10 Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
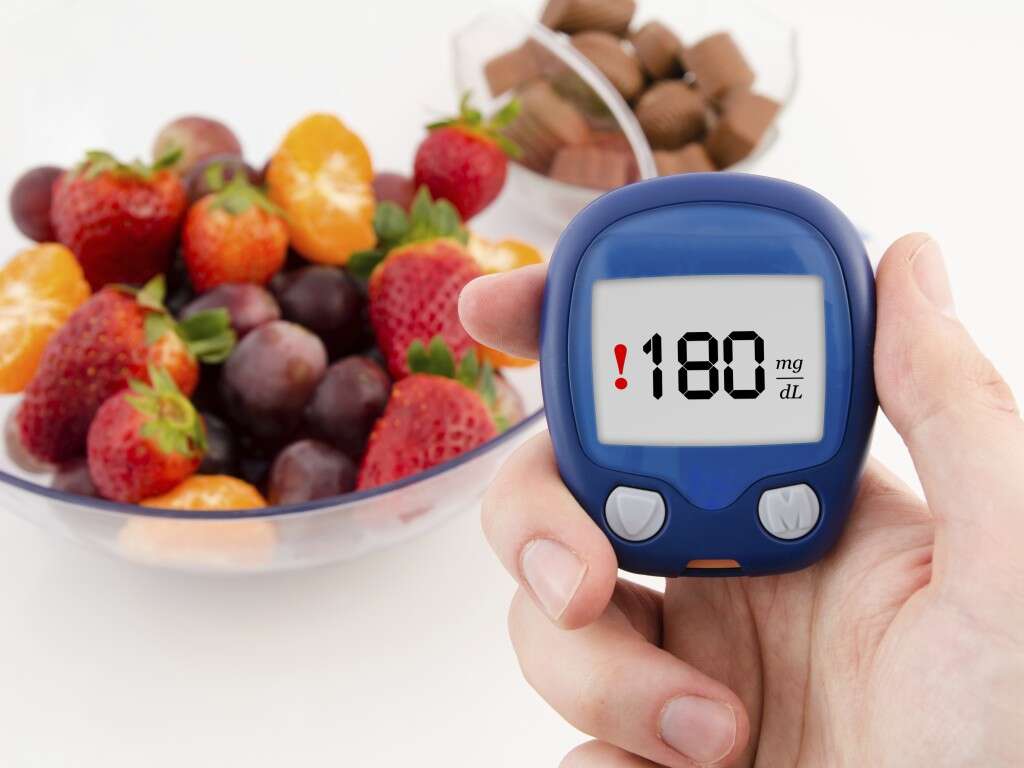
Hypoglycemia is a condition where a person’s blood glucose level is much lower than normal. And while the condition is mainly associated with diabetes, it can also occur in nondiabetics. Low blood sugar means that the body has less energy-producing glucose than it needs for normal functions.
However, hypoglycemia is not a disease by itself; it is an indicator of a possible underlying health condition. Some of the causes of hypoglycemia include starvation, excessive alcohol consumption, hormonal imbalance including overproduction of insulin, and illnesses such as hepatitis.
Occasional hypoglycemia is treated by giving a high sugar food or drink to help return the blood sugar levels to a healthy range. Chronic hypoglycemia, on the other hand, requires investigation to identify its cause followed by appropriate treatment. But what are the signs and symptoms of low blood glucose? Below are 10 hypoglycemia symptoms:
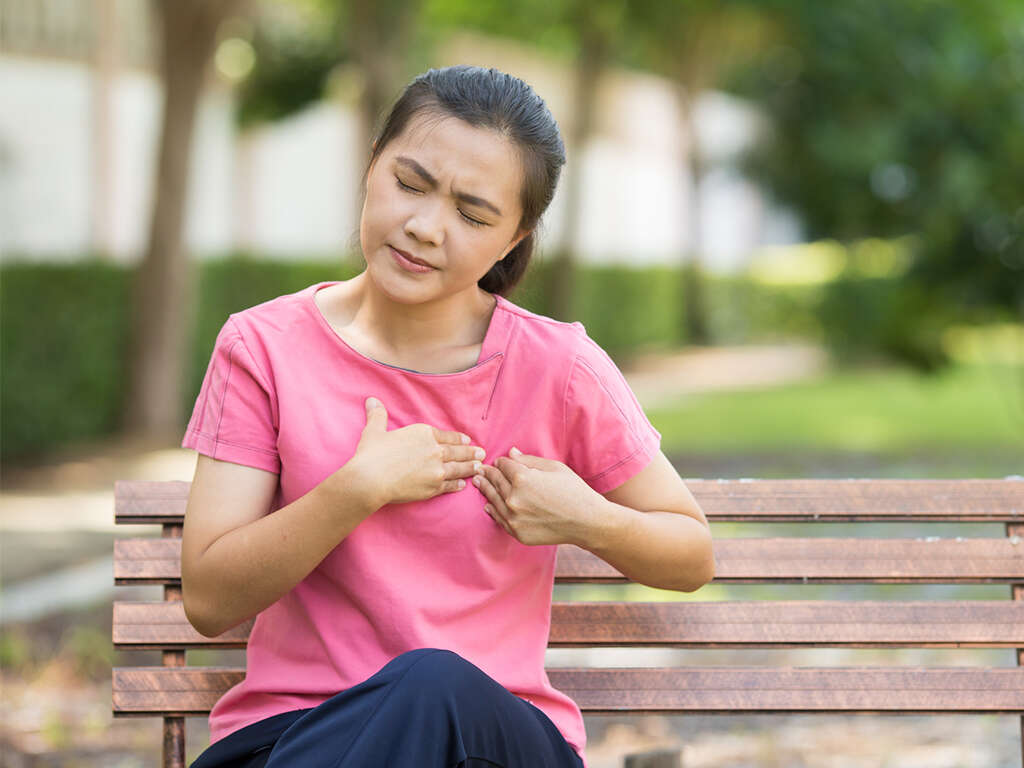

Symptom #1: Sweating
It is normal to sweat when the atmospheric temperature rises. The sweating function is controlled by the autonomic part of the nervous system, which is also responsible for skin and other functions. Sweating is meant to help the skin and the body to keep cool in spite of the external temperature.
However, if sweating occurs irrespective of the temperature, it may be an indication of an underlying problem including low blood sugar. Sweating is one of the first symptoms of hypoglycemia. Low blood glucose levels can cause a fight or flight response, which can trigger sweating. It may also cause a racing heart as well as chills.
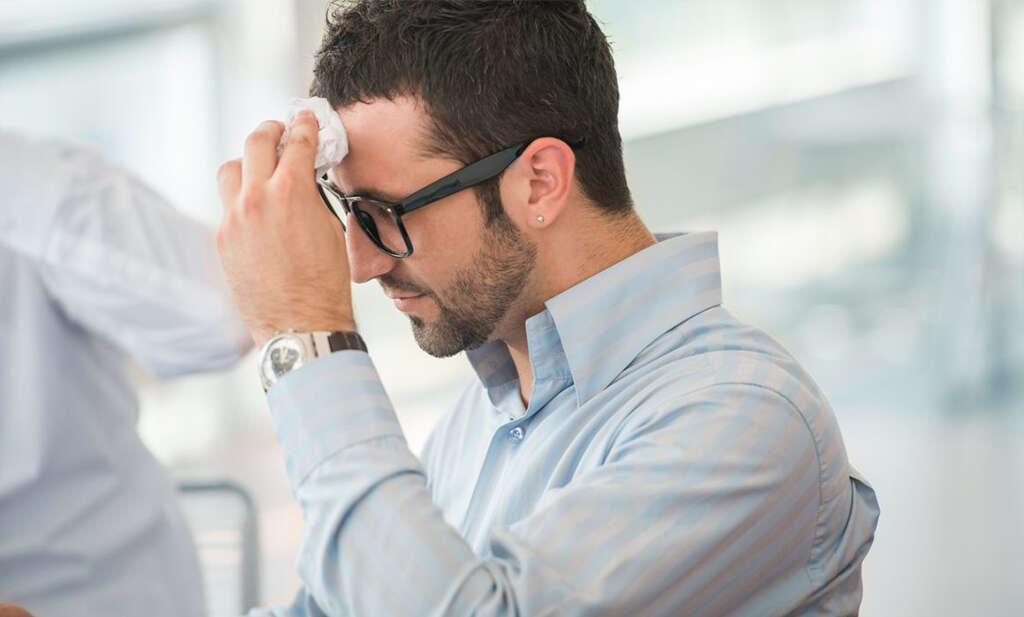

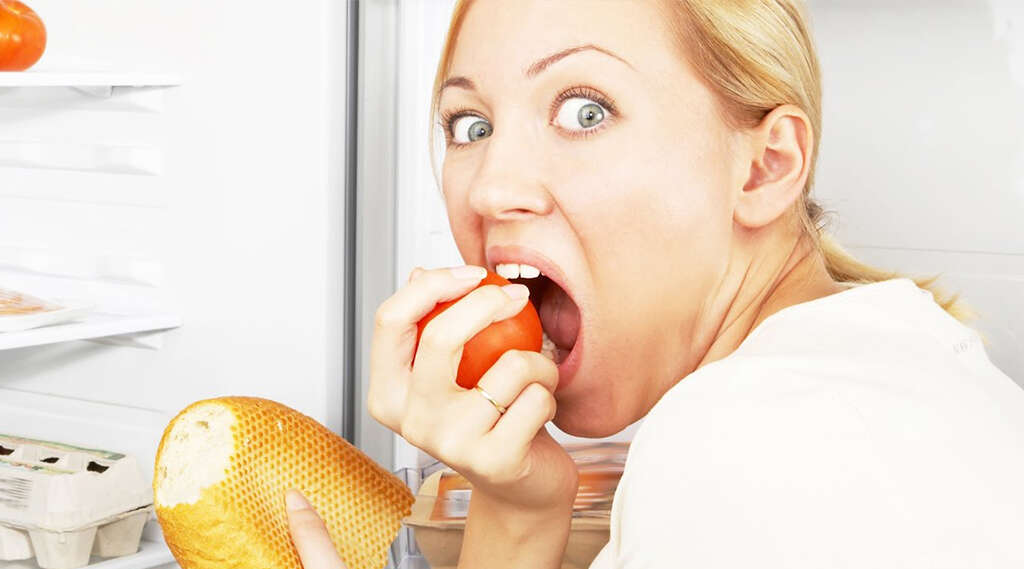
Symptom #2: Hunger
As your glucose level starts to drop, the hypothalamus will trigger a feeling of hunger to signal your body that it is time to eat. Patients with diabetes must maintain a healthy and regular eating schedule to avoid any complications, especially if they are insulin-dependent.
When your glucose level falls significantly, the feeling of hunger can become overwhelming and quite annoying. This symptom is a natural response and as soon as you replenish your energy sources, it should go away.

Symptom #3: Dizziness
Feeling dizzy could be a symptom of hypoglycemia. The feeling of weakness and lightheadedness, as if you will pass out, occurs when the blood flowing to the brain is low in glucose. This means that the brain is not getting adequate energy to perform its functions. The results are similar to those of inadequate blood supply to the brain.
If you are having dizziness and it’s been hours since you had a meal, you need to eat or drink without delay. For faster results, take a high sugar food or drink. If the feeling does not go away soon, you probably have a more serious problem in which case you should seek medical care. In case you experience recurrent dizziness and you are not on treatment for diabetes, it is recommended that you get tested.

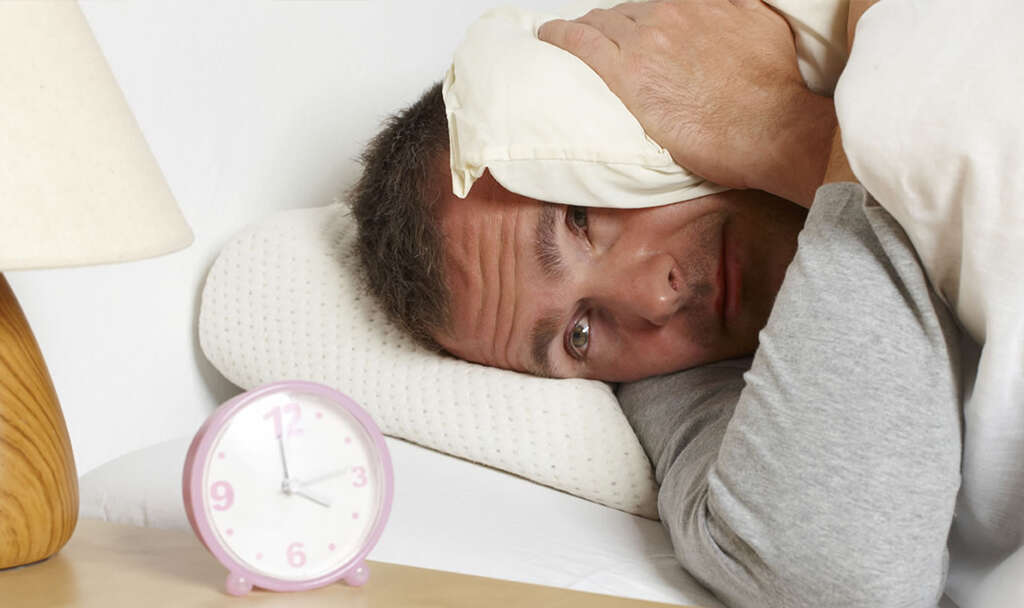
Symptom #4: Sleep Disturbances
There are many reasons why you may experience sleep disturbances at night. And while it is not obvious, waking up from sleep at night could be one more hypoglycemia symptom. Having very low blood glucose levels means that the cells of your body are not getting enough energy for their functions.
When this happens, your endocrine system activates to release adrenal hormones which signal the liver to produce more glucose from its glycogen reserves. When this happens during your sleep, the increased adrenal hormones and the feeling of hunger may interfere with your sleep by causing you to wake up.

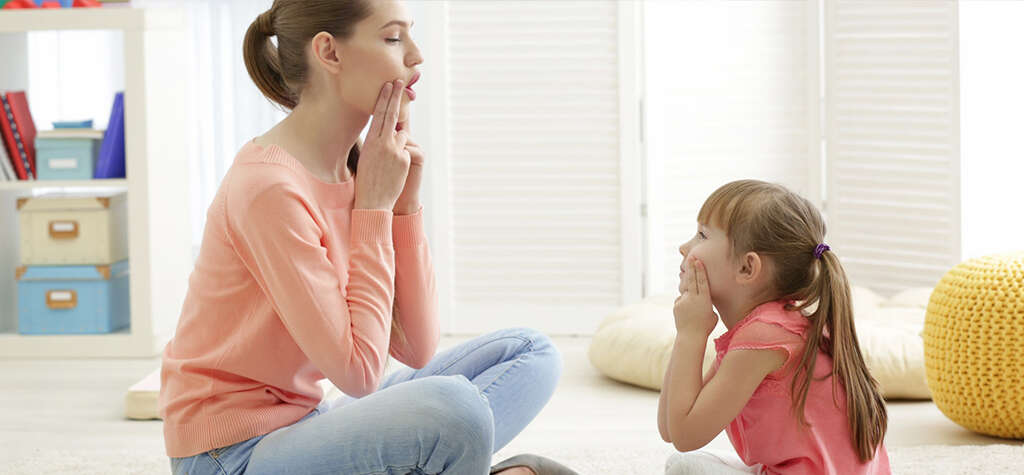
Symptom #5: Slurred Speech
Slurred speech can be an indicator of hypoglycemia. As with many other functions, the speech process requires energy that is produced from glucose. When your bloodstream is low in glucose, the brain and the vocal chords have little energy to process and execute speech.
This causes you to have slurred speech. But this may not be apparent to you because your brain will also be processing the speech slowly. However, to other people you will sound like you have had too much to drink. If you are diabetic and have had such an experience, it helps to inform those close to you what to do in case they notice you having slurred speech. As mentioned elsewhere, low blood glucose can be treated by taking sugary foods or drinks.

Symptom #6: Fatigue
Extreme tiredness and fatigue can indicate that you have low blood sugar. Similar to most hypoglycemia symptoms, fatigue or feeling tired occurs because the body is deficient of glucose which is the main source of energy. As a result, your body cells, tissues, and organs are incapable of functioning normally.
As a result, your body, right from the brain to the toes, may feel tired or fatigued. You may feel unable to carry out otherwise simple tasks such as walking. In case you feel fatigued for no reason, but you have not had a meal for some hours, eat or drink something high in sugar.

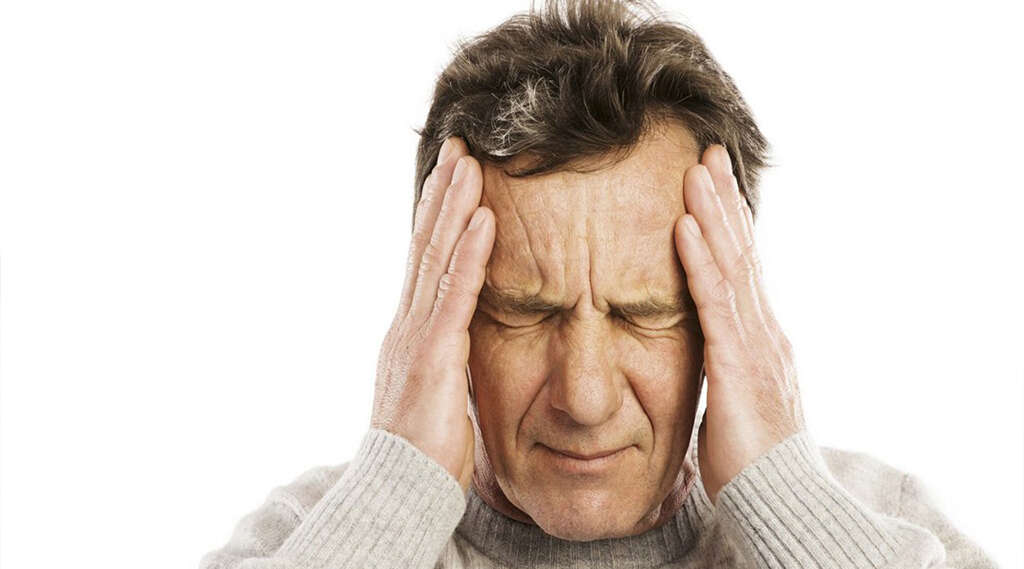
Symptom #7: Headache
Headaches can be caused by many conditions including flu, colds, and dehydration. They can also occur when your blood is low in glucose. Working out hard, fasting, irregular meals, and dieting can cause hypoglycemia. This happens because the glucose within the bloodstream is depleted. Without replenishing the glucose by eating or drinking, your body experiences low energy stress symptoms.
A headache is one such symptom. Hypoglycemic headaches are usually severe. The headache may also be accompanied by nausea, sweating, mood changes, and craving for sweet things. For this reason, all you may need to treat such a headache would be a high sugar food or drink.

Symptom #8: Anxiety
Hypoglycemia causes the adrenal glands to release an increased amount of adrenaline, which is meant to cause the liver to produce and release more glucose into the bloodstream. Unfortunately, the high level of adrenaline may not all be used up in the liver and therefore remains in the bloodstream. This can lead to feelings of anxiety.
The high adrenaline levels may also cause mood changes, nervousness, and irritability. Other hypoglycemia symptoms that may arise due to increased adrenaline levels include increased heart rate and heart palpations. Whether you have diabetes or not and feel anxious for no reason, you probably need to have a snack. If this feeling does not go away, you may need to talk to a doctor.

Symptom #9: Mood Changes
If you experience mood changes that don’t fit in with your character, you probably have hypoglycemia. These mood changes may include sudden anger, crying hysterically, and the feeling that you need to be left alone. These mood changes may be mild or severe depending on the level of hypoglycemia. Mood changes may be accompanied by other hypoglycemia symptoms like anxiety, sweating, and palpitations.
If you have diabetes and are on treatment, you may be aware of what you need to do to get over these symptoms. If you are not a diagnosed diabetic, take a sugary snack or drink to calm down the mood swings. If you experience such a symptom repeatedly, you should consult a doctor for assessment and treatment.

Symptom #10: Faster Heartbeat
Having low blood sugar can cause the heart to beat faster than normal. This happens because when the brain senses that the body cannot get adequate energy to perform its functions properly, it signals the adrenal glands to increase production of adrenaline. The adrenaline hormone causes the liver to increase production of glucose from stored glycogen.
Adrenaline is also the fight or flight hormone that prepares the body to deal with emergencies. As a consequence of the increased adrenaline, the heart beats faster than normal in order to supply more blood to deliver glucose and oxygen throughout the body. Heart palpitations are additional hypoglycemia symptoms that may affect the heart.