What Is Horner's Syndrome?
6. Common Symptoms of Horner’s Syndrome
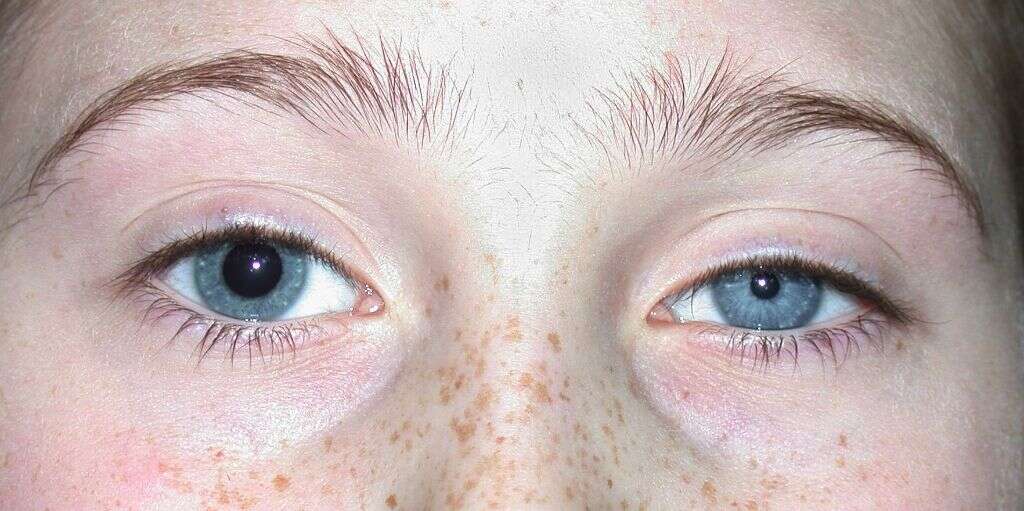
Horner’s syndrome manifests around the eye on one side of the face in several specific ways. The size of the pupil shrinks and remains small, which can be apparent when compared to the size of the other eye’s pupil. The pupil may also have delayed responses with dilation or not change at all when light conditions shift. The eyelid of the impacted eye also droops significantly, which obstructs vision and is noticeable to others. The lower eyelid may seem somewhat elevated and make the eye appear slightly more closed than usual.
A person with Horner’s syndrome is likely to experience all of these symptoms around the eye. In addition, the side of the face that has been impacted no longer produces sweat. This dryness can be easy for a person to notice, especially in humid climates or during tense situations.
Advertisement