What Is Gangrene?
When we fall ill, it is usually a case of having some symptoms that are not too much of a problem, even if they can be uncomfortable. In most cases, it requires some medication, maybe a box of tissues, and plenty of rest. The majority of the time the patient will make a full recovery in just a few days or so.
Some diseases are less straight forward, however. Some diseases can even cause some symptoms that can be terrifying and also very dangerous. One example of such as disease is gangrene, and it is one of the most disturbing of all. It is also extremely dangerous, and medical assistance must be sought as soon as it is suspected.
1. Gangrene
The cells in our bodies will die at some point. This is quite natural and is not usually a problem as they will simply be disposed of and replaced with fresh cells. If our cells were to die unexpectedly, however, then this system might not work as it usually would. In some instances, our cells can be killed but not disposed of and replaced as they usually would be.
Gangrene is a condition where our body’s cells die but are not dealt with as usual. This leaves behind dead tissue that will then begin to decompose. It is a very unpleasant condition as parts of the patient’s body literally rots away.
2. Wet Gangrene
There are three main types of gangrene, each of which can produce different symptoms. One of them is known as wet gangrene. As with the others, it is a very dangerous medical condition. This type happens when the patient has been infected by certain types of bacteria.
The presence of the bacteria can cause the patient’s bodily tissues to begin to break down. This will also cause the tissues to become moist, hence how the condition got its name. With wet gangrene there is a real chance of the infection spreading quickly, making it especially important to get treatment as soon as possible.
3. Dry Gangrene
All of our body’s cells need a constant supply of fresh oxygen in order to survive. This oxygen is delivered by our blood in a network of blood vessels that feeds the entire body. If this network was somehow damaged, the supply of oxygen will be disturbed. This can the cause the affected cells to die.
As the cells die, so the tissues will begin to decay. The affected tissues will tend to turn black and fall away. It can happen internally and the patient’s essential organs will often be infected. Dry gangrene tends to develop slowly, but is still a condition that should be treated immediately.
4. Gas Gangrene
Gas gangrene is caused by a bacterium known as Clostridia. It is also known as clostridial myonecrosis. It gets its name because the bacteria cause the build up of gases and toxins in the tissues. The accumulation of gas causes the patient to develop large, gas filled ‘bubbles’ on their skin.
In addition to the bubbles, gas gangrene will also cause the affected tissues to die and decay. Approximately 1,000 cases are reported in the United States every year, and it is potentially deadly. Treatment must begin as soon as the condition is detected to help save the patient’s body parts – and their life.
5. Physical Causes
There are numerous potential causes of gangrene. In dry gangrene in particular, it tends to be down to some form of injury that blocks the flow of blood to certain parts of the body. This usually happens in the extremities. Dry gangrene in particular is a potential complication of surgery so it is wise to look out for the signs after an operation.
Another relatively common cause is frostbite, and some people will lose fingers and/or toes if they don’t keep their extremities will protected from the cold. Injury that crushes bodily tissues is another potential cause, while excessive alcohol and drug use is another.

6. Medical Causes
Gangrene is also sometimes caused by certain medical conditions. For example, some conditions can cause the patient’s immune system to become weaker than usual. This, in turn, can make the patient more susceptible to the bacteria that are responsible for causing gangrene in some cases. This means an infection is more likely to take hold than otherwise.
Other medical causes of gangrene include those that affect the flow of blood. This includes arteriosclerosis, which means the patient’s arteries have hardened. Other conditions include blood clots, diabetes, hernias, and appendicitis. Raynaud’s disease, which affects the blood flow, is another potential cause of gangrene.
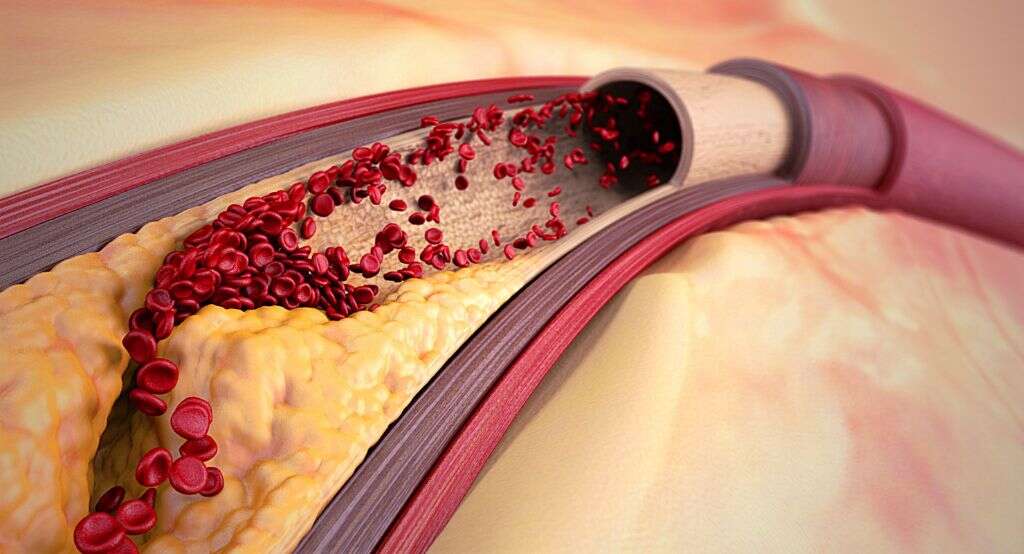
7. Internal Gangrene Symptoms
As mentioned, different types of cancer will have different symptoms, and some types are easier to detect than others are. Internal gangrene can be harder to recognize because, as the name suggests, the symptoms will not appear visibly on the patient’s skin.
Typical symptoms of internal gangrene will often include a long lasting fever that cannot be explained. A low blood pressure is always likely, and the patient can also experience pain that cannot be explained. In many cases, the patient can also begin to become easily confused, which is a sign that should always encourage somebody to see a doctor.

8. External Gangrene Symptoms
External gangrene tends to be noticed faster than internal gangrene, simply because the symptoms are clearly visible. One of the first signs is that the patient will develop a line on their skin around the infected tissues. This line will usually be red in color and can turn black as the condition develop.
Other symptoms of external gangrene include the loss of the sense of touch in affected areas of the body. The patient is also likely to experience sores that keep on returning, and any sores present may be filled with puss. The patient’s skin can also start changing color, often to green/black, and the affected tissues can give of a foul odor.

9. Diagnosis
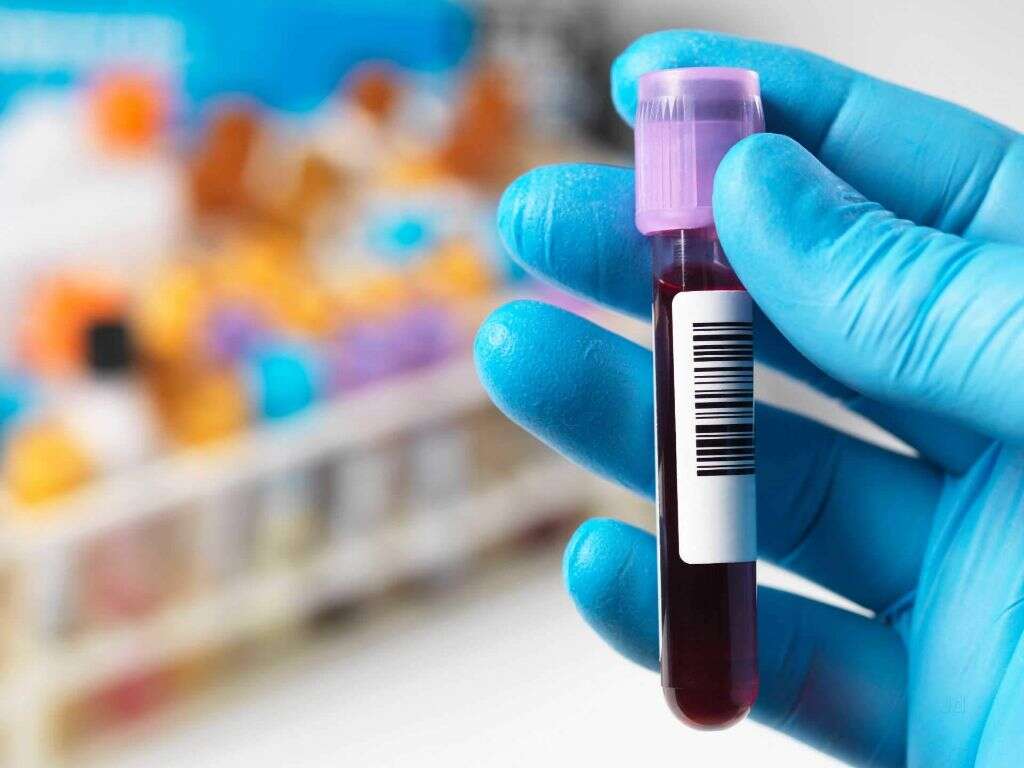
The symptoms of gangrene are often enough to give medical professionals a good idea of what the problem is. Regardless, it will still be necessary to perform tests to reach a confirmed diagnosis. This will often involve taking a sample of the affected tissues to look for signs of gangrene.
In addition, a blood sample can be taken to also look for symptoms that gangrene is present. It will also be important to look for the underlying cause, which will often mean scans to help look for issues with the patient’s circulation. The specific treatment will depend on what exactly is causing the gangrene.

10. Treatment
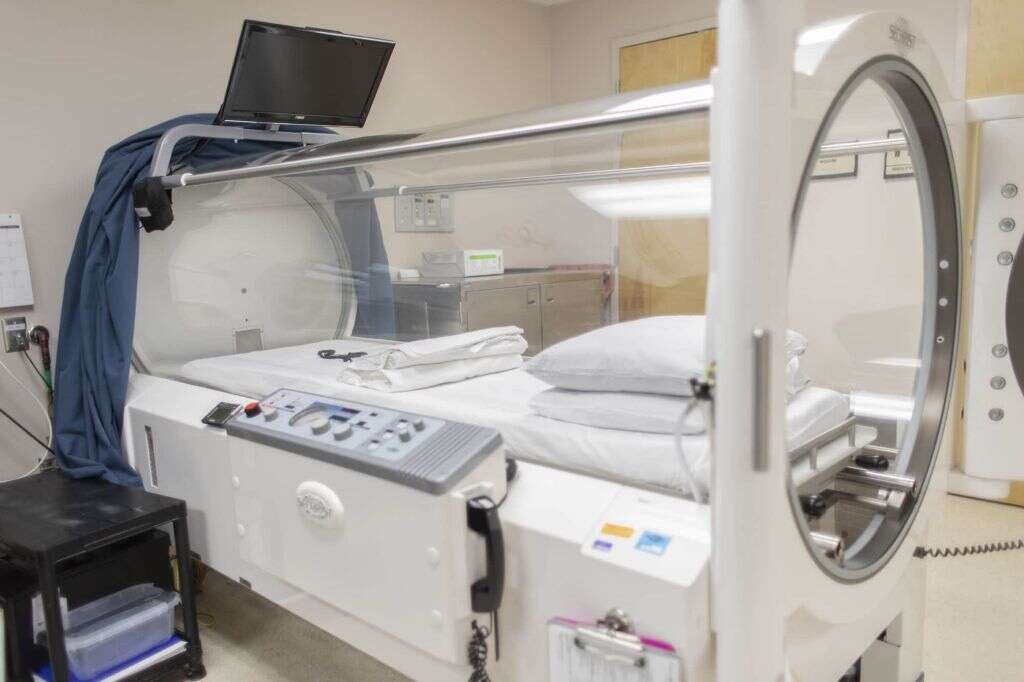
If a bacterial infection is the cause, then antibiotics will be needed to help prevent the infection from spreading further. These will usually be administered intravenously. In some cases, the patient will be placed in a hyperbaric oxygen chamber to help slow the growth of the bacteria.
Dead tissue cannot be recovered, and will need to be removed. This is done with help from chemicals and/or surgical tools. In some cases, it is even performed with help from maggots. Surgery may be performed to help improve blood flow, and it may be necessary to amputate in severe cases. Gangrene will often be fatal if not treated.