What Is Calciphylaxis?
Calciphylaxis is the result of the hardening of blood vessels which leads to skin lesions or ulcers. The actual cause is not completely understood; however, it has been linked to the presence of certain diseases combined with high levels of calcium, phosphate, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D.
This condition is closely associated with kidney disease. It is a very serious condition with no known cure, and the symptoms are life-threatening to anybody with the condition. Fatality rates are high, and treatment tends to focus around making the patient feel as comfortable as possible while also slowing the disease.
1. Calciphylaxis
Calciphylaxis is a rare condition, which is a good thing considering it is also very serious. It is often associated with serious kidney problems but it is also found in some people with healthy kidneys. It is thought to happen in most cases because the patient’s kidneys are unable to keep the blood pure enough.
The condition means that calcium has hardened the blood vessels, skin, and fat in a process known as calcification. It can lead to some very serious symptoms indeed, and the condition will be fatal in many cases. There is as yet no treatment for the underlying cause, and the patient is usually treated for their symptoms.

2. Causes
The reason for the buildup of calcium is not entirely clear. One suspected cause is that there may be an imbalance in how the patient is metabolizing minerals. This could lead to an increase in calcium levels in the blood, and this can lead to the build up of the mineral in the blood vessels.
It is suspected that kidney disease is the reason behind the metabolism of calcium, and the condition certainly is more prevalent in patients with kidney problems. More research needs to be done into the condition to understand what the problem is and, hopefully, how to treat it.

3. Abnormal Mineral Levels
One symptom of calciphylaxis, in addition to being a potential cause, is higher than usual mineral levels in the patient’s blood. This includes higher than usual levels of phosphate in addition to higher than usual levels of calcium. Levels of vitamin D may also be abnormal in some patients.
Excess vitamin D can cause problems because it can cause the patient to absorb more calcium and phosphorous than is normal. Some patients with calciphylaxis will also have hyperparathyroidism. This will affect the parathyroid glands, which release hormones that help with the regulation of calcium, phosphorous, and vitamin D in the body.

4. Blood Clotting
It is essential that the blood is able to pass freely through the body at all times. If the flow was to be impeded, then valuable supplies might be prevented from being taken to where they are needed. One of the key symptoms in patients with calciphylaxis is that the blood can begin to clot.
The blood clots can cause the death of cells in the body, while the death of cells in the body can also contribute to blood clots. Severe clots can even lead to potentially deadly scenarios such as strokes and heart attacks. Blood clots should always be taken seriously regardless of the suspected cause.
5. Fatigue
The toll on the patient’s body caused by calciphylaxis can be quite exhausting for the patient. The patient can feel weak and tired all of the time no matter how much rest they may get. They can also be experiencing cramps and body aches all over their body.
The condition can also take its toll on the patient psychologically, and many will develop depression. Depression is another condition that should be taken very seriously and the patient should get all the support that they need. This often means medication, whereas counselling is also often very important in helping patients with depression.

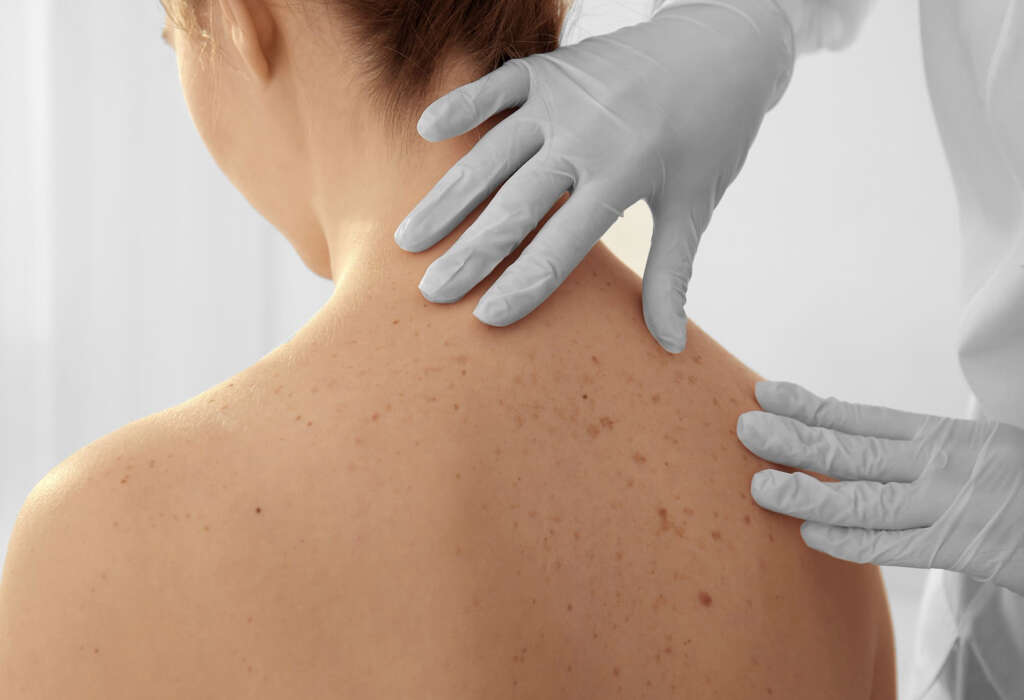
6. Skin Lesions
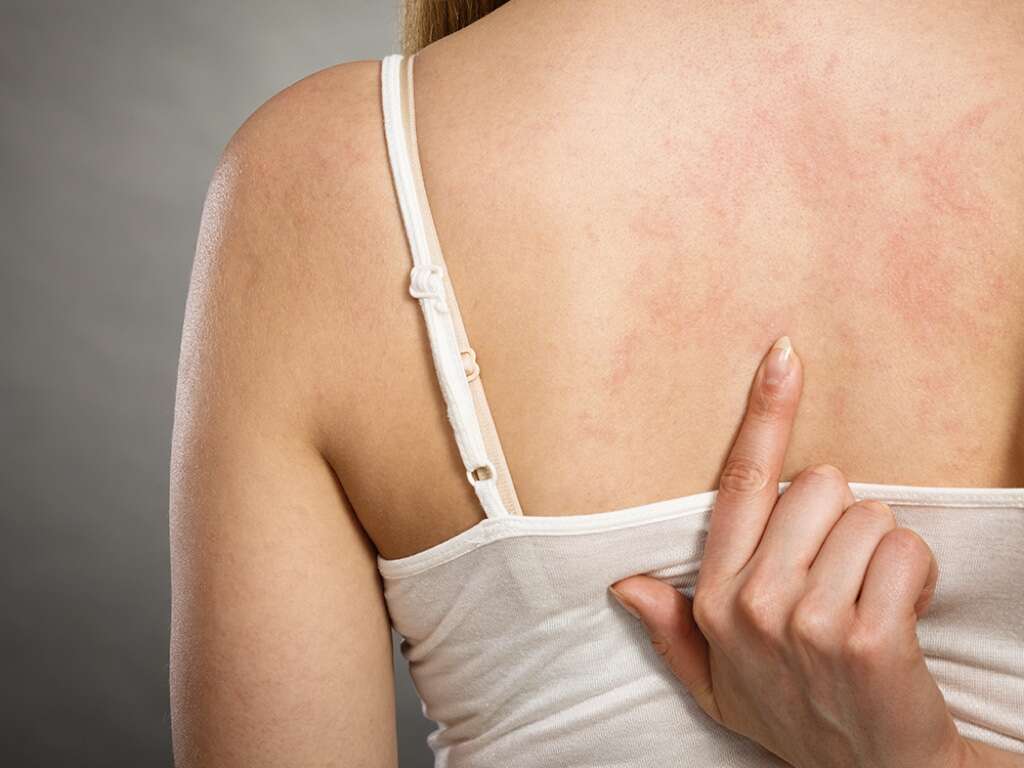
The main symptom of calciphylaxis, and perhaps the most distressing, is severe skin lesions. The lesions will usually start on the lower parts of the body. Fatty areas such as the buttocks, abdomen, and breasts are also among the first affected. The lesions will take a long time to heal, if they heal at all.
These lesions can become painful ulcers. What makes them a real problem is that the open wounds are prone to infection, and the infections can be severe. Indeed, fatalities from calciphylaxis are often down to severe infections. In many cases, there is a constant battle to try and keep the patient as free from infection as possible.
7. Kidney Disease
As already mentioned, people that have kidney disease are particularly prone to developing calciphylaxis. People that are in dialysis are in the highest threat bracket of them all. People with kidney disease are also more likely to develop calciphylaxis if they also have certain other medical conditions.
One of these conditions is obesity, and diabetics with kidney disease are also at a higher risk of developing the condition. Certain medications and supplements can also increase the risk factor. These include supplements that contain phosphate binders. Warfarin and systemic corticosteroids can also make a kidney patient more likely to develop calciphylaxis.
8. Non-Kidney Risk Factors
While there does appear to be a strong link between calciphylaxis and kidney disease, it is not always the case. Some people with healthy kidneys will also develop calciphylaxis, and there are some other medical conditions associated with calciphylaxis. People with some autoimmune such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and Chron’s disease are at a higher risk, as a people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBS).
Protein S and Protein C deficiencies can also increase the risk, as can primary hyperparathyroidism. People with cancer are also more likely to develop the condition than other people are. While these conditions may increase somebody’s chances of developing calciphylaxis, the odds still remain low.
9. Diagnosis
The first thing that might raise suspicions of calciphylaxis is skin lesions. This alone is not enough to reach a conclusive diagnosis, however, and further tests will need to be done. This will include blood tests to check certain elements in the blood.
A skin biopsy will also often need to be taken to help determine what the cause of the lesions are. Tests may also be performed to determine the functionality of the kidneys and of the liver. Tests may also be performed to help get a better understanding of any infections the patient might have.
10. Treatment
As things stand, there is no known cure for calciphylaxis. This means that instead of focusing on the underlying cause, medical professionals will instead need to focus on treating the patient’s symptoms. This includes medications that help prevent the blood clots that calciphylaxis can cause. Medication to restore normal levels of calcium and phosphorous are also used.
Perhaps the hardest task of all is to try and keep the patient’s wounds free from infection. This is done with the help of anti-biotics to try and keep bacteria populations under control. Dressings will also be necessary to help prevent and fight infections.