10 Causes of Spleen Pain
Cause #6: Sickle cell disease
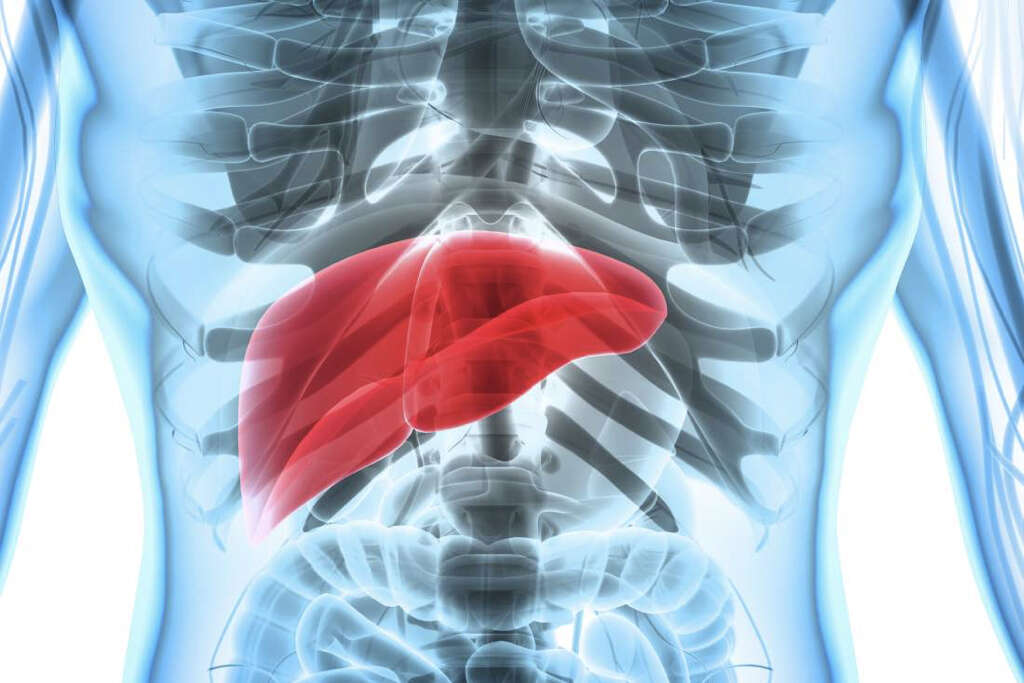
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that manifests in early childhood. It results from a mutation in hemoglobin (Hb), a protein molecule located in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. This mutation generates abnormal hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S (HbS) that, in “stressful” conditions for the red blood cells (RBCs), polymerizes and aggregates resulting in sickle-shaped RBCs (i.e. the shape of a reaping hook). This causes the red blood cell to continuously sickle and de-sickle, resulting in damage to its outer membrane. Thus, organs like the spleen (part of the reticuloendothelial system) remove these damaged RBCs from the circulation.
Patients with sickle cell anemia can develop a serious complication known as splenic sequestration that can cause severe abdominal pain. It occurs when high quantities of blood made up by sickled RBCs become trapped in the spleen causing it to grow in size. Splenic infarctions (tissue death) result in scarring of the tissue and a loss of function (functional asplenia or auto splenectomy). Splenic sequestration is characterized by rapid enlargement of the spleen, and life-threatening anemia that, if not treated promptly, can result in hypovolemic shock and death (low levels of blood in the systemic circulation that results in lack of blood to most organs).
Advertisement