10 Symptoms Of High Cholesterol
Cholesterol is an essential component of the human bloodstream. It is a waxy, fat-like substance produced in the liver that aids in the creation of cell membranes and some hormones. While it does serve an important purpose in the body, at too high levels it can lead to health problems.
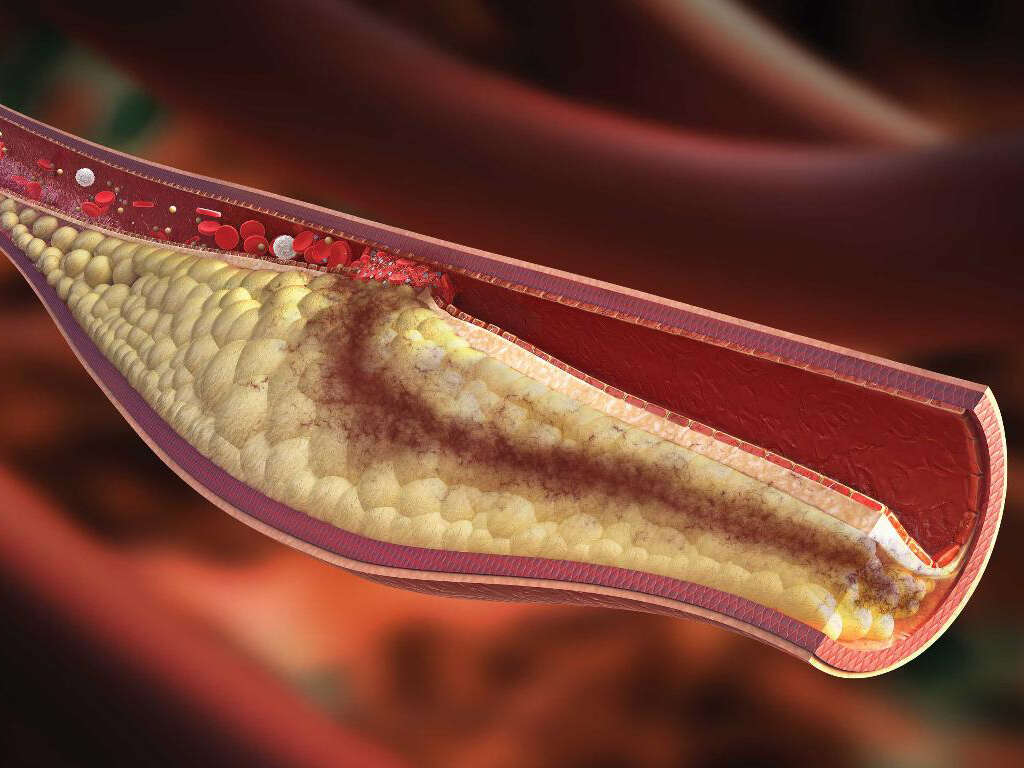
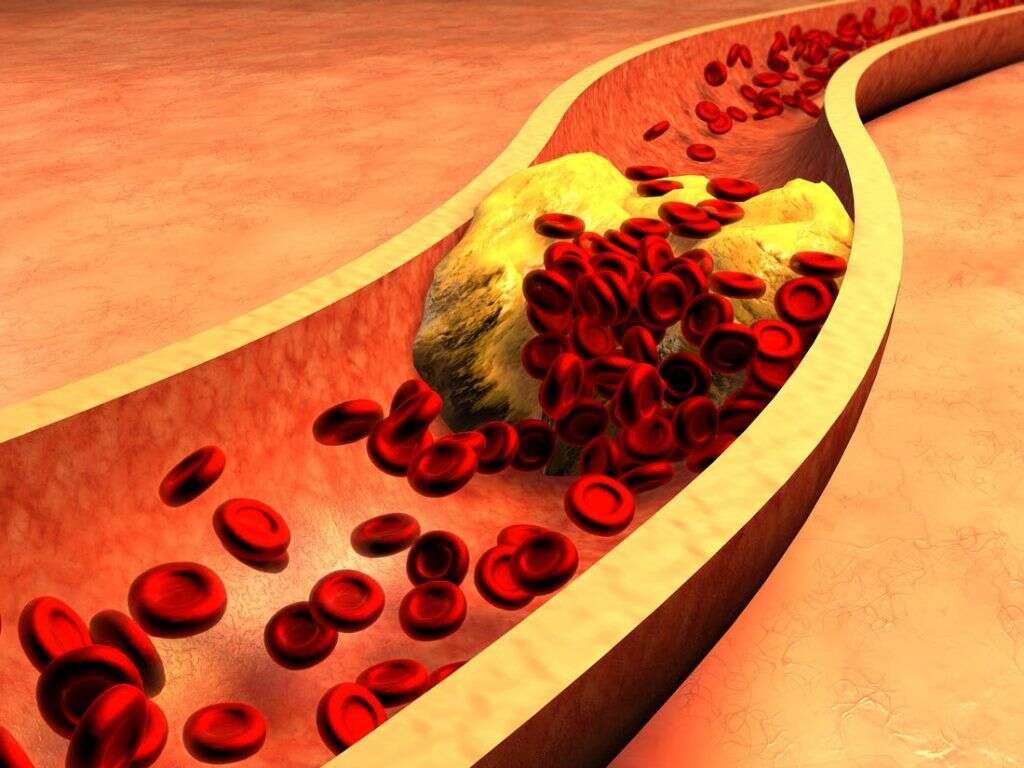
When there is a high level of cholesterol in the blood, plaque forms in the arteries. This build-up makes arteries more rigid and narrow, allowing less and less blood to travel with time. If the condition continues unabated, it can lead to severe organ damage, particularly in the heart and brain through such occurrences as cardiac arrests and stroke. High cholesterol does not have obvious symptoms but is likely given certain risk factors and the results of some blood tests.

1. Atherosclerosis
With a high level of cholesterol, there is the narrowing and hardening of arteries caused by the buildup of plaque and other deposits. This condition is referred to as atherosclerosis. It results in a reduced level of blood flow. When arteries that feed heart muscles are constricted in this way, it can lead to chest pain and eventually coronary heart disease.
Should blood clots passing through these blood channels become unable to get by due to the reduced space, it can cause them to plug an artery leading to a heart attack. When the same occurs in blood vessels that feed the brain, it can also lead to stroke.
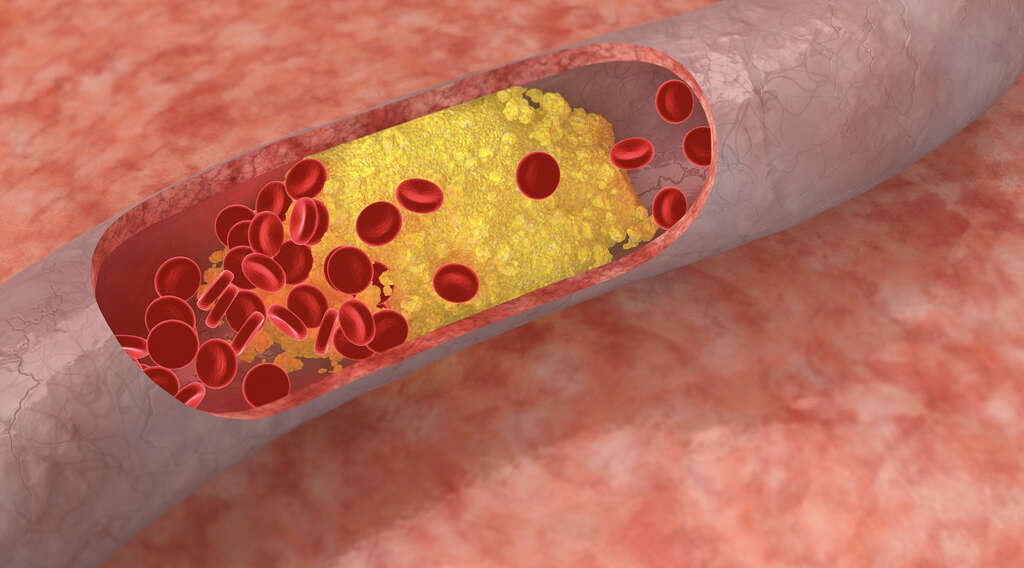
2. High LDL Levels
Cholesterol travels around the body through particles called lipoproteins. Humans have two types of lipoproteins. The high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). LDL is commonly called bad cholesterol.
It is what builds up in the arteries, causing them to become clogged. High LDL levels are often caused by the high consumption of food with too much fat. The best way to determine if you have a safe level of LDL in the blood is to undertake a blood lipid profile test. A healthy person should have an LDL cholesterol level of less than 100mg/dL. This test should be retaken every few years to monitor LDL levels.

3. Low HDL Levels
HDL is also referred to as good cholesterol. This lipoprotein helps to deliver LDL to the liver where it can be eliminated from the body. Having a high level of HDL is good for human health. An HDL cholesterol reading of 50mg/dL or higher is advisable. If the result is less than this, a person runs a higher risk of suffering heart disease.
Low HDL levels can also be caused by a poor diet with high-fat content. A sedentary lifestyle, and the often resulting obesity, can also contribute to this problem. Exercise can help to boost HDL levels and also increase the size of LDL particles that makes them harder to attach to arterial walls.

4. High Triglyceride Levels
This is another fat type of fat found in the blood. Its levels are also checked during a lipid profile test. When we eat, the body converts the calories we do not immediately need for energy into triglycerides. Later, when energy is needed and we are not eating, certain hormones will tap into our fat cells to release the triglycerides, providing an energy source.
Healthy individuals should have a triglyceride reading of less than 15mg/dL. Higher than this is an indicator of high cholesterol levels. Just as with high cholesterol, high triglycerides contribute towards the hardening and thickening of arteries. This increases the risk of cardiovascular problems and at the extreme can cause an inflammation of the pancreas. Lifestyle changes including a healthier diet and regular exercise can help alleviate this condition.

5. Obesity
Obesity occurs when a person carries an excessive amount of body fat. It can badly affect health as it increases the risk of all kinds of illnesses including cardiovascular problems and multiple cancers. It can also affect outward physical appearance leading to social problems and self-confidence.
Obesity is commonly gauged using the Body Mass Index (BMI). Having a BMI of 30 or higher indicates that you are obese. Many suffer this condition as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and high-calorie diet rich in fats and sugar. High cholesterol levels are common amongst those that are obese. Healthier habits like an improved diet and exercise can help to reduce weight and lower cholesterol levels.

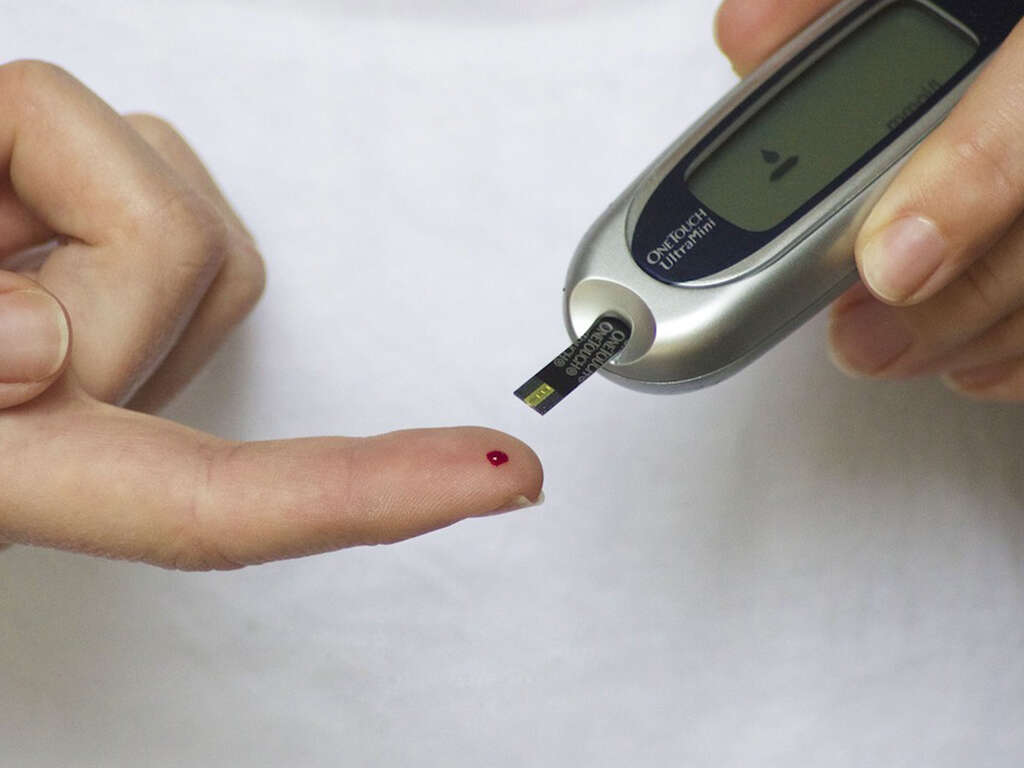
6. Diabetes
While not all sufferers of high cholesterol have diabetes, many diabetes sufferers do get lipid profile results with low HDL and high LDL levels. Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by abnormally high levels of sugar in the blood. Both high cholesterol and diabetes have a negative effect on your lipid profile. Together, they also damage arterial linings.
Those diagnosed with diabetes and high cholesterol often consume a poor diet. High-calorie meals with high-fat content and sugars are a big contributing factor. Making healthier food choices, being more physically active, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking help. Working towards losing excess weight can also help make these symptoms more manageable.

7. Smoking
High cholesterol damages the walls of arteries by encouraging the build-up of plaque. As more plaque accumulates on the arterial walls, these blood passages become narrower and harder. Smoking contributes negatively to this by introducing chemicals into the blood vessels that encourage blood to thicken and clots to form.
These chemicals also cause inflammation and swelling in the blood vessels that promote more plaque buildup and result in even narrower blood passages. When combined with increased clots, it further increases the risk of coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease (PAD), stroke, and aneurysms. Quitting smoking, alongside other lifestyle changes can help to reverse this damage and reduce the risk of a future health crisis.

8. Increased Age
High cholesterol features high LDL levels and low HDL levels. Age can affect how cholesterol levels are regulated by the body. The liver is responsible for the removal of excessive amounts of LDL in the bloodstream. As we age, organs like the liver become less effective at their job.
With the liver less able to remove LDL as we get older, seniors are at an increased risk of developing high cholesterol. Making suitable changes in diet that will limit the development of LDL and encourage higher HDL becomes more important the older we get. A healthier lifestyle featuring more physical activity, not smoking, and less drinking of alcohol also helps.

9. High Blood Pressure
Those with consistently high blood pressure are at an increased risk for high cholesterol. Also known as hypertension, this condition places a major strain on the heart as it has to work harder to pump blood through the body. When coupled with compromised blood vessels that have hardened and become narrow due to high cholesterol, it can lead to several cardiovascular conditions including heart failure, kidney failure, and stroke.
Lowering cholesterol can help to improve the condition of arteries. They become more supple and able to better cope with fluctuating blood pressure. Without as much plaque clogging the way, there is also less risk of blockages that can damage organs.

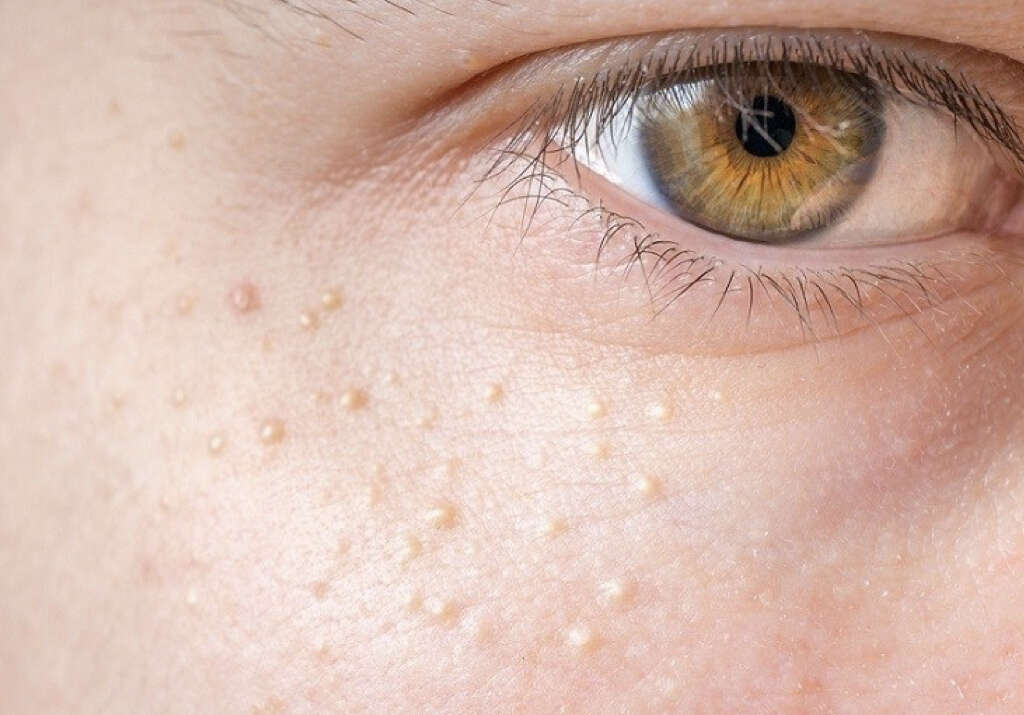
10. Cholesterol Deposits
Soft, fatty, and yellowish lumps can sometimes be seen underneath the eyelids of a person with high cholesterol. They mostly appear close to the inner corner of the eye. When a single growth is found, it is called a xanthelasma. When they are multiple, the condition is referred to as xanthelasmata. These cholesterol deposits are considered harmless but can be a good signifier of cholesterol, thyroid, or liver problems.
While they can be unattractive, they are typically not painful and rarely cause vision problems. This symptom is more commonly experienced by women. It is not uncommon for them to register abnormally high lipid levels, even when other health parameters are normal.