What Is Calcinosis Cutis?
Calcium is very important for us. It is important for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. In addition, it is also an electrolyte, which means it helps electrical signals to be passed around the body. It helps to keep our heart pumping, also helps to maintain the right balances of fluid in our cells.
Despite all the good it does for us, calcium can sometimes cause problems, one of which is calcinosis cutis. It is a condition that is caused when calcium salts begin to accumulate to form small, hard lumps. It ranges from being mildly irritating to the patient, to downright dangerous.
1. Calcinosis Cutis
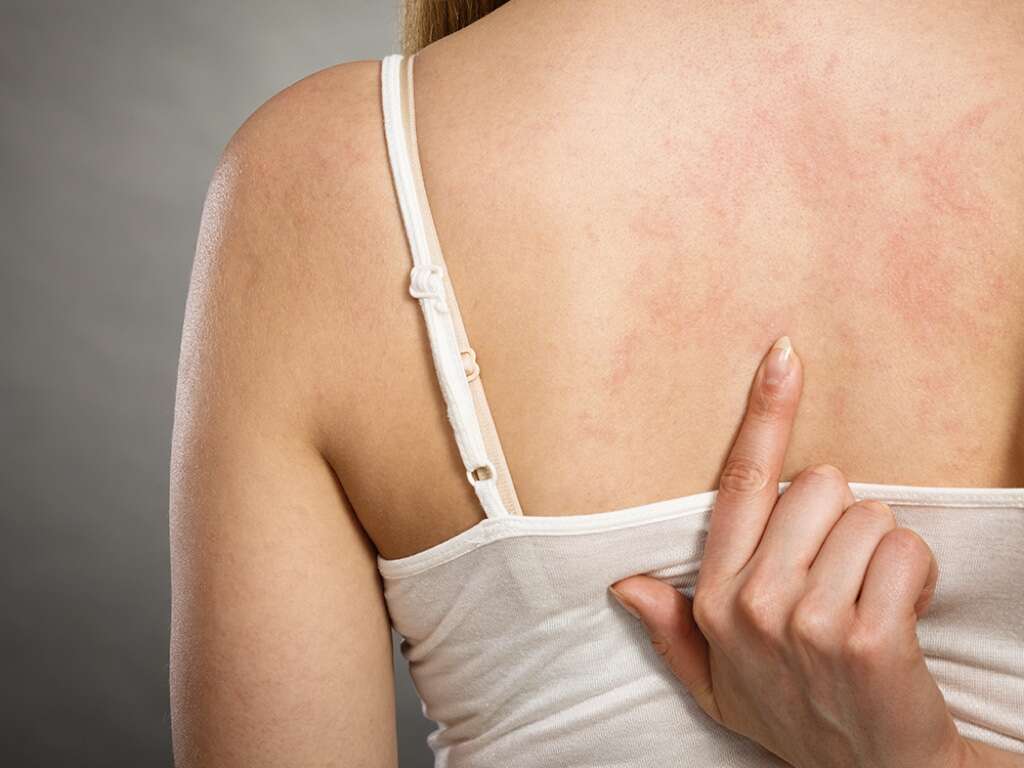
Calcinosis cutis means that calcium salt present in the body has started to crystalize. It is a rare condition and it can be caused by a wide range of things. Patients with the condition will tend to discover hard lumps just beneath the surface of the skin. They are often very small in size but can be larger in some cases.
Many people with the condition will be fortunate enough to have no symptoms. For many others, however it can be very painful to the point where it makes their day to day lives a lot harder. Treatment is available and the treatment will depend on the patient’s circumstances and the exact nature of the condition.

2. Dystrophic Calcification
Dystrophic calcification is the most common variety of the disease. It tends to happen in patients that have recently experienced inflammation or damage in the skin in some way. The types of damage responsible will tend to be caused by conditions such as connective tissue disease, infections, and tumors.
In some cases, dystrophic calcification can even be caused by severe acne. It happens because when tissue cells die, a small amount of phosphate proteins are released. These proteins can then begin to calcify, and this can lead to the formation of the lumps. The lumps will appear in the area where the tissue damage took place.
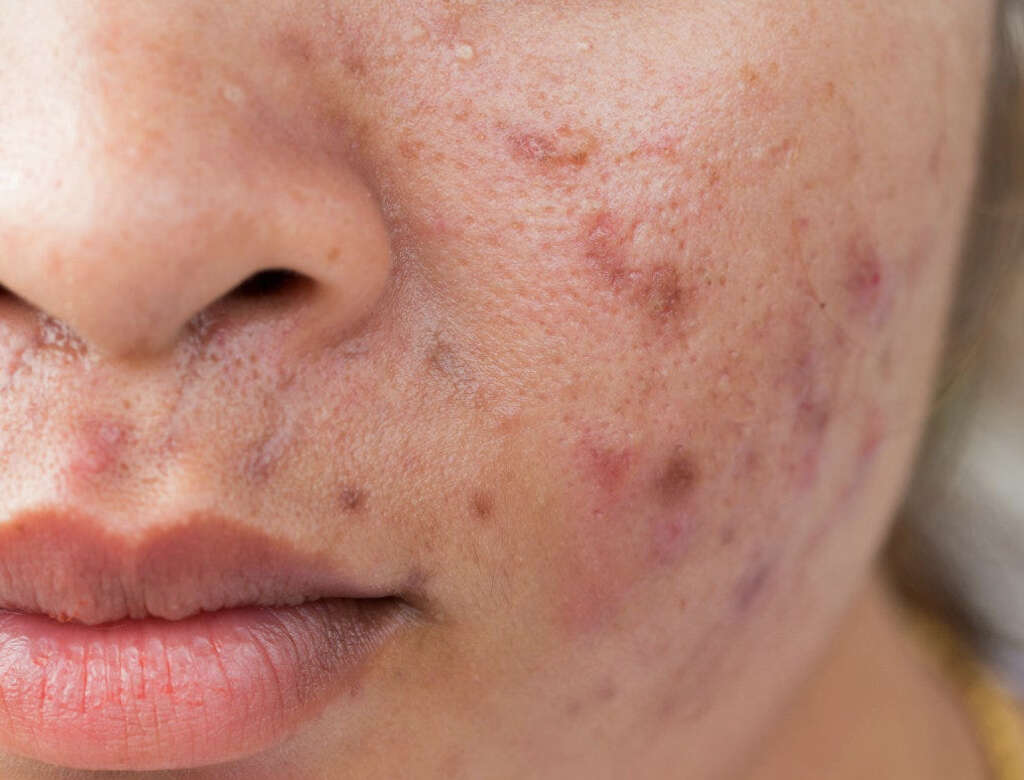
3. Idiopathic Calcification
The word idiopathic refers to a condition that showed up all of a sudden and/or which has no apparent cause. With that in mind, the cause of idiopathic calcification is not known. There will also be no abnormal levels of phosphorous or calcium in the patient. There are 3 different sub types, and they will usually be localized.
Some patients will find modules appearing on their scrotum. Others will have nodules appearing just below the surface of the skin. The latter type is known as subepidermal nodules. There are also familial nodules, and these will usually be found in young children and adolescents.
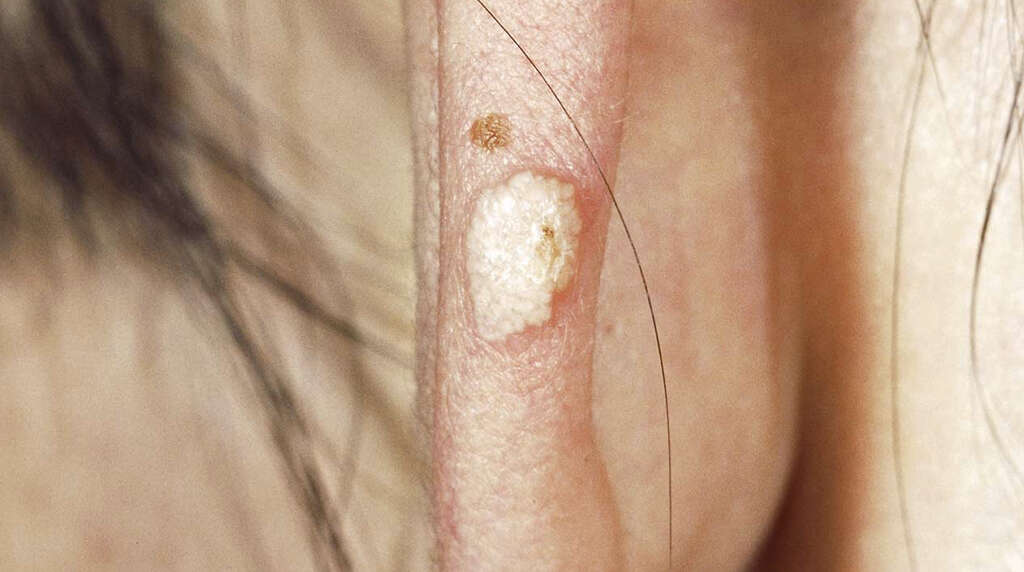
4. Metastatic Calcification
Metastatic calcification occurs when phosphate levels in the body are higher than they should be. This causes calcium salts to be produced, and these cause nodules to begin to form on the patient’s skin. There are several potential causes behind the high levels of phosphate and calcium.
One of which is having too much vitamin D in the body, a vitamin that helps the body to absorb phosphate and calcium from food. Other causes include having too much calcium in your diet, some bone diseases, and sarcoidosis. The most common cause of metastatic calcification is chronic kidney failure, which can mean certain elements are not filtered out from the blood.

5. Iatrogenic Calcification
The exact reason why iatrogenic calcification occurs is not well understood. It is, however, known that the condition occurs after the patient has undergone certain medical procedures or therapy. Some of these procedures will lead to calcium salt deposits developing as an unintended, and unwelcome, side effect.
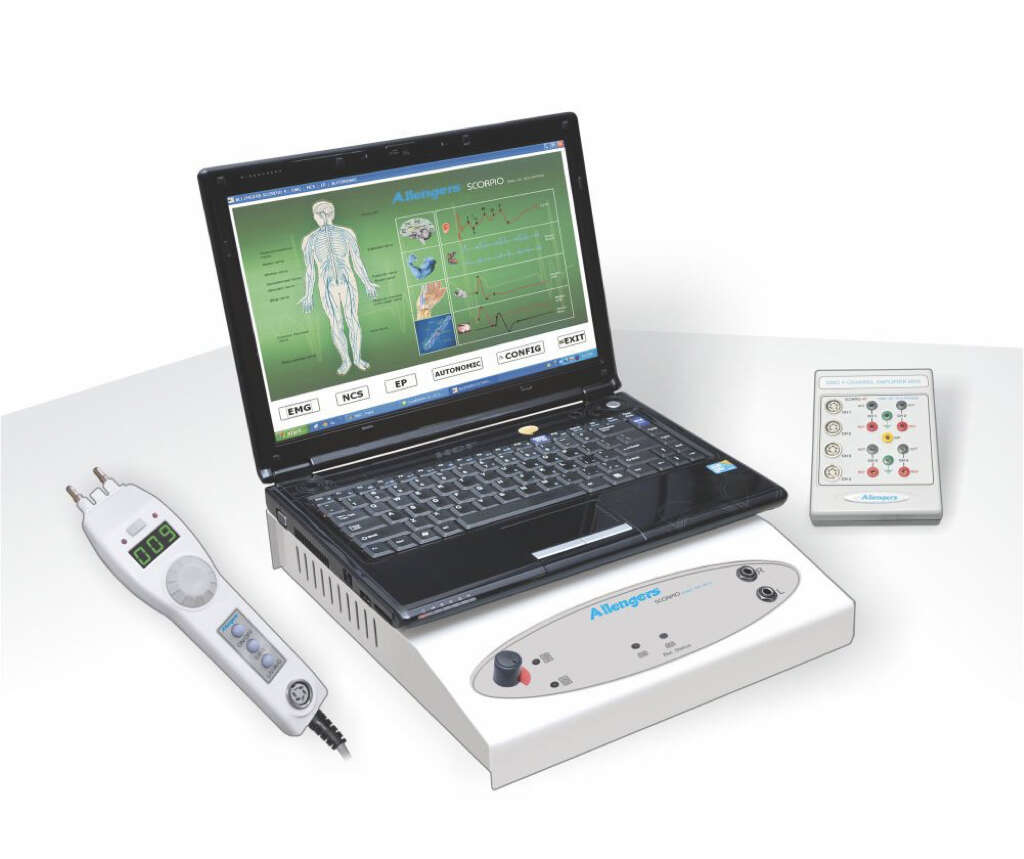
Some patients will develop the lumps after an electromyograph or electroencephalograph. This is down to the saturated calcium chloride electrode paste used in the procedure. Some treatments for tuberculosis can also result in the condition. Perhaps the most common cause of all is heel sticks, which are used to take blood from newborn babies.

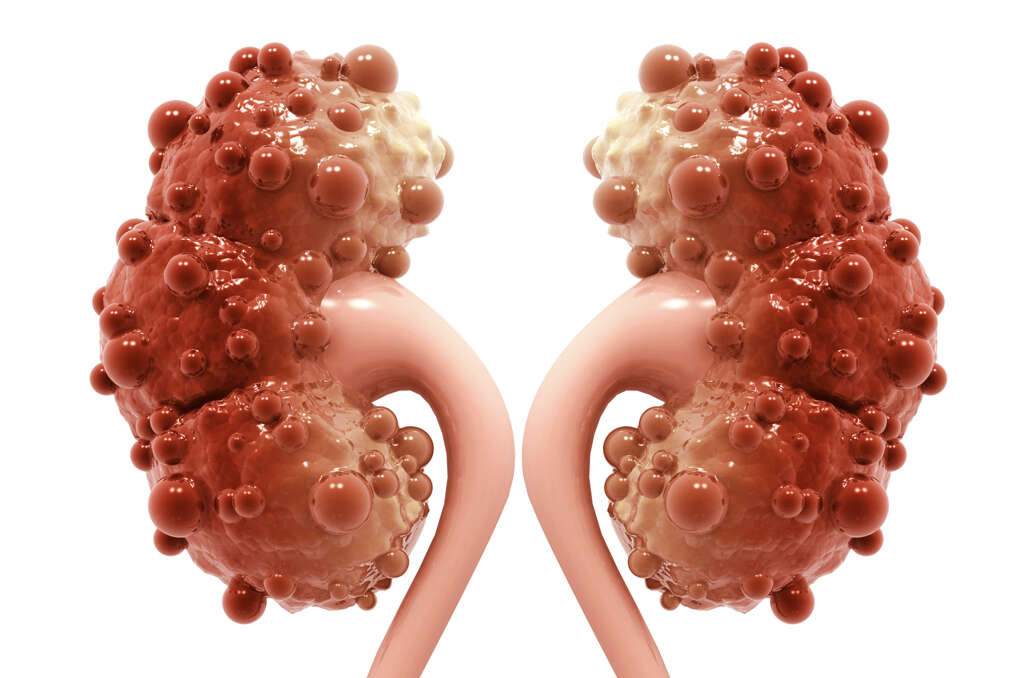
6. Calciphylaxis
Calciphylaxis is a very serious condition. It is, thankfully, also very rare. The condition is not completely understood but we do know it tends to affect people that have an issue with their kidneys in one way or another. The patient will have abnormal levels of phosphate and calcium, and the condition affects the patient’s blood vessels.
The condition is potentially serious because it can cause skin ulcers that can lead to life-threatening infections. It can also cause blood clots which can also be life-threatening. In addition to kidney condition, calciphylaxis is also associated with diabetes, obesity, scleroderma, and hyperparathyroidism.
7. Symptoms
The symptoms of calcinosis cutis will depend largely on which type the patient is suffering from. Perhaps the most typical of the symptoms is the formation of hard lumps beneath the skin. These will often show through the skin and will be yellow/white in color.
The lumps will tend to appear in different places according to the specific type of calcinosis cutis. Depending on their location, they may be painless, or they may be agonizing. As mentioned, calciphylaxis can cause ulcers on the surface of the skin that can be very dangerous for the patient. Calciphylaxis an also result in blood clots.

8. Complications
As mentioned, calcinosis cutis can be very painful for some people and make life difficult for them. For example, it will sometimes form in their fingertips and this can make it painful for them to hold on to objects. They can sometimes appear around the joints and this can also be very painful in some situations.
While the other types of calcinosis cutis tend not to be dangerous, calciphylaxis can be very dangerous indeed. The blood clots that the condition can cause can lead to life-threatening events like a heart attack or stroke. The ulcers the condition causes can also lead to some very severe infections.
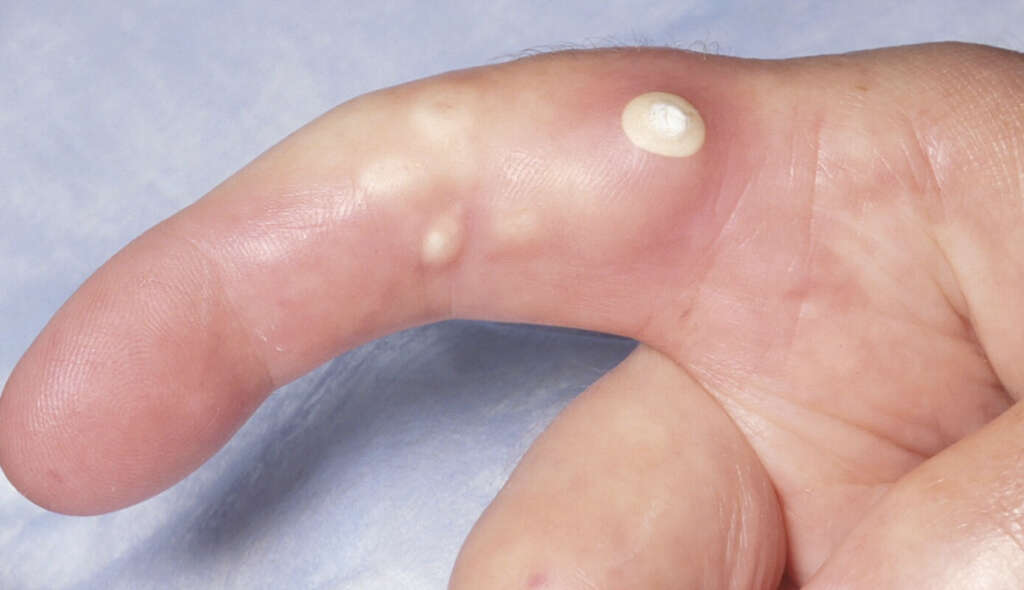
9. Diagnosis
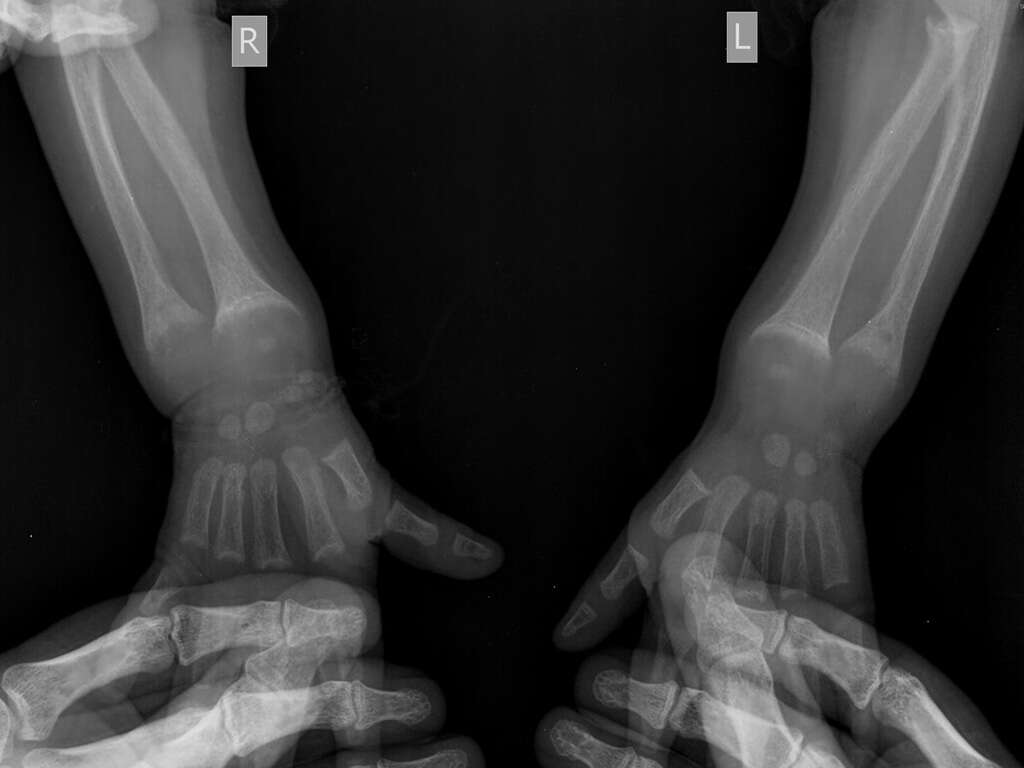
When calcinosis cutis is suspected, it is important to determine exactly which type it is. This is so the appropriate treatment can be administered. In addition to an examination by a doctor, laboratory tests will also be necessary. These include, but are not limited to, blood tests, bone scans, CT scans, X-rays, and biopsies.
The latest method is to use Raman spectroscopic analysis, or Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), which are both types of vibrational spectroscopy. This method helps to tell is the exact chemical composition of the lumps, while it can also help to predict the progression of the condition.
10. Treatment
Treatment of calcinosis cutis tends to involve treating the patient’s symptoms and addressing the underlying cause where possible. The methods of treatment will vary according to what the underlying cause is. Some drugs have been used, with mixed success, and these include tablet form and intravenous medication.
In some cases, it may be recommended that the lumps are removed surgically. This tends to be the case if they are making it difficult for the patient to go about their day to day lives. They might also become infected frequently which might also make surgery necessary. The lumps will sometimes return some time after surgery.