What Is an Atheroma?
Our cardiovascular system ensures that all of our bodies are supplied with oxygen and nutrition. It consists of a network of blood vessels that transport blood away from the heart to where it is needed, and then back to the lungs and heart again. It is essential to us, so we need to keep it in good working order.
One of the most important things is to ensure that our blood is able to flow freely through our blood vessels. Over time, however, our blood cells can eventually become blocked, thus limiting the ability of the blood to flow through them. One example of this is atheromas, and they have the potential to be very dangerous.
1. Atheromas
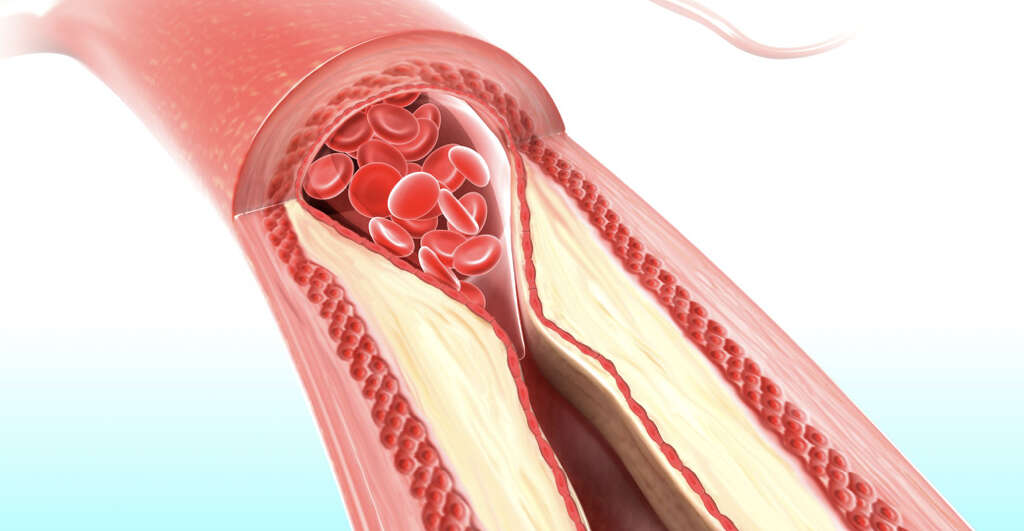
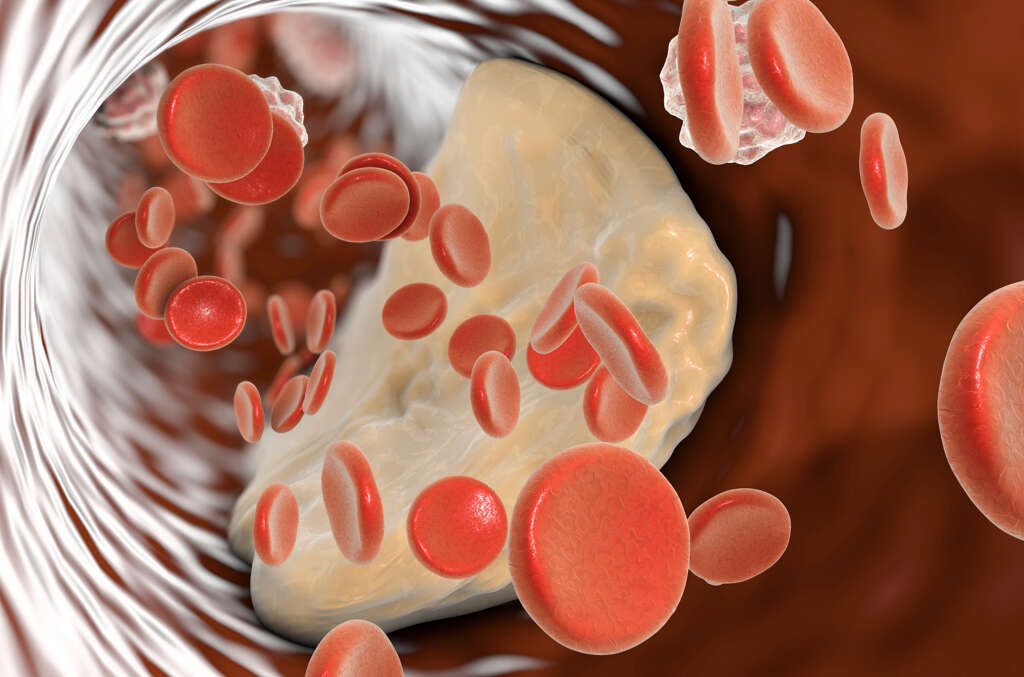
As time goes by, materials can slowly begin to accumulate on the insides of our blood vessels. The kind of materials that can cause this include calcium deposits, inflammatory cells, and fats. The presence of the atheromas in themselves is not a problem and the blood will continue to flow past them as normal.
If atheromas are able to build up significantly enough, however, then they can begin the impede the flow of the blood. This has the potential to cause some life-threatening conditions. While they will often go unnoticed, it is wise to take precautions to help limit their development.
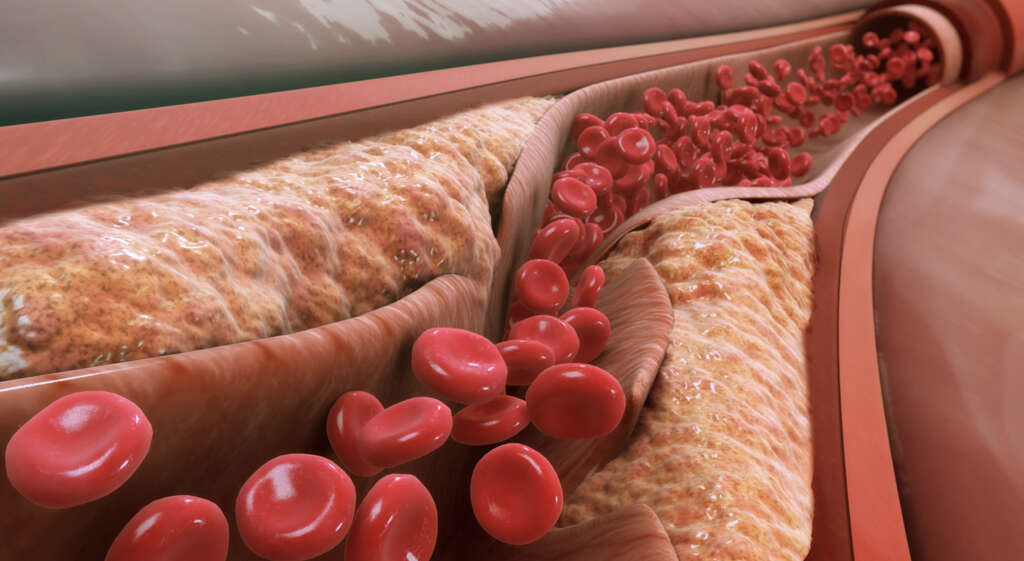
2. Atherosclerosis
As mentioned, atheromas can build up to the point where they begin to obstruct the flow of blood through the blood cells. Atherosclerosis is the name given to the medical condition where the arteries have become significantly narrower due to the presence of atheromas. In addition to being narrower than usual, the artery walls, which are usually flexible, will also become harder.
Atherosclerosis can lead to some potentially very serious conditions of the cardio-vascular system. They can cause a considerable negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. They can also be extremely dangerous and patients will often need to undertake considerable life-style changes.
3. Causes
We know that atheromas are caused by a build up of materials on the artery walls. We are not sure exactly how this happens, however. It is thought that it may have something to do with damage to the endothelium. This is a lining that helps to protect the interior wall of our arteries.
Injury to this lining can be caused by a number of things such as smoking, obesity, diabetes, ageing, and some inflammatory conditions. When this damage occurs, the body then repairs the damage by producing what are known as foam cells. These cells then allow the build up of these different materials thus allowing atheromas to form.

4. Gradual Development
As mentioned, atheromas will develop very gradually over time. This means that the patient can go for many years without experiencing any symptoms whatsoever. While the lack of symptoms for so long might sound like a positive thing, it actually helps to make atheromas more dangerous.
Because there are no symptoms, atheromas can grow to dangerous levels undetected, until it is too late. In some cases, one can be torn away from the artery wall and this can cause the artery to become completely blocked. This is often an immediate medical emergency and it will be fatal in many cases.
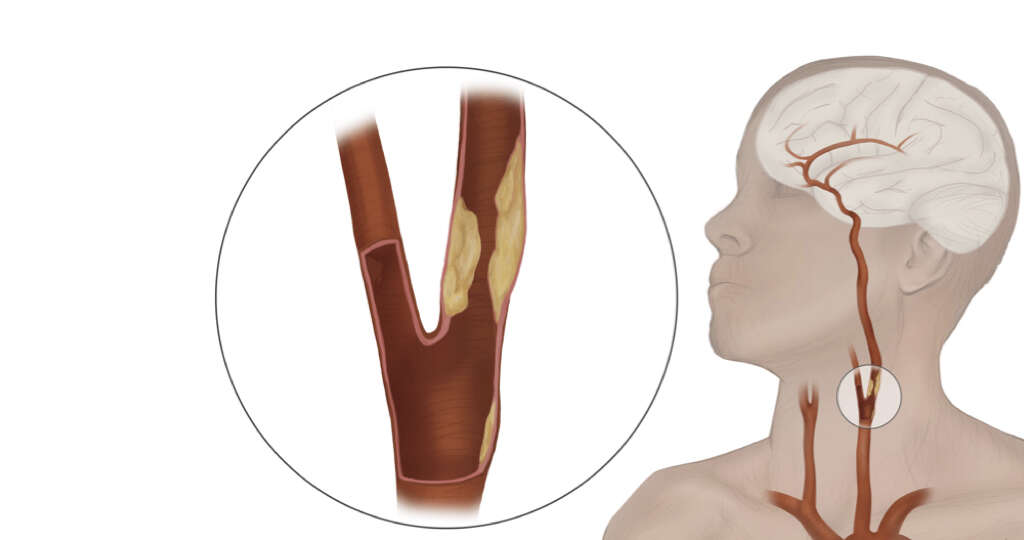
5. Cerebral/Carotid
Atheromas can affect arteries anywhere in the body, and this includes the cerebral/carotid arteries. These are the arteries that supply the head, face, and brain with fresh blood. If these were to be blocked then the brain may not get the nutrients that it needs, and this has the potential to be very serious.
Blocking of these arteries can result in what is known as a transient ischemic attack. This is basically a type of mini stroke. Symptoms of the condition include slurred speech, vision loss, severe headaches, loss of balance, and paralysis on one side of the body. A stroke can be fatal, so the patient should be taken to an emergency room immediately.
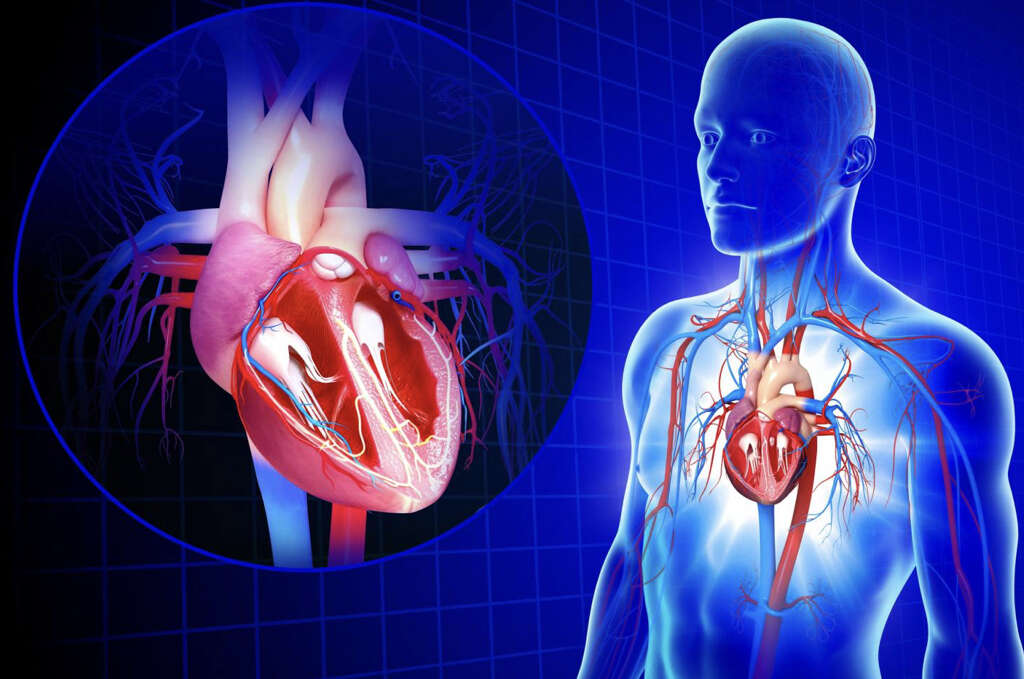
6. Cardiovascular
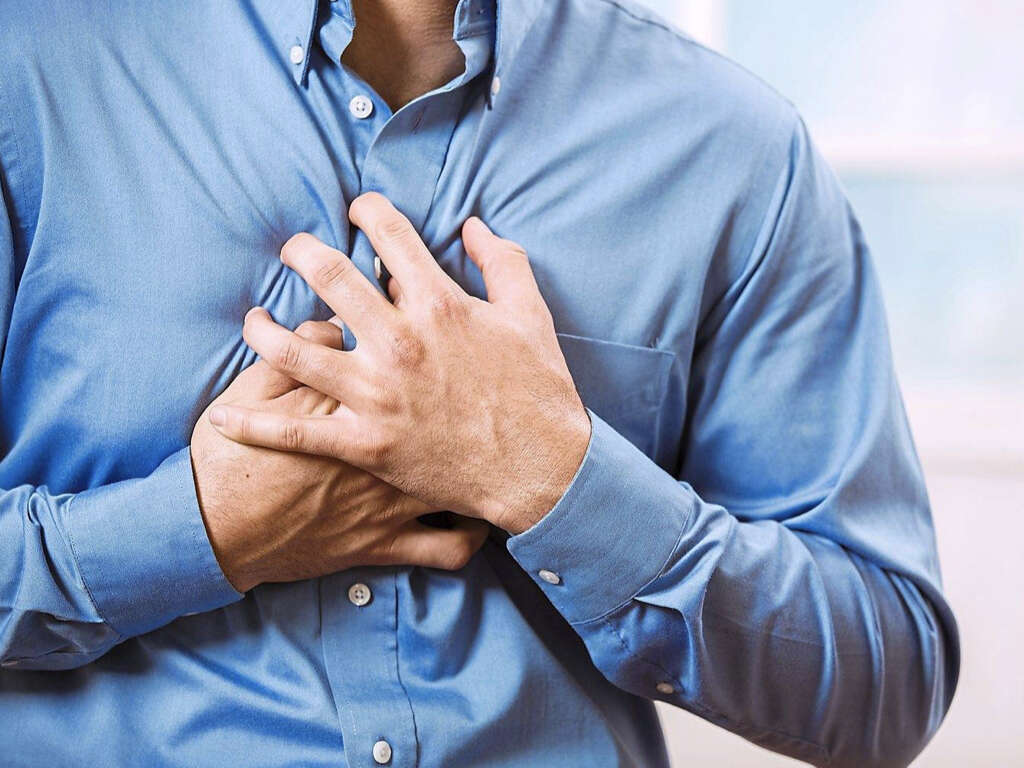
Our hearts need a constant supply of blood just as the rest of the body does. If the supply was to be stopped for some reason then the heart would not be able to function properly. This condition can be very dangerous indeed, and it can be caused by the build up of atheromas.
Atheromas in the arteries supplying the heart can result in heart disease. In some cases, it can even result in a heart attack, which means the heart stops beating altogether. Symptoms of a heart attack include sweating, chest pain, difficulty breathing, jaw and arm pain, and weakness. A suspect heart attack should always be treated as an immediate medical emergency.
7. Peripheral Arteries
Blood needs to be transported throughout the entire body. This includes the parts furthermost from the center of the body such as the hands and feet. There are known as the peripheries, and they are fed by the periphery arteries. Atheromas can develop here, meaning the blood supply to the outer parts of the body is blocked.
This can result in a number of symptoms including cramps. The skin can become bright red and feet can become cold to the touch. Patients will also sometimes experience an aching or burning sensation in their feet. Any sores or wounds located on the feet will also likely heal more slowly than usual.

8. Prevention
It is not possible to keep yourself completely safe from atheromas. However, we are able to live our lives in ways that can help to reduce the likelihood that serious atheromas will develop. This generally means making lifestyle decisions that will help you to live a healthy life overall.
One of the best decisions anybody can make is to abstain from smoking. This is for many other reasons in addition to preventing atheromas. It is also important to eat the right diet, particularly avoiding trans fats and saturated fats. Plenty of fruit and veg is also recommended, as is getting plenty of exercise.

9. Diagnosis
As mentioned, atheromas will often go undetected for a long time, and they will sometimes be found by chance. If you are showing symptoms of conditions like heart disease, for example, then your doctor may request certain tests to find out what the cause of the problem is.
Tests to look for atheromas include an angiography that helps to give medical professionals a visualization of your cardiovascular system. An echocardiogram will also be used, which is similar to an ultrasound. Another method is the ankle-brachial index which can help to look for differences in the blood pressure between the ankle and the arm. Once the correct diagnosis is reached, medical professionals can devise a suitable treatment plan.

10. Medical Treatment
Treating atheromas often means the patient has to make considerable lifestyle changes to help limit the condition’s development. The patient will also be given medication to help them manage the condition. This includes drugs that will help to keep the blood pressure down and to reduce cholesterol.
If the condition presents an immediate risk to the patient’s safety then surgery may be recommended. This includes procedures that can help to keep the artery wide enough to allow blood to pass through. A bypass might also be performed, which means that the flow of blood is diverted to circumvent the blocked artery.