What Is Appendicitis?
We have all experienced pain in our abdomen area. These are sometimes down to infections, often bacteria, that can irritate the digestive system and make us feel quite ill. At other times it might be down to having eaten foods that our digestive system struggles to cope with.
Regardless of the cause, stomach pains are quite common and unlikely to have us wishing to see a doctor. While we might be eager to try and brush it off as not serious however, we should certainly take notice in some situations. If the pain you are experiencing is severe, then you should see a doctor as soon as possible, because it could be a dangerous condition like appendicitis.

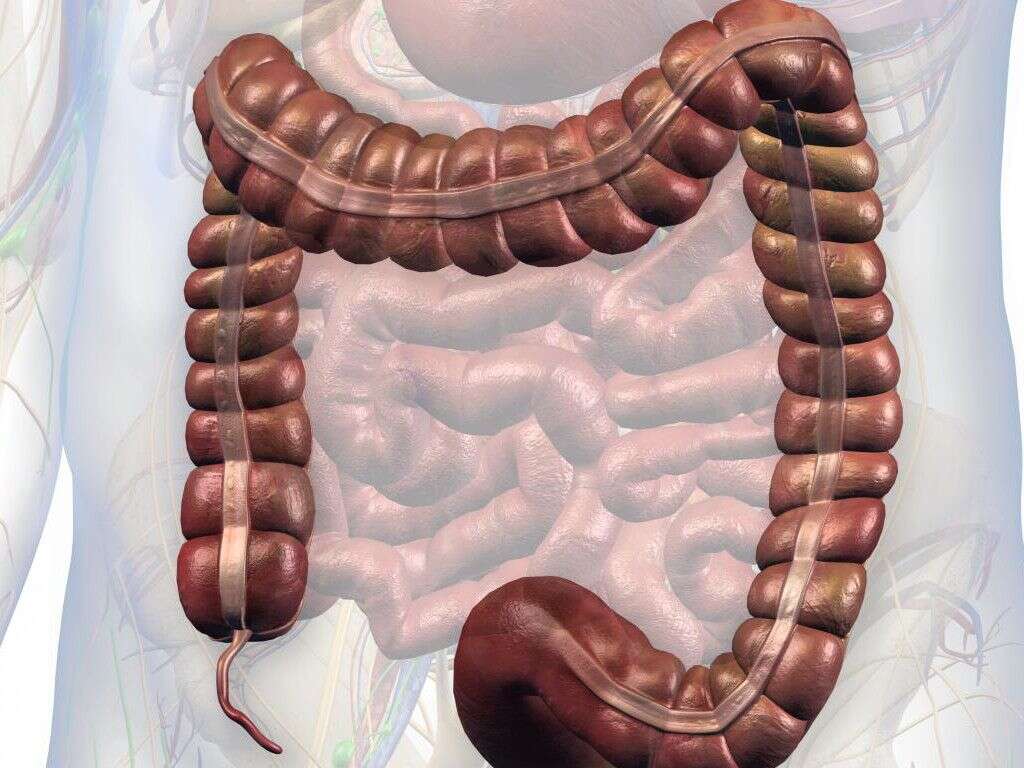
1. Appendix
The appendix is a small organ that is located in the colon. It is not clear exactly what its purpose is, and it is thought to be the remains of a vestigial organ that was once more important for us. We are now able to live quite comfortably without an appendix, and it can be removed should it be deemed necessary.
Although the appendix serves little to no purpose, however, it can still be problematic. It is possible for the organ to become inflamed in a condition known as appendicitis. It can be a very painful condition, and it can also be extremely dangerous.
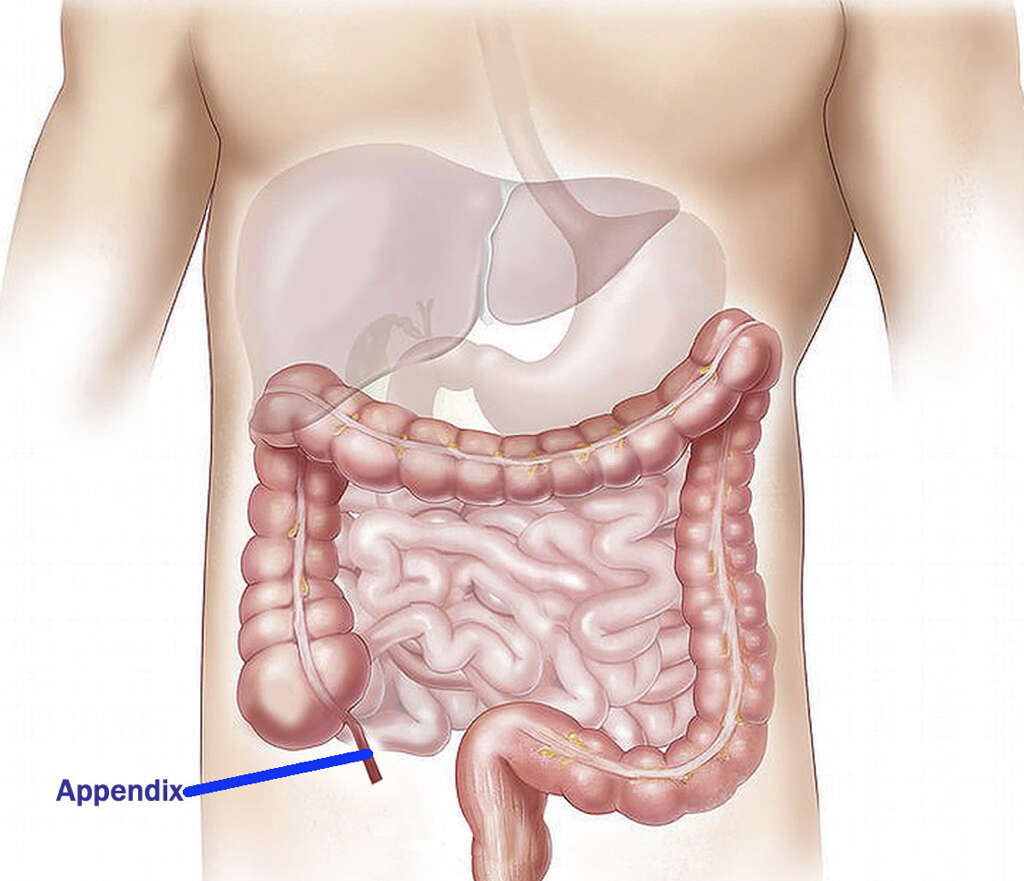
2. Appendicitis
Appendicitis is the medical term for an inflamed appendix. It can affect people of all ages, but it usually happens in people before they reach 30 years old, and after they are 10 years old. It is a condition that can be very painful. It is also potentially very dangerous.
If you do experience severe pain in the area where your appendix is then you should get medical attention. Appendicitis does have the potential to develop into a potentially life-threatening situation. The condition is treatable, however, but it is still important that the patient is found medical assistance as soon as possible.
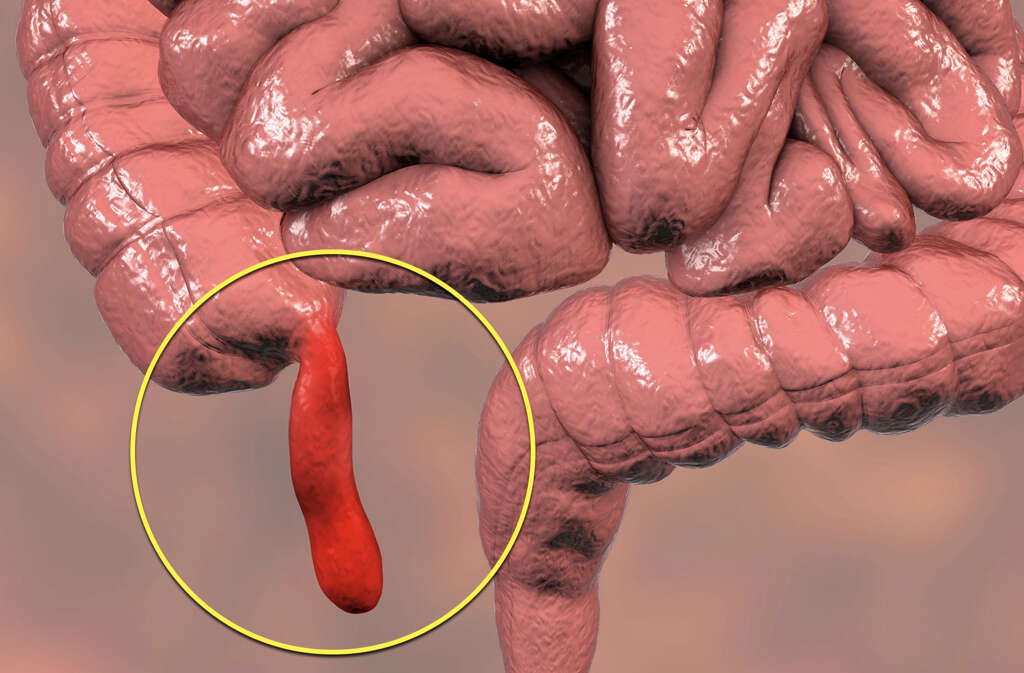
3. Causes
Appendicitis is typically caused by a blockage in the appendix, and this is often caused by fecal matter. The blockages are also sometimes caused by cancer, while infections can also cause swelling that will result in a blockage. When there is a blockage, bacteria can begin to accumulate in the appendix.
As bacteria begin to multiply in the organ, so the organ can become infected, and this can cause the appendix to become inflamed. The organ can also become filled with pus and, if the swelling is severe enough, the appendix can rupture. This is potentially a very serious condition that will pose a very real threat to the patient’s life.
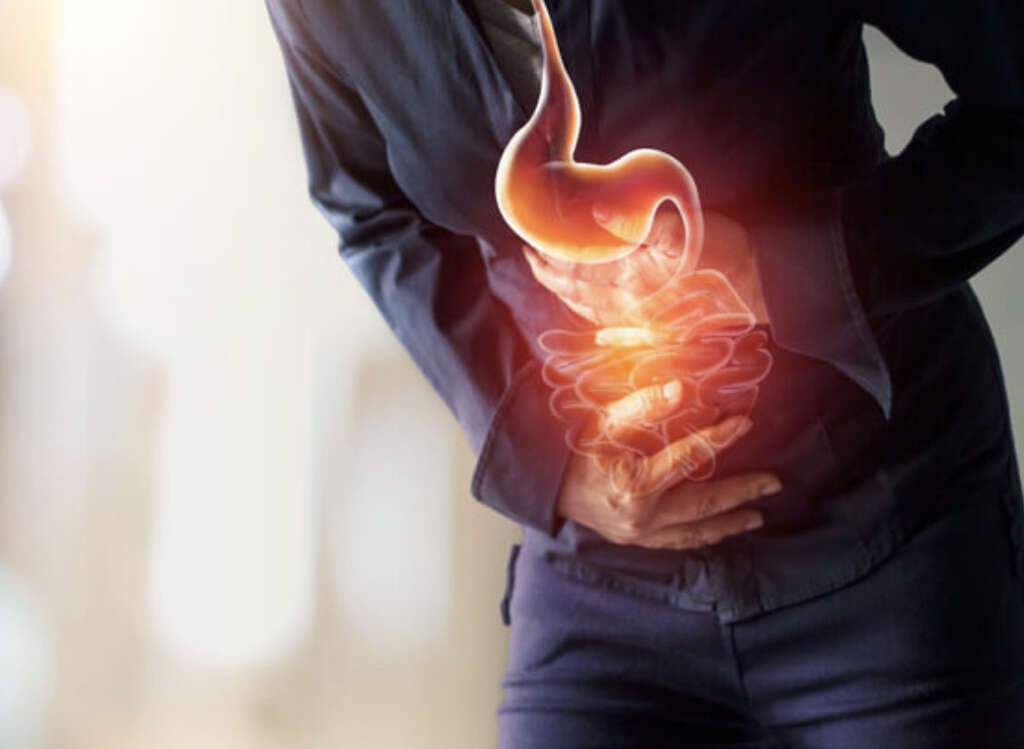

4. Symptoms
Perhaps the most common symptom of appendicitis is the pain it can cause. It will usually come on suddenly, and it will usually start in the navel region. The pain will then tend to move towards the lower right region of the abdomen. The location of the pain can depend on a number of factors,
For example, people that are pregnant will likely experience pain in the upper part of the abdomen. The pain is also likely to become worse if you try to walk, or if you make sudden movements such as moving from coughing. The pain is usually intense enough to let the patient know that they have a problem.

5. Other Symptoms
In addition to pain, appendicitis will also sometimes cause other symptoms that can range in severity. These symptoms will tend to include nausea, and this will also sometimes cause the patient to vomit. A fever is also likely to be present, which can be mild at first, only for it to get gradually worse as the appendicitis develops.
Appendicitis will also cause flatulence in some patients, and many will also experience bloating that can be quite uncomfortable. It is also likely that the patient will experience diarrhea or constipation. A loss of appetite will also be a symptom in many cases.

6. Ruptured Appendix
As mentioned, the appendix can swell to the point that it ruptures. This will cause the contents of the organ to spill out into the body; this includes the pus and toxins that are caused by the infection. This is extremely dangerous in many cases and must be treated as a medical emergency.
A ruptured appendix can cause peritonitis, which is an infection of the interior lining of the abdomen. It can also cause abscesses to form in the abdomen, and there is also a risk of the abscess bursting and releasing toxins into the system. It will be likely be fatal if medical assistance is not found soon enough.
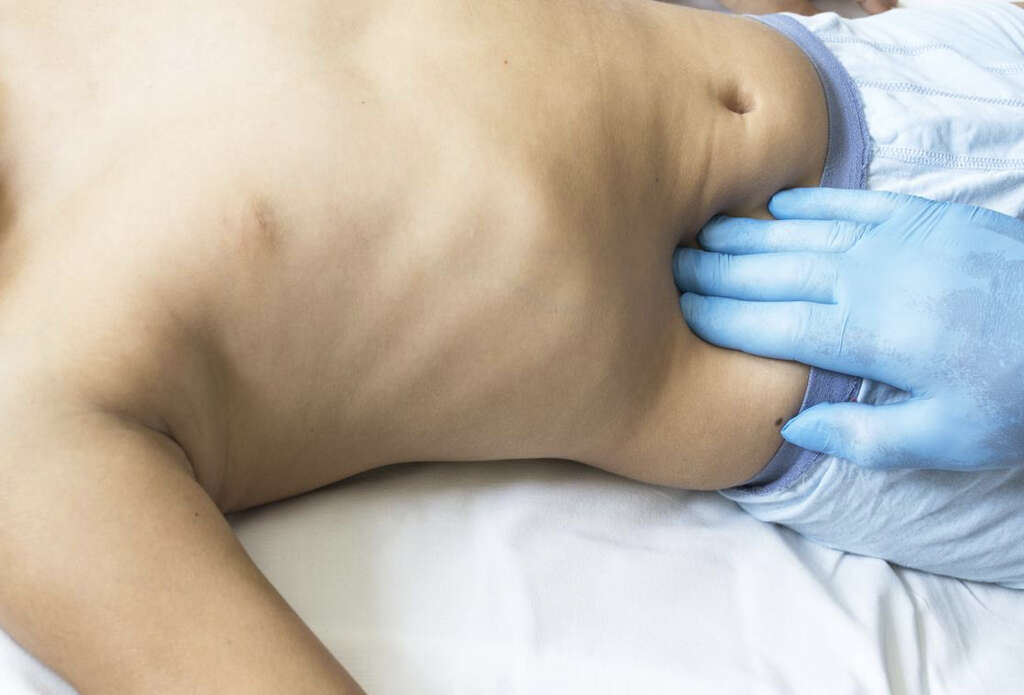
7. Risk Factors
As mentioned, people aged between 10 and 30 years old are more likely to develop appendicitis. People also have a greater chance of getting appendicitis if there is a history of the condition in their family. Males are also more likely to develop the condition than females are.
Also, in a higher risk bracket are people that have diabetes, and those that use steroids. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is another potential contributing factor to the condition. Those with cystic fibrosis, which is a chronic lung disorder, are also at a higher risk of developing appendicitis. This is especially the case in young males.

8. Diagnosis
Your doctor is likely to want to perform a physical exam, and also ask you questions about your symptoms and your medical history. If appendicitis is suspected then further tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, this will include a rectal exam which involves inserting a finger into the rectum.
A urine test may be performed to help eliminate kidney stones and/or a urinary tract infection. A blood sample may also be taken so it can be sent to a laboratory to look for signs of an infection. If the doctor has not yet been able to reach a diagnosis, imaging equipment may be used to help get a visual look at what is happening internally.
9. Surgery
People with appendicitis will usually be given antibiotics to help treat the infection. If an abscess has formed then it will need to be drained. This is usually performed by passing a tube through the skin and into the abscess to drain it. Once the abscess has been drained and the infection is under control, an appendectomy will likely be performed.
An appendectomy is the technical term for having the appendix removed altogether. Depending on the circumstances, this might be performed by open surgery, which involves cutting the patient open to access the organ. Another option is laparoscopic surgery, which involves performing the procedure through small incisions instead.

10. Recovery
Appendicitis is a serious condition, and an appendectomy is a significant procedure. This means that the patient should expect it to be a few weeks before they have fully recovered. During this time, the patient should avoid strenuous activity, especially for the first two weeks or so.
While the patient is operating, a doctor is likely to prescribe medication to help relieve the pain. Certain painkillers, especially opiates, will need to be used with caution, however. If the patient does begin to feel intense pain and/or bleeding during recovery then they should get medical assistance as soon as they can.