10 Viral Infection Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Viral vs Bacterial – What's the Difference?' HSC Public Health Agency, www.publichealth.hscni.net/news/viral-vs-bacterial-–-what's-difference.
- 2. 'Viral Infection | Viral Infection Symptoms.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 19 Oct. 2020, medlineplus.gov/viralinfections.html.
- 3. NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.
- 4. 'Viral Infections.' Sepsis Alliance, 18 Sept. 2020, www.sepsis.org/sepsisand/viral-infections/.
- 5. 'Is It a Bacterial Infection or Virus?' Duke Health, www.dukehealth.org/blog/it-bacterial-infection-or-virus.
- 6. 'Viral Meningitis.' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 6 Aug. 2019, www.cdc.gov/meningitis/viral.html.
Viruses and bacteria are both microscopic germs that can give a person sniffles. But while antibiotics are effective against bacterial infections, they don’t help treat viral infections. Treating most common viral infections, like the simple cold, involves a few days of rest, fluids and home remedies. With the overuse of antibiotics being a pressing medical issue, it’s helpful to know when an infection is probably viral.1‘Viral vs Bacterial – What’s the Difference?’ HSC Public Health Agency, www.publichealth.hscni.net/news/viral-vs-bacterial-–-what’s-difference.
Viruses cause HIV, Ebola and the flu, but each presents with vastly different symptoms. Knowing some general common viral symptoms can help a person differentiate between viral and bacterial illnesses and help them realize when a viral infection needs medical attention.2‘Viral Infection | Viral Infection Symptoms.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 19 Oct. 2020, medlineplus.gov/viralinfections.html.

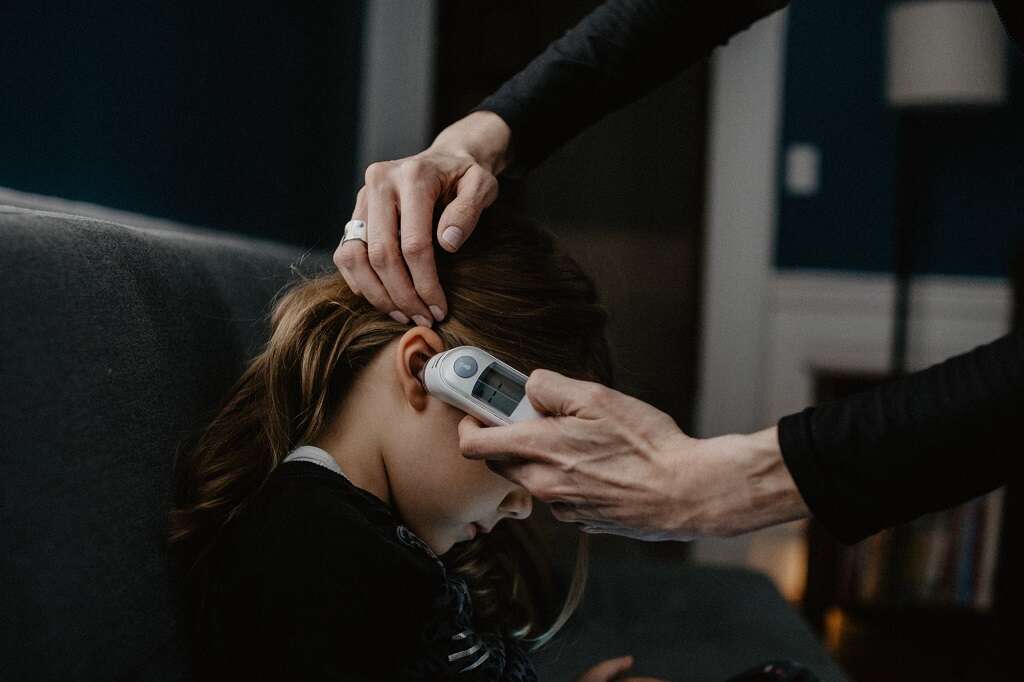
1. High Temperature
One of the hallmarks of infection is a fever. A common symptom of the flu, a fever may be managed with extra fluids and over-the-counter medicines, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
Not every infection causes a fever, but the presence of fever and its grade are good indicators of the severity of the infection. Viral infections tend to cause lower fevers than bacterial infections. If a fever rises as the illness progresses, it may indicate the infection is bacterial in nature or a secondary infection is present, and antibiotics may be needed.5‘Is It a Bacterial Infection or Virus?’ Duke Health, www.dukehealth.org/blog/it-bacterial-infection-or-virus.

2. Sore Throat
A sore throat can be a particularly unpleasant symptom of viral infections. The common cold, flu and upper respiratory infections can all present with a painful, scratchy throat that makes swallowing difficult.5‘Is It a Bacterial Infection or Virus?’ Duke Health, www.dukehealth.org/blog/it-bacterial-infection-or-virus.
Drinking lots of fluids or eating may be painful when a person has a sore throat, but dehydration should be avoided because it may delay recovery from a cold or flu. It’s wise to seek medical advice if the swollen glands in the neck accompany the sore throat.3NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.
3. Cough
A dry cough is a common symptom of the common cold and influenza. In some cases, a cough may be the only noticeable symptom of an infection. When dealing with a cough, practicing good hygiene is important. Frequent handwashing and covering the mouth when coughing can help keep others healthy.1‘Viral vs Bacterial – What’s the Difference?’ HSC Public Health Agency, www.publichealth.hscni.net/news/viral-vs-bacterial-–-what’s-difference.
While coughing can leave someone a bit winded, breathing should not be difficult. A person should seek medical help if breathing difficulties develop.3NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.
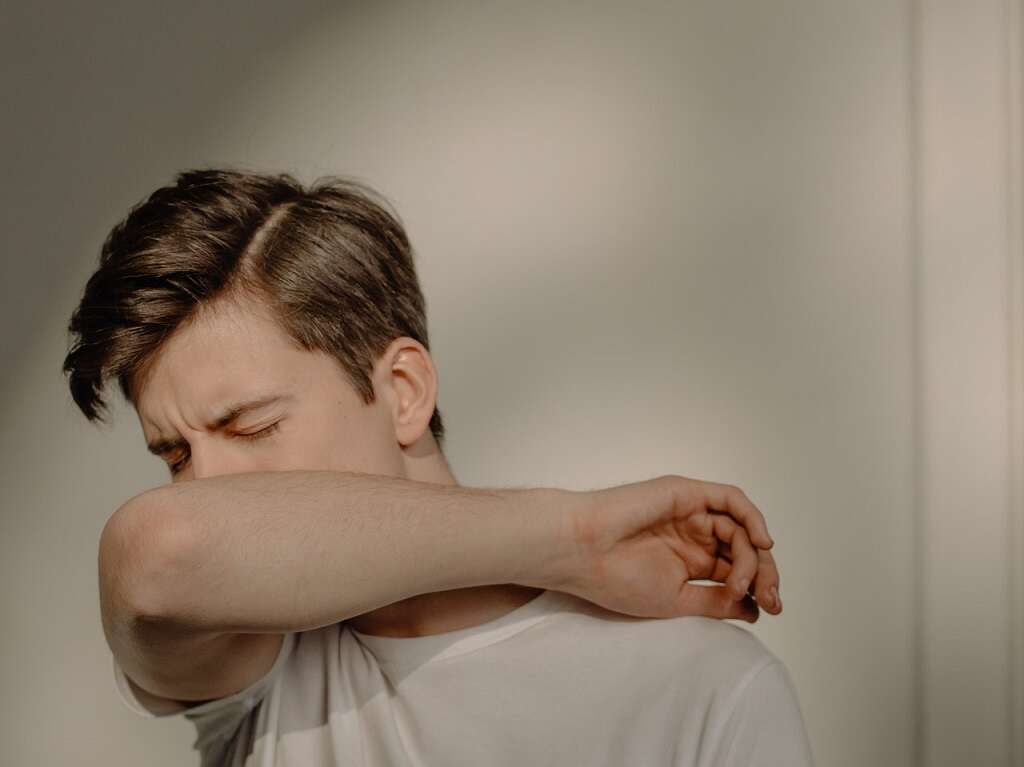

4. Sneezing
Sneezing is another symptom that helps viruses spread. If a person is sneezing, they should limit contact with other people, cover their mouth, use tissues and wash their hands frequently.
A stuffy nose commonly occurs alongside sneezing. Taking over-the-counter decongestants and using a higher pillow at night can help someone with a blocked nose breathe more easily and remain more comfortable. Check with you doctor, because sneezing is also a very common symptom of allergies.

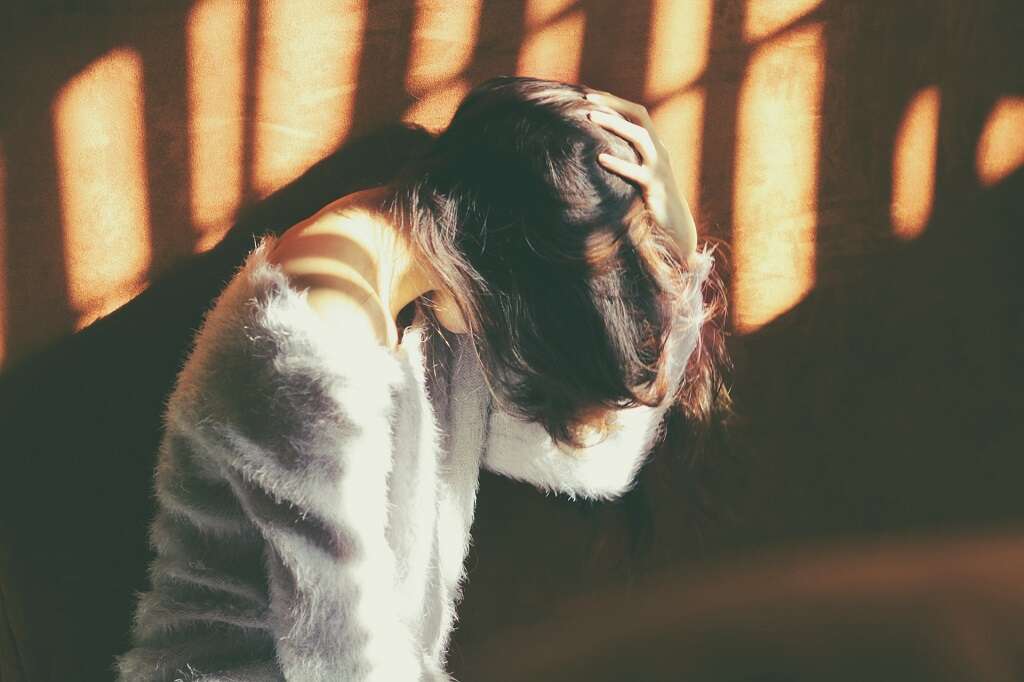
5. Headache
Many types of viral infections come with a headache. Both the common cold and influenza often present with a headache that may require extra hydration and treatment with over-the-counter painkillers.3NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.
Headaches can also be a symptom of more serious viral infections, such as viral meningitis. If a headache is particularly painful and is accompanied by sensitivity to light, speak to a doctor. If symptoms are severe, you may need medical attention right away.4‘Viral Infections.’ Sepsis Alliance, 18 Sept. 2020, www.sepsis.org/sepsisand/viral-infections/.

6. Muscle Aches
Muscle aches are a common symptom of the flu. Aches and pains can affect a person’s joints or muscles, and moving may be difficult and may take more energy. It may take days for the pains to start diminishing and up to two weeks for them to vanish completely.
Muscle pain isn’t a symptom of all viral infections, but acetaminophen and ibuprofen may help to manage aches when they happen. A person should talk to a doctor if the pain is sharp or severe.3NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.

7. Difficulty Sleeping
With all the discomforts that come with viral infections, it may be no surprise that many people with infections have trouble getting to sleep.1‘Viral vs Bacterial – What’s the Difference?’ HSC Public Health Agency, www.publichealth.hscni.net/news/viral-vs-bacterial-–-what’s-difference. Proper rest is an important part of recovery, so it helps to stay in bed even if sleeping is difficult.
A humidifier or a medication, such as a cough syrup, may help ease symptoms enough to permit the patient to get a good night’s rest.3NHS Choices, NHS, hereforyouhampshire.nhs.uk/ColdOrFlu.html.

8. Nausea and Vomiting
Some types of viral infections affect the stomach, causing the development of nausea and vomiting. Since vomiting can lead to dehydration, drinking plenty of clear fluid is critical.
Nausea is a concern when it accompanies a headache, rash and fever. This combination of symptoms may be an indication of viral meningitis. This is a complication of many different types of viral infections where the lining of the brain and spinal cord are inflamed.6‘Viral Meningitis.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 6 Aug. 2019, www.cdc.gov/meningitis/viral.html.

9. Stiff Neck
While a stiff neck usually isn’t related to a serious condition, it’s a key symptom of viral meningitis. It can be easy to mistake a stiff neck for muscle aches and to chalk up the fever and headache to the flu. But if it’s difficult for someone to move their neck, that’s a cue to contact a doctor.4‘Viral Infections.’ Sepsis Alliance, 18 Sept. 2020, www.sepsis.org/sepsisand/viral-infections/.
Viral meningitis tends to be less severe than bacterial meningitis, but it can still be dangerous, especially for babies and people with weak immune systems.6‘Viral Meningitis.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 6 Aug. 2019, www.cdc.gov/meningitis/viral.html.

10. Confusion
Most common viral infections go away with rest and time. But even normally minor illnesses, such as the common cold, pose risks. One concern, regardless of age or health, is a secondary or more severe infection. Complications, such as sepsis, meningitis or secondary bacterial infection, can be deadly.
If a person suddenly becomes confused and difficult to rouse, a more serious infection may be present. If a person exhibits sudden mental decline while ill, they need medical attention right away.4‘Viral Infections.’ Sepsis Alliance, 18 Sept. 2020, www.sepsis.org/sepsisand/viral-infections/.