10 Giant Cell Arteritis Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Giant cell arteritis: Symptoms and causes.' Mayo Clinic, 2 Sept. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/giant-cell-arteritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20372758
- 2. 'Giant cell arteritis.' MedlinePlus - Health Information from the National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000448.htm
- 3. 'Giant cell arteritis.' Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program | Providing Information About Rare or Genetic Diseases, 21 Sept. 2018, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9615/giant-cell-arteritis
- 4. 'Large-vessel giant cell arteritis: diagnosis, monitoring and management.' OUP Academic, 23 Feb. 2018, academic.oup.com/rheumatology/article/57/suppl/2/ii32/4898137
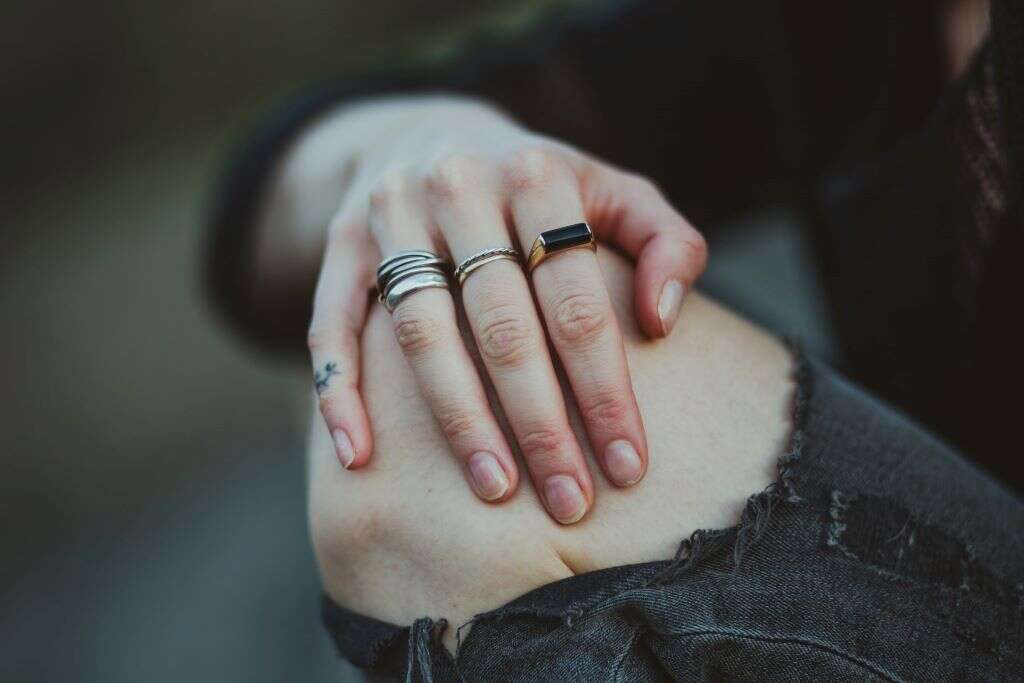
Joint Pain and Swelling
The inflammation caused by giant cell arteritis may affect other parts of the body besides the head. Tissues that line the joints might become inflamed, causing pain in the limbs and during or after movement.
There can sometimes be swelling in a person's hands or feet. Fluid build-up can cause something called pitting edema. This is when there's noticeable swelling and a person can press on their skin and leave a small dent or pit behind.3‘Giant cell arteritis.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program | Providing Information About Rare or Genetic Diseases, 21 Sept. 2018, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/9615/giant-cell-arteritis
Advertisement