What Is HFMD?
As we get older, we will be exposed to more and more pathogens as time goes by. Each time we are exposed to a pathogen, our immune system will learn to fight against it, helping to protect us against infections in the future. This means we are less likely to catch certain disease the older we get.
One example of this is hand foot and mouth disease. It is a common disease that is harmless in the vast majority of cases. As most adults have developed an immunity to it, it is only usually found in children, although some adults will still catch it. Here we take a close look at the disease, what the symptoms are, and what we can do about it.
1. Overview
Hand foot and mouth disease is a disease that is usually found in young children. It is a very common disease and, thankfully, it is also mild. The disease will cause symptoms that can be uncomfortable, especially in young children, but they are not going to be serious.
Despite having the same name, the disease in humans is not the same as the disease that is common in animals. This means that the disease cannot be caught from animals even if they are infected with the animal variety of the disease. The disease should clear up within 10 days or so with no harm being done to the patient.
2. Causes
Hand foot and mouth disease is usually caused by the coxsackievirus A16 virus. It belongs in the enterovirus family of viruses, and there are other enteroviruses that can cause hand foot and mouth disease. It tends to be contracted after infected particles have been ingested.
The main methods of transmission include through saliva, and in droplets generated from sneezing or coughing. It can also be caught from the fluid of burst blisters, and also from the fecal matter of infected people. The condition is more common in young children partly because they put their hands in their mouths more frequently, and also because they tend to stay in groups.

3. Contagiousness
One of the reasons that hand foot and mouth disease is so common is that it is very contagious. In warmer climates, the disease is prevalent all year round, while it is most likely to be encountered in summer and autumn in temperate climates. Many people that contract the virus will show no symptoms at all.
Although somebody may not be showing symptoms, they will still be contagious. This can help spread the disease further because the patient will unlikely be taking precautions that might otherwise help prevent the spread. Patient’s are going to be at their most contagious during the first week of falling ill, and they will continue to be contagious for several weeks after they have seemingly recovered.
4. Blisters
Among the most common symptoms of hand foot and mouth disease is a rash. The rash is not usually itchy, and it can be found on the soles of the feet, the palms of the hands, and sometimes on the patient’s buttocks. While the rash may not be itchy, other symptoms of the disease can be far more uncomfortable.
Such symptoms include blisters located on the gums, on the insides of the patient’s cheeks, and on the tongue. These can be very painful and it can be particularly difficult for young children to bear. These symptoms will generally follow a day or two after other symptoms start to show.

5. Fever
Hand foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus, meaning the immune system will be doing what it can to deal with the intruder. This means that one of the common symptoms of hand foot and mouth disease is a fever, which is a natural immune system response to the presence of a pathogen.
Other symptoms of the disease include malaise, which is a general feeling of being unwell. A sore throat can also be present, and the patient may also lose their appetite. The patient may also become uncharacteristically irritable. Very young children are unable to tell us what their symptoms are, so it is wise to get medical advice if something seems wrong.
6. Risk Factors
As mentioned, young children are more likely to catch hand foot and mouth disease than children are. One of the main reasons for this is that they are likely to pick up the virus from objects around them and then ingest the virus after placing their hands in their mouths. Those in day care centers in particular are at a high risk of catching the disease.
Adults can also get the disease, however, and those that work with young children are at a higher risk. Parents with young children are also more likely to pick up the disease. Adults are less likely to catch it, however, because their immune systems will likely have developed the ability to fight the virus.

7. Prevention
The contagious nature of hand foot and mouths disease means it is all but impossible to have complete protection against it. That does not mean to say you can’t make yourself safer than otherwise, however. One of the most effective methods is to wash your hands regularly and encourage your children to do the same.
In addition to washing hands, make sure that surfaces are kept clean, using disinfectants where practical. You should also keep any sick children at home to help prevent spreading the disease further. If you do cough or sneeze, try to do so in a tissue or similar to help prevent contaminated droplets from infecting other people.
8. Complications
In the vast majority of cases, the patient will make a full recovery. Hand foot and mouth disease will result in serious problems in a very small number of cases, however. One of them is dehydration, which tends to be caused by a lack of appetite and difficulty eating due to the pain the disease can cause.
In the more severe cases, the virus can result in a potentially fatal inflammation of the brain known as encephalitis. Also, the membrane that protects the spinal cord and brain can become inflamed in a disease known as meningitis. Meningitis is also potentially fatal in the more severe cases.
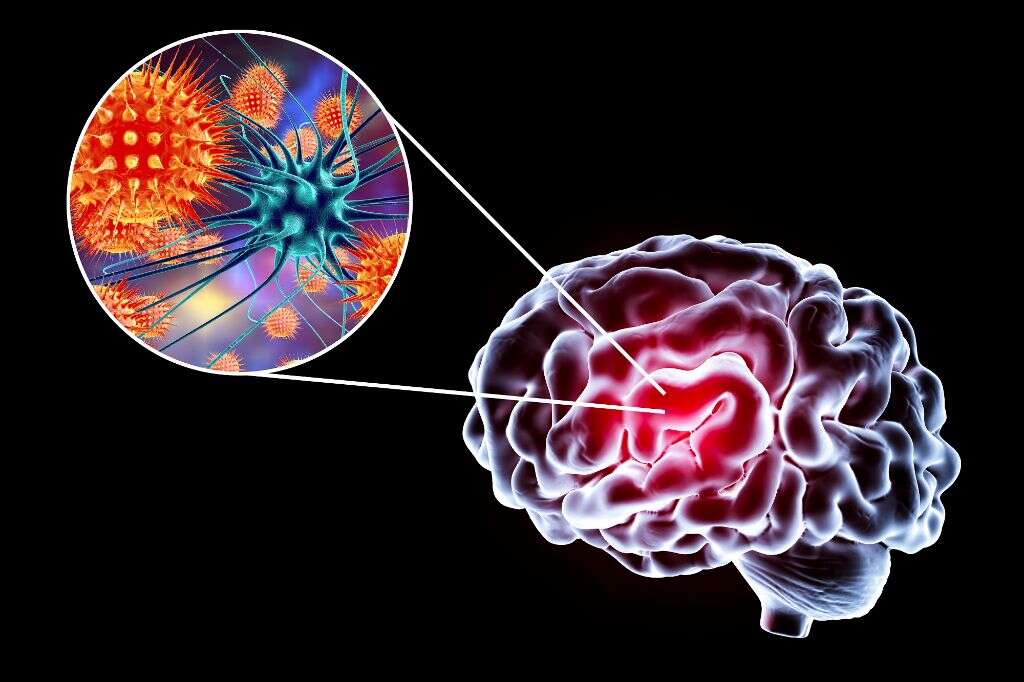
9. Diagnosis
In many cases, a doctor will be able to make a diagnosis based on a brief physical examination. Hand foot and mouth disease is a common condition in children so it is usually reasonable to assume what the problem is without further investigation. If the diagnosis is made and the condition gets worse, the patient should be taken back to see the doctor again.
Depending on the circumstances, a doctor might want to get a more solid diagnosis. This will likely mean requesting a stool sample or taking a throat swab so they can be sent to a laboratory for analysis. This can help experts identify the pathogen causing the condition, thus helping to confirm the diagnosis.
10. Treatment
Treatment for hand foot and mouth disease usually involves having the patient rest as much as possible and drink plenty of fluids. The immune system should be able to handle the virus itself. Antiviral medication may be suggested in the more severe cases, however. In the meantime, medication will likely be suggested to help treat the patient’s symptoms.
This will likely mean mild pain killers, like Tylenol and ibuprofen. An oral anesthetic may also be prescribed to help reduce the pain of the patient’s mouth sores. It is also recommended to avoid certain foods that can make sores worse, while using salt water in the mouth can also help to relieve pain.