What Is Borderline Personality Disorder?
As an animal that lives in very large communities, we need to be able to socialize well with other people. This means working well with colleagues, having fun with friends, and spending quality time with family. These are things that most of us have little trouble with, but not everybody can say the same.
Borderline personality disorder is a condition where the patient has difficulties dealing with other people. They can hold abnormal feelings towards other people that can make it difficult for them to maintain relationships, and the patient can also hold abnormal feelings toward themselves. It can have a severe impact on the patient’s life, but it can be managed in many cases.

1. Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder is a condition that can have a considerable negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. It is a type of mental health disorder and it affects the way the patient feels about other people, and about themselves. It typically causes the patient to have problems with relationships, among other issues.
The symptoms tend to show in patients when they are young adults. In many cases, the severity of the symptoms will improve as the patient gets older. There is no cure for the condition, but treatment can help to improve the quality of the patient’s life.
2. Relationship Issues
As mentioned, the patient will likely have regular difficulties with relationships. Relationships they do have can be erratic and unstable, with the patient’s feelings towards their partner changing all the time. One moment, they can feel as though their partner is the perfect person for them. The next, they can think the exact opposite.
The patient will also likely have an extreme fear of being abandoned. Such is the extent of their fear that they may take extreme actions to try and prevent themselves from being abandoned. The fear that they are going to be abandoned will often be unfounded.

3. Mood Swings
Borderline personality disorder can cause the patient to experience erratic mood swings. Their moods can go from being extremely happy to extremely down in just a few moments, and for no apparent reason. They can also last from a few hours, to a few days in some cases.
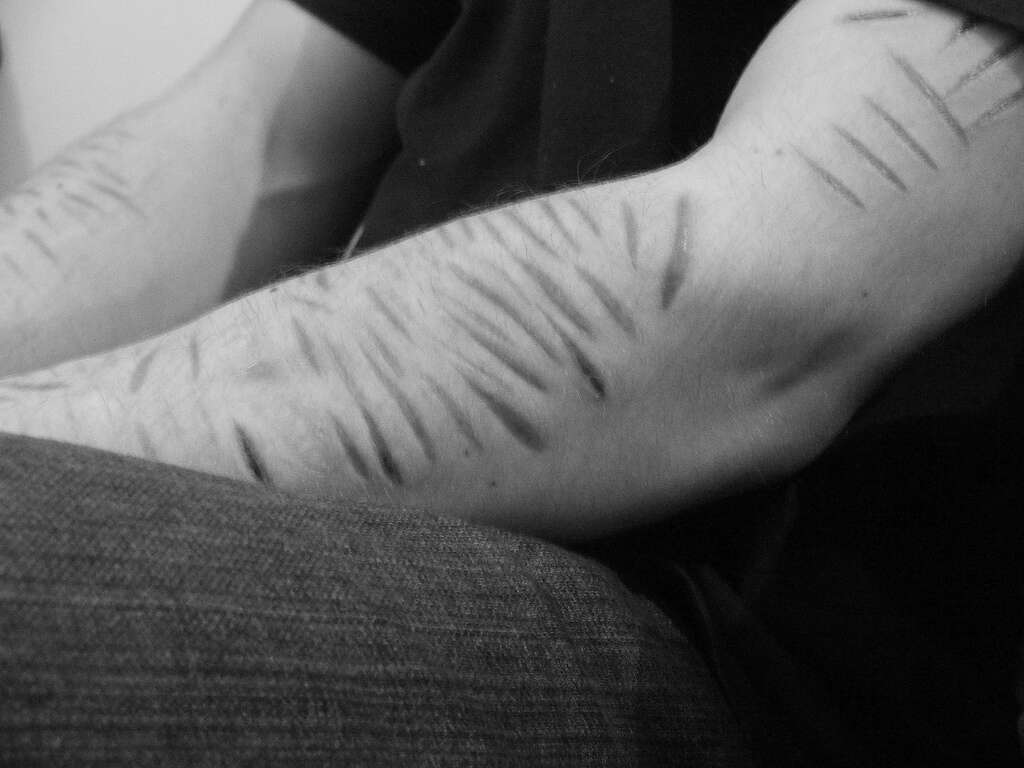
The patient will also sometimes cause harm to themselves, and they may also make threats to take their own lives. This will often be in reaction to a perceived rejection or threat of abandonment. The patient will also often feel empty, and will also lose their temper. They will sometimes become extremely angry and even get into physical altercations for petty reasons.

4. Self-Identity
People with the disorder will experience spells of paranoia, and they can lose touch with reality. How the patient sees themselves can also change very rapidly. The patient can suddenly see themselves as a bad or worthless person. Their values and goals can also change very easily.
Borderline personality disorder can also result in the patient embarking on reckless behavior. This can mean things like suddenly ending a fruitful relationship for no reason, or quitting a promising job. They might also go on spending sprees, gamble, and participate in unprotected sex with multiple partners. They are also more likely to start abusing drugs and alcohol.

5. Complications
The symptoms of borderline personality disorder can also cause a great deal of disruption in the patient’s life. For example, the patient might not finish their education, and they can experience ongoing difficulties in keeping jobs. The patient will also sometimes have problems with the authorities, and some will end up being imprisoned for their behavior.
The patient may also frequently end up in a hospital with injuries, some of which will have been self-inflicted. Relationships can be rocky, and borderline personality disorder makes it more likely the patient will be involved in toxic relationships. Sexually transmitted diseases are also more likely, as are unplanned pregnancies.

6. Associated Mental Health Conditions
Borderline personality disorder is also sometimes associated with other mental health conditions. This is often caused and/or exasperated by abuse of alcohol and other drugs, and abuse of substances can result in a vicious cycle. The patient might also have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is another associated mental health condition.
Patients with borderline personality disorder will also sometimes have eating disorders and/or anxiety disorders. Bipolar disorder is another possibility, and some will also suffer from depression. Mental health conditions like depression can lead to the patient to take their own life so they should be taken very seriously.

7. Who’s At Risk
It is difficult to say exactly who is likely to develop borderline personality disorder. However, the condition is associated with people that have had traumatic experiences in the past. Those can include those who had parents who abused substances when the patient was still young.
People that grew up in unstable households that saw a lot of conflict are also more likely to develop the condition. The condition is also more prevalent in people that suffered physical and/or sexual abuse when they were children. There is also thought to be a genetic link, and those with a history of the condition in their family are also more likely to develop it.

8. Diagnosis
Doctors will not usually attempt to diagnose borderline personality disorder until the patient has reached their adult years. This is because the patient’s symptoms might simply be a case of rowdy behavior that is typical of many young people. In the majority of cases, troublesome children and teenagers will settle down as they grow older.
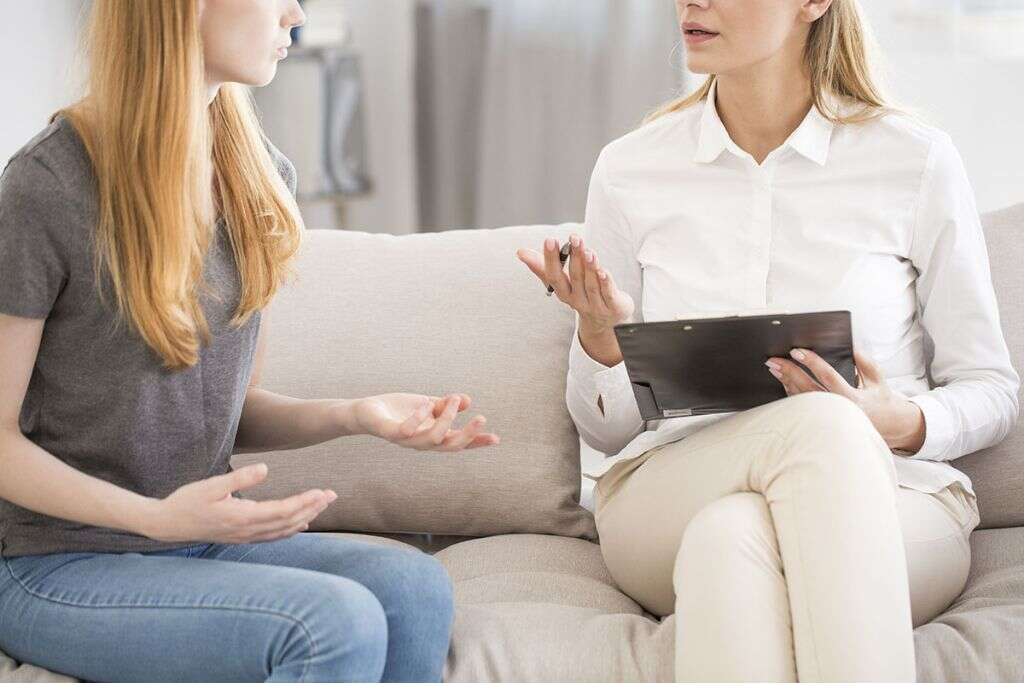
If borderline personality disorder is suspected in an adult, then the patient will be asked to have a counseling session with a mental health expert. The expert will be able to speak with them about their past experiences, their symptoms, and how these things impact their lives. If the patient meets the right criteria, they can then be diagnosed.

9. Medication
There is as yet no medication that can treat borderline personality disorder directly. However, medication is available that will help to ease the severity of the patient’s symptoms. Medication may also be used to help treat any other mental health conditions the patient might have.
The types of medication used typically include antipsychotics and antidepressant. Sedatives will also sometimes be needed in the more severe cases. It may also be necessary to have the patient hospitalized where they will be able to receive more intensive care. This may also be deemed necessary for the safety of the patient, and other people.
10. Psychotherapy
In addition to medication, psychotherapy may also be used to help treat borderline personality disorder. There are numerous types of psychotherapy treatment, some of which will involve helping the patient to identify their emotions better, and how to manage their emotions.
The patient can also learn to manage their compulsions better, and better understand how their actions impact other people. The patient can also learn how to act in relationships and understand how other people might be feeling. Overall, psychotherapy is often very effective in helping the patient manage their condition, and many will even go on to live relatively normal lives.










