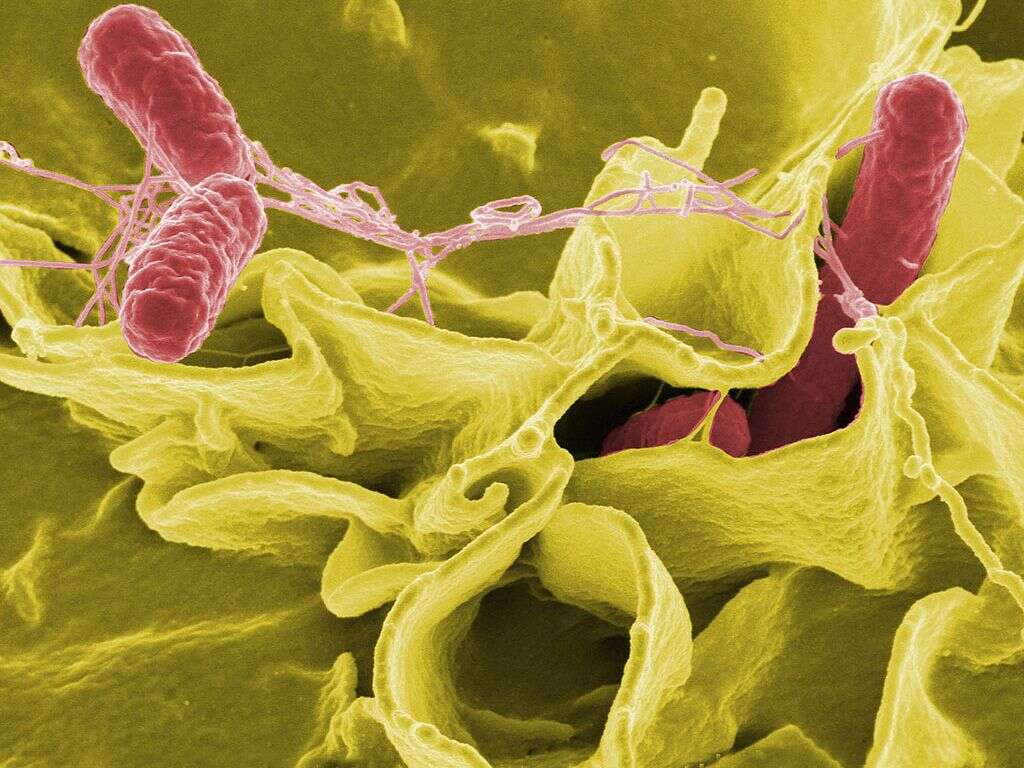
10 Symptoms of E. Coli Infection
Escherichia Coli is a bacterium of the Escherichia genus. It is usually found in our large intestines where they live in balance with other bacteria causing no harm. These bacteria have the potential to colonize different tissues and cause havoc. There are many types of E. Coli, each with different action mechanisms to colonize and damage our cells.
Escherichia Coli is a common cause of many infectious conditions, such as urinary tract infections (UTI), travelers’ diarrhea, meningitis, foodborne diseases, and many more. In the US, E. Coli is the leading cause of urinary tract infections and it is associated with up to 15% of the cases of traveler’s diarrhea in the developing countries.1Escherichia Coli (E. Coli) Infections. Epidemiology. Author: Tarun Madappa MD - https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/217485-overview#a6
1. Fever
A fever is an increase in body temperature. Usually, the temperature should be above 38⁰C (100.4⁰F) in order to be considered as a fever, but this depends on the site where the temperature is being measured. A fever is usually a response of the body to a threat. By increasing the body’s thermostat set point, we start to shiver to generate heat in order to reach the new temperature that has been set.
In the case of an E. Coli infection, a fever is a common symptom associated with many conditions such as a urinary tract infection, meningitis, and gastroenteritis to name a few. In adults, a fever is not dangerous on its own, but in young children, a high fever may lead to febrile seizures, so it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.

2. Dysuria
Dysuria is the medical term used to describe the presence of pain during urination. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions such as a urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, and sexually transmitted diseases (STD) to name a few.
E. Coli is the most common cause of urinary tract infections in the US, and one of the most common symptoms associated with this condition is dysuria. Pain associated with a UTI can be quite annoying for patients and it can be one of the early and only symptoms that show up in cases of uncomplicated UTIs.

3. Increased Urinary Frequency
An increase in the normal urinary frequency is known as pollakiuria. This is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. It can be a condition on its own, or it can be linked to another condition in the urinary system such as urinary tract infections (UTI), kidney stones, and issues with bladder emptying.
In the case of an E. Coli infection that causes a UTI, many patients complain of increased urinary frequency throughout the day. This issue may even cause urgent restroom stops to urinate and can be quite disrupting and annoying.

4. Diarrhea
Diarrhea is defined as the passage of 3 or more loose or liquid stools in a single day. This is a non-specific symptom that is associated with many conditions. Depending on the duration of this symptom, it can be classified into acute diarrhea (usually lasts a few days) and chronic diarrhea (over 14 days). Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, and this is especially important in young children and elderly patients.
There a several types of E. Coli that can cause acute watery diarrhea. Depending on the E. Coli subtype, the patient may experience watery diarrhea like the ones suffering from traveler’s diarrhea. Other subtypes invade the gastrointestinal tract mucosa causing bloody stools, fever, and abdominal pain.

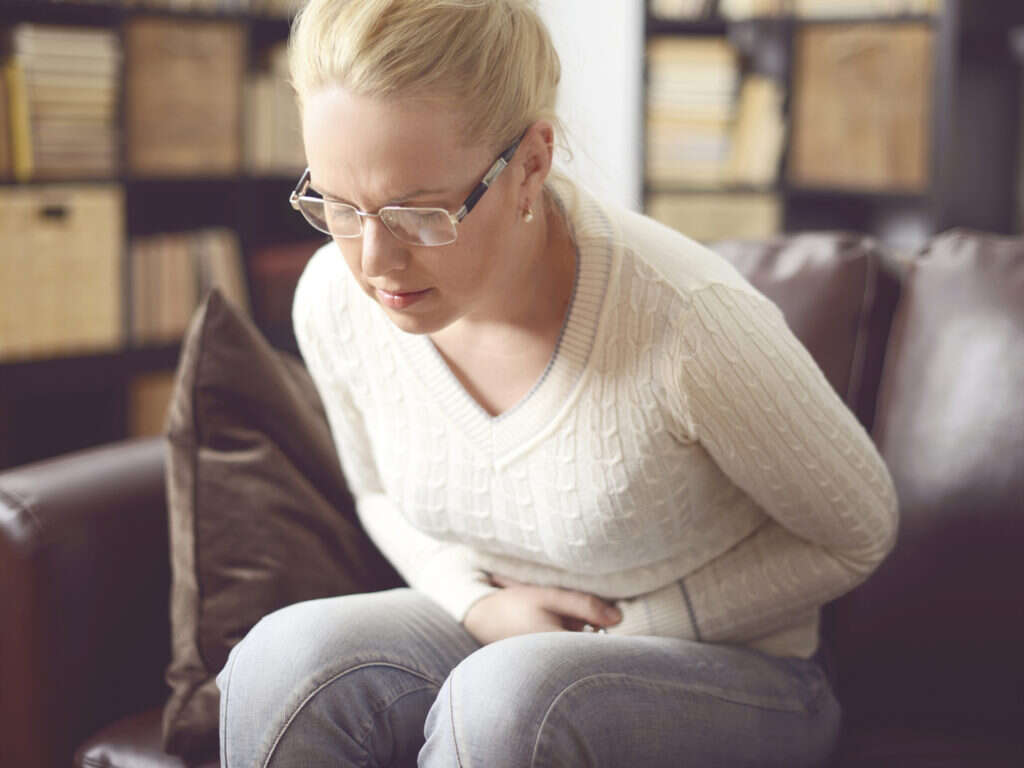
5. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
Some subtypes of E. Coli are known to cause dysentery, which is basically defined as a severe case of diarrhea with accompanying symptoms like fever, bloody stools, and abdominal cramps. Dehydration is a common complication seen in cases of dysentery, therefore it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis.

6. Nausea
Nausea is commonly defined as the urge to vomit. It can appear suddenly but, in some cases, it has an insidious onset. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions, but it can also be triggered by certain events or things in our surroundings.
Patients with a complicated urinary tract infection may experience nausea as an early symptom. This is usually the case in patients where the infection progresses and spreads into the kidneys (pyelonephritis). In some cases, nausea can be so intense that may cause the patient to vomit, but this is not a common finding.

7. Irritability
Irritability is a hard symptom to describe due to its subjective nature. Most pediatricians agree that irritability can be described as the abrupt change in behavior of a child which is characterized by excessive crying and restlessness despite multiple comforting attempts. This is one of the most important symptoms in young children as they are unable to express their symptoms using words. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions.
E. Coli is one of the most common causes of neonatal meningitis. Irritability can be the first and sometimes the only sign of acute bacterial meningitis in the newborn. This is a very serious condition that requires urgent medical treatment to prevent further complications.

8. Neck Rigidity
Neck rigidity is defined as difficulty or inability to properly move the neck due to stiffness and/or pain. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions but it is particularly relevant in cases where meningitis or meningeal irritation is suspected. It is important to know that having a stiff neck is not necessarily associated with an infection of the central nervous system. Many other conditions can cause neck stiffness, therefore it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.
E. Coli is a known cause of acute bacterial meningitis in children and less frequently in adults as well. In these patients, neck rigidity can be present but sometimes can be hard to assess, especially in younger children.

9. Shortness of Breath
Dyspnea is the medical term used to describe sudden shortness of breath. It is characterized by having difficulty breathing which may or may not be associated with a feeling of tightness in the chest. Dyspnea is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with both respiratory and circulatory conditions. It is important to state that exercise-induced dyspnea is usually a normal and transitory state of air hunger which is not directly related to a disease, whereas, resting shortness of breath is usually a sign that something might be wrong.
E. Coli can colonize the respiratory tract and eventually develop into pneumonia. It is not a common cause of pneumonia but it can be seen in patients with an E. Coli urinary tract infection and patients that might have aspirated gastric content. Patients with this condition usually experience shortness of breath, a wet or dry cough, and fever.
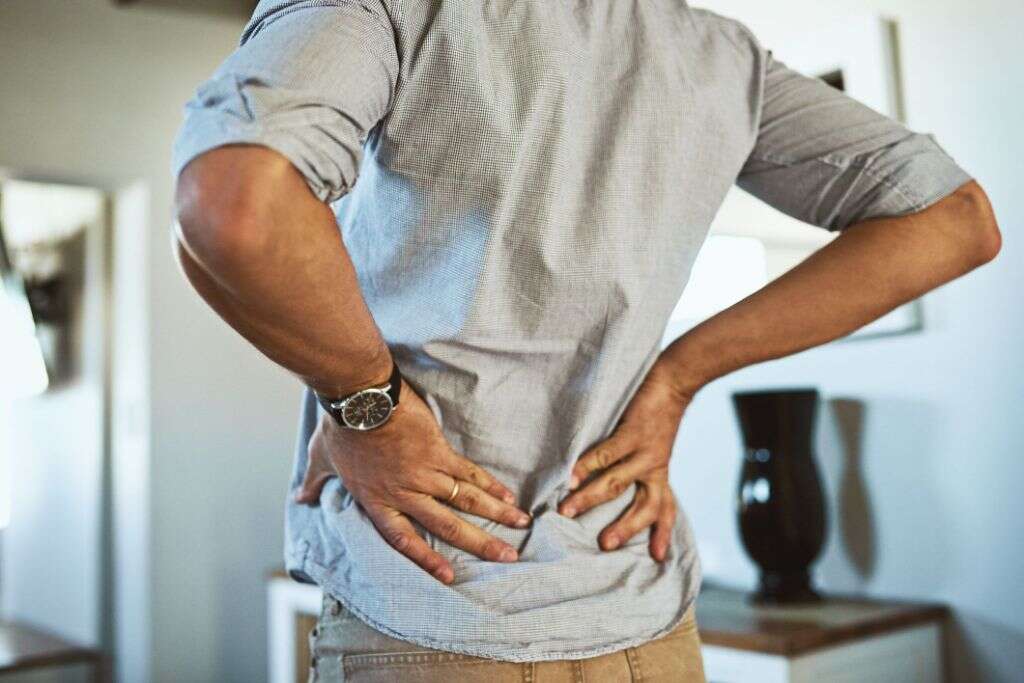
10. Lower Back Pain
Pain in the lower back is one of the most common medical complaints worldwide. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. It can have an acute onset which is usually seen in conditions affecting the musculature of the back, but sometimes it can have an insidious onset which makes it harder to diagnose.
Patients with a urinary tract infection caused by E. Coli may experience lower back pain. As the disease progresses, the infection might reach the kidneys (pyelonephritis), causing lower back pain to appear. Tenderness in the costovertebral angle, which is the point where the ribs meet with the spine on each side, might also be associated.