriorate very fast, leading to coma and even death if left untreated.
Diabetic patients need to recognize the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and address them early.











