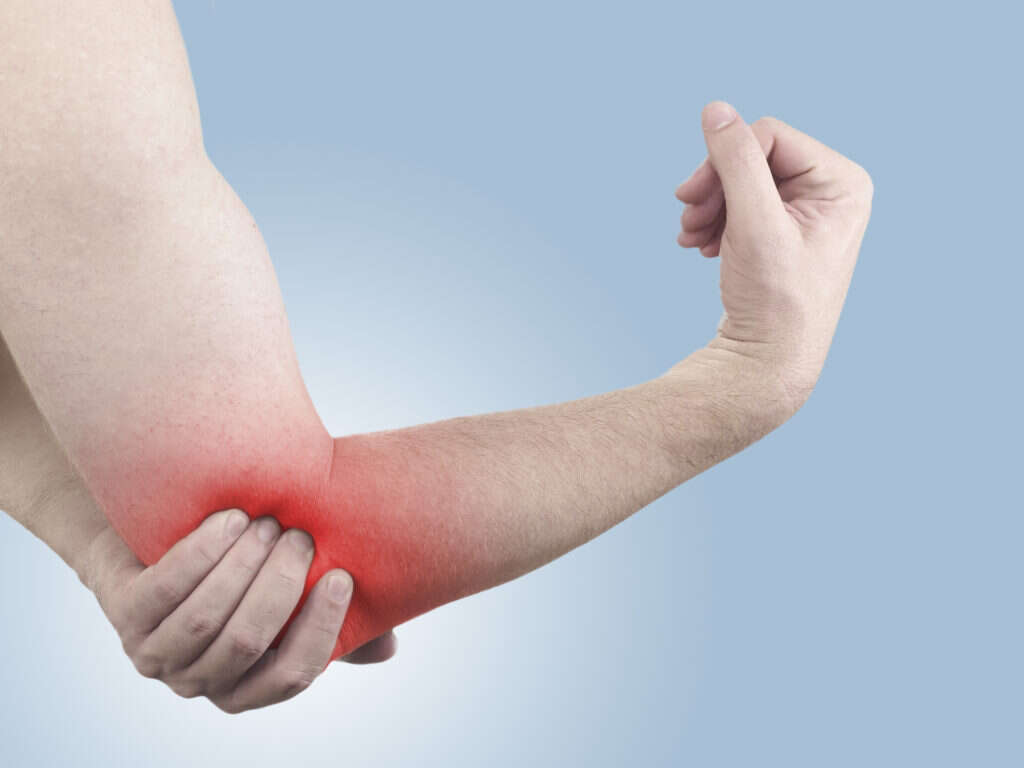
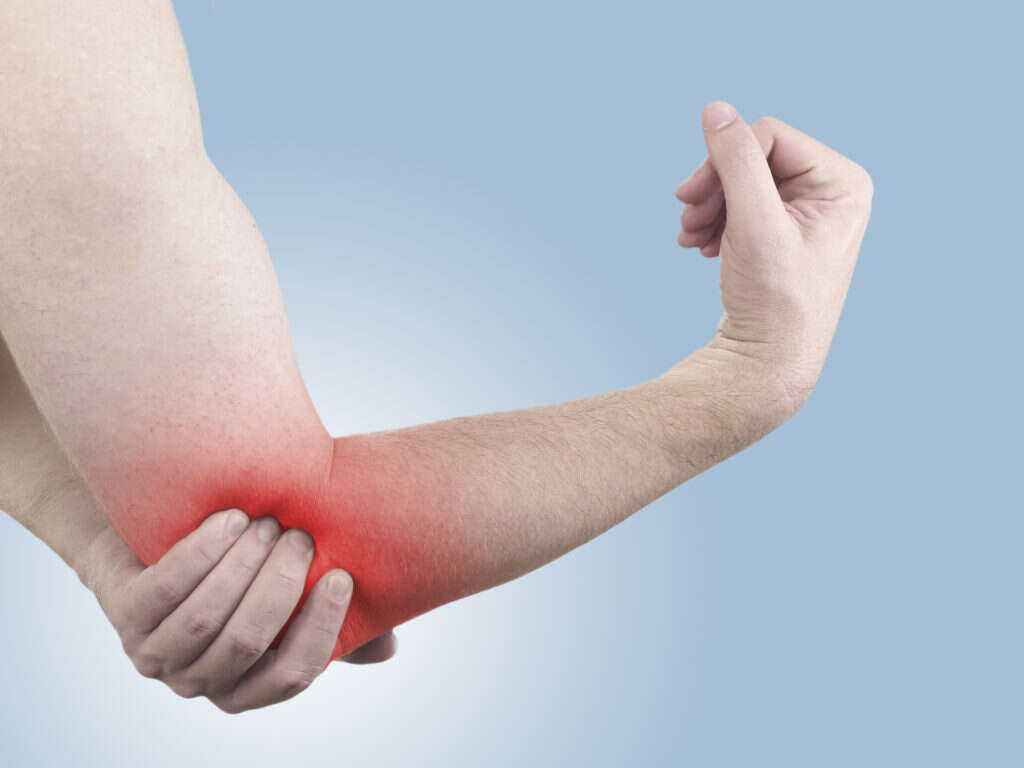
Golfer's Elbow Symptoms, Treatments and More
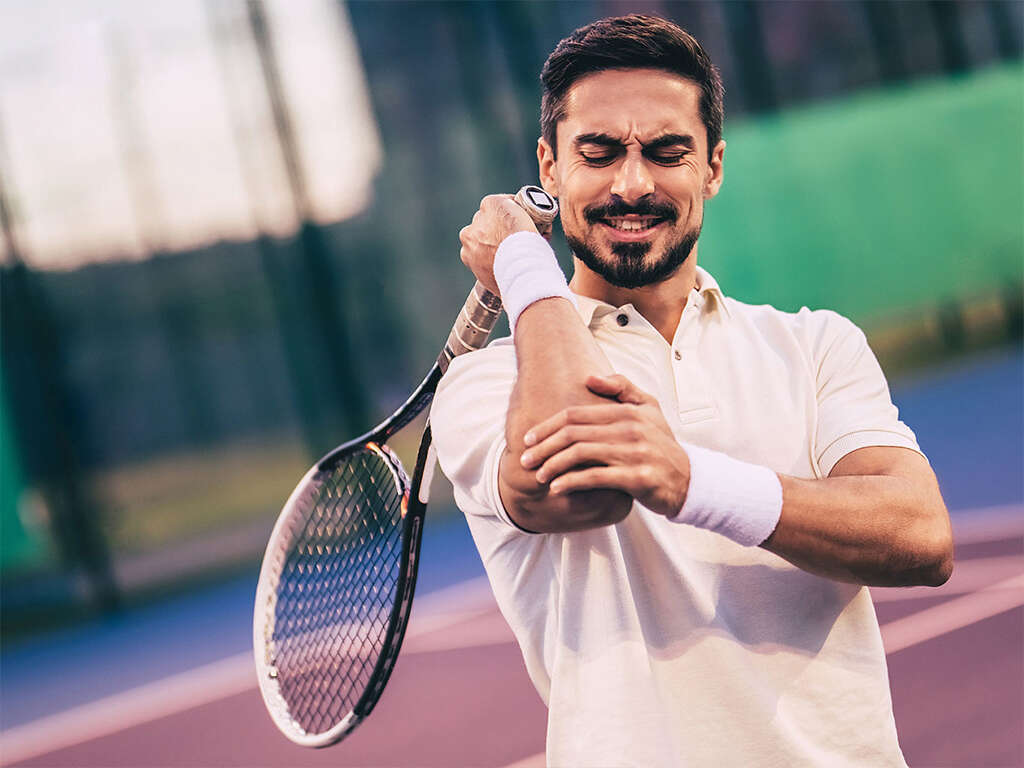
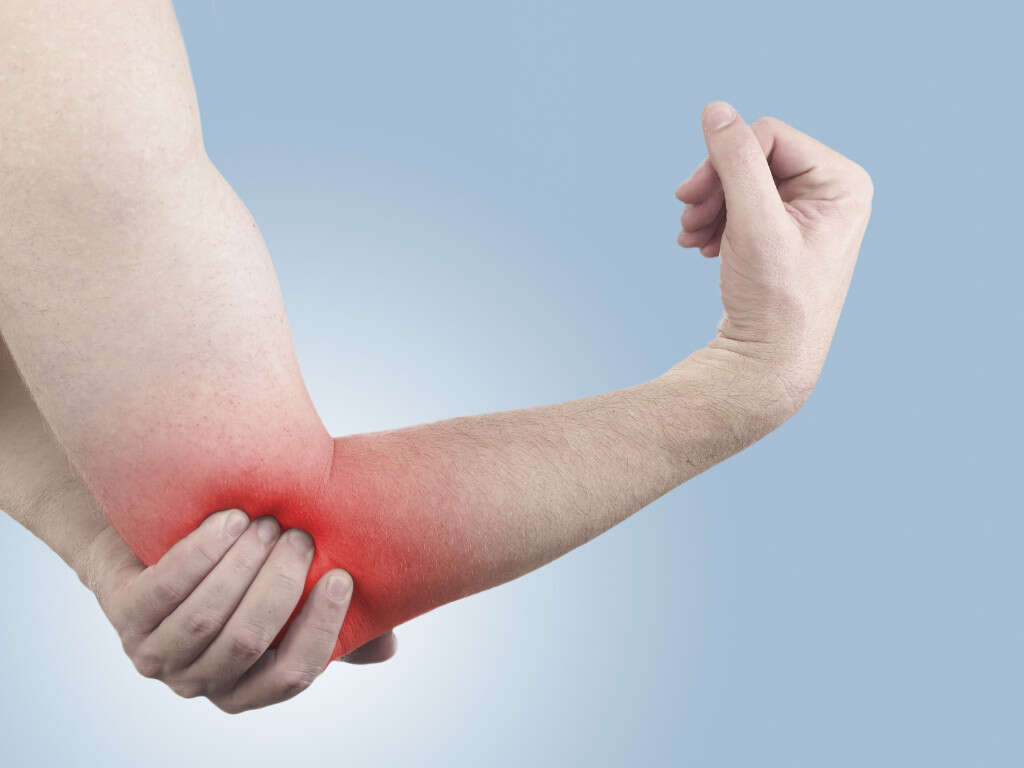
Golfer's elbow is a painful condition that develops from repetitive movements of the wrist that involve excessive force, such as swinging a golf club for 18-holes. It's also known as medial epicondylitis. Similar to tennis elbow, Golfer's elbow isn't restricted to individuals who play sports regularly.
It's typical to start with at-home treatment, such as rest, ice and NSAIDs for mild pain relief. However, if pain continues, a trip to the doctor may be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause and start a treatment plan that reduces pain and prevents recurrences.
Define Golfer's Elbow
Although Golfer's Elbow and Tennis Elbow are similar, the conditions impact the elbow in different locations. For example, golfer's elbow causes pain along the palm side of the forearm. In contrast, tennis elbow occurs on the outside of the elbow.
As a result, patients can develop both conditions at once, which can be extremely painful. In addition, as the condition worsens, the pain may extend from the elbow and wrist on the little finger side of the arm. Further, certain actions can increase or decrease pain, such as bending the wrist toward the palm.
Symptoms
Several symptoms can arise from a golfer's elbow, but the most significant and telling is pain. The pain occurs mostly in the inner side of the forearm and gets worse with movement. Patients might also feel tenderness in the elbow area.
Individuals may also notice stiffness in the elbow, making certain activities more difficult, such as clenching a fist. Other symptoms include weakness in the hands and wrists, numbness and tingling sensations.

Golfer's Elbow Causes
The condition, known in the medical community as medial epicondylitis, occurs following damages to the tendons and muscles that handle wrist and finger movements. Although golf is a common cause of golfer's elbow, there are several other reasons it develops.
Tennis players and other racket sports using improper techniques can lead to the painful condition. Other sports and physical activities that may lead to golfer's elbow include throwing sports, weight training and forceful, repetitive movements on the job, such as construction or plumbing work.
Diagnosis
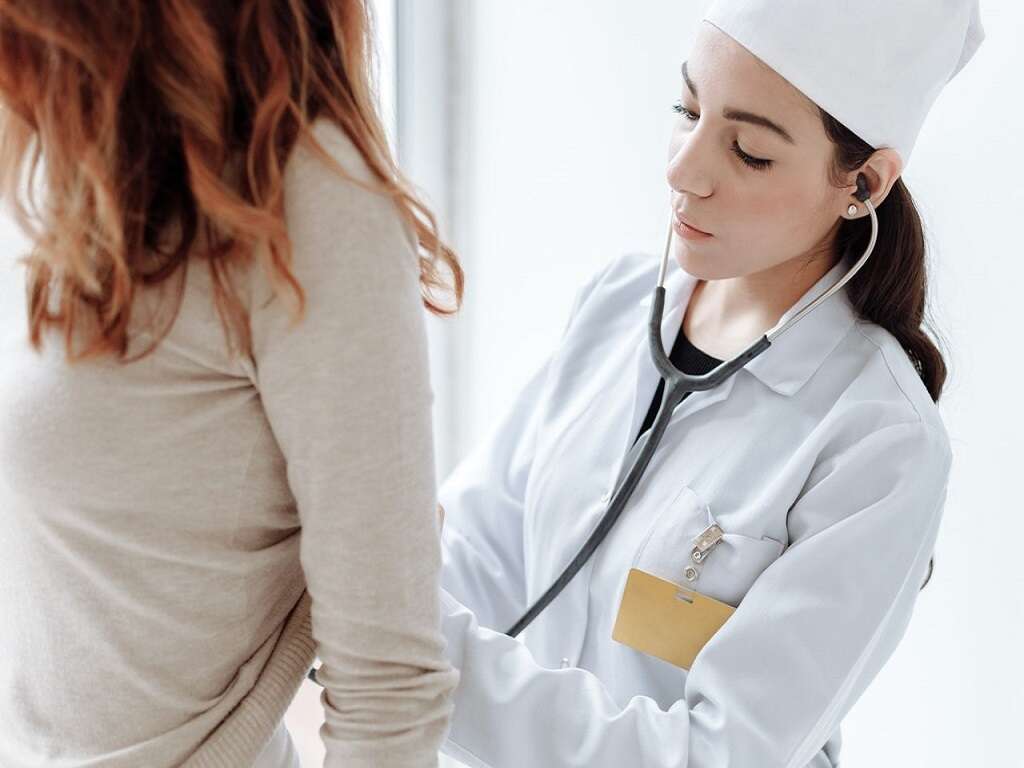
During the initial diagnosis, the physician may complete a physical examination to check for swelling and view the wrist, elbow, shoulder and arm's movements. While it might be painful, the medical practitioner may press on certain areas of the elbow and around it to check for other conditions with similar symptoms.
If the doctor believes there might be a fracture, an X-ray is performed to rule out a break and move forward with the proper treatment.
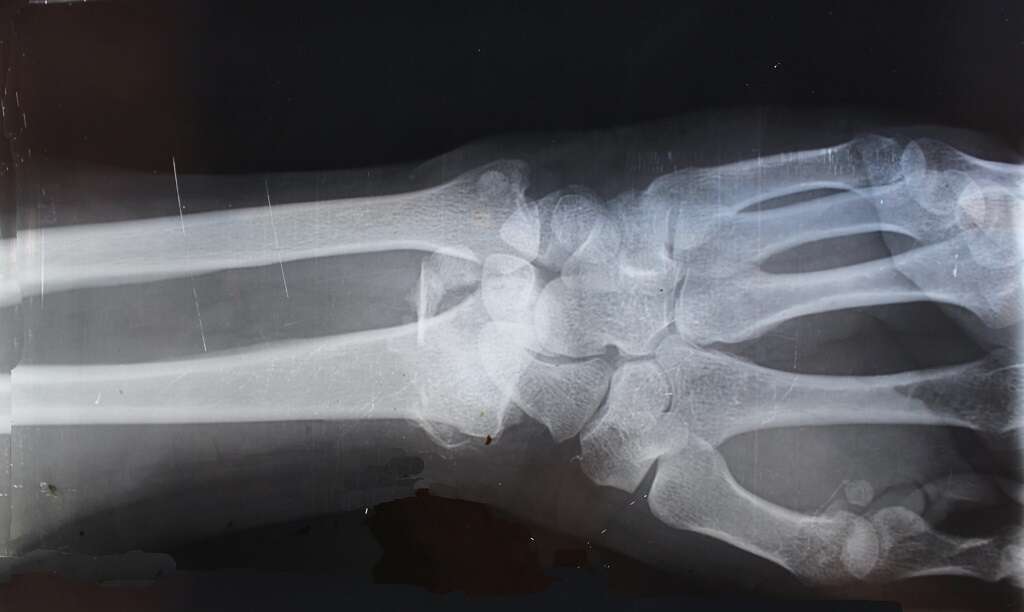
Tests to Confirm Golfer's Elbow
Outside of an X-ray, the physician might request comprehensive imaging studies. The most typical is an MRI, which checks for any deformities or signs of infection that may be causing the pain. However, an MRI is unlikely to be used in the diagnosis.
During follow-up care, the doctor might get a second x-ray for persistent pain following traditional treatments. However, sometimes when there's heavy inflammation, minor fractures might not show up on the imaging.
Potential Treatments
The first course of action involves avoiding the triggers that are causing the pain. For example, patients that are regularly hitting the green or putting area need to put away their clubs for a few weeks. Additionally, individuals incurring the pain in a workplace setting might need another work assignment while they rest.
If rest at home doesn't improve the symptoms, medication might be the next option. Patients begin with NSAIDs, which are over-the-counter remedies, and may need stronger pain medicine to help.

Home Remedies
Home remedies for a golfer's elbow go beyond rest, avoiding the activity that causes the pain and taking NSAIDs to dull the pain. Individuals can also ice the injury, apply heat if it works better and wear a brace to restrict movements.
During these steps, patients should continue to do stretches to prevent stiffness and work to strengthen the muscles around the elbow to prevent future reoccurrences. Combine these stretches with any physical activity that doesn't cause pain in the elbow area.
Preventing Golfer's Elbow
The best way to treat a golfer's elbow is to prevent it from occurring. Once you've experienced the pain, you'll most likely agree that the best treatment is prevention. If repetitive movements can't be avoided, the easiest way to prevent a golfer's elbow is by strengthening the forearm.
Additional ways to avoid the condition include improving your technique when playing golf or other at-risk sports, practicing proper form when moving heavy objects and improving flexibility.

Risk Factors
The risk factors of a golfer's elbow are straightforward. People who often perform repetitive tasks are the most likely to develop these conditions. Common sports include tennis, golf, baseball, softball, weight lifting and rowing.
By using proper form when playing these sports or training, individuals can avoid the excruciating joint and muscle pain people with golfer's elbow experience. They can also learn new techniques to reduce the damage from impact.
Exercises for Golfer's Elbow
Along with over-the-counter pain-relievers, pain patches and prevention techniques, there are some specific exercises that might reduce the symptoms of golfer's elbow. For example, isometric wrist strengthening may be helpful in both prevention and treatment.
Other light exercise and stretching practices can be helpful in reducing symptoms. Movements that strengthen the forearm and encourage proper elbow movement may be helpful. You should always consult a doctor before moving forward with a golfer's elbow treatment plan.