What Is Raynaud's Syndrome?
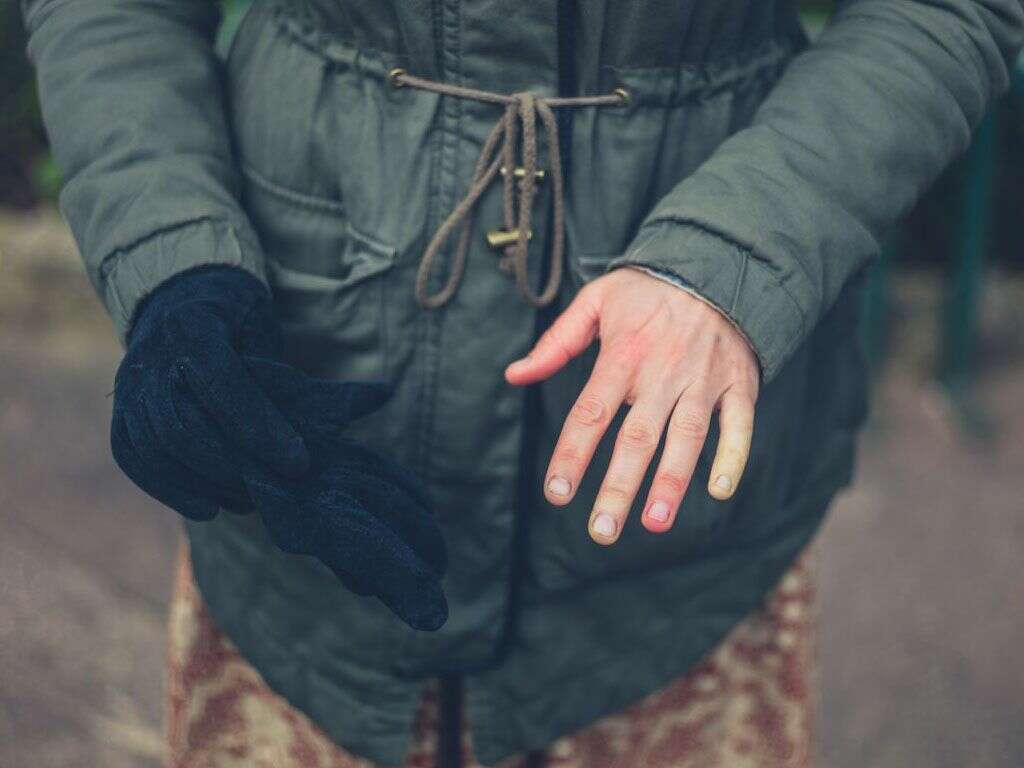
Raynaud’s syndrome is a condition that impacts the flow of blood to specific parts of the body. The most frequently affected areas are the fingers and toes, though it can also happen to the knees, nipples, nose and ears.
Constriction of the smaller vessels in the affected area causes the lack of movement of blood into the area. Vasospasms is the name given to episodes of constricting vessels. These events can be triggered by cold temperatures or stress. There are two types of Raynaud’s: primary and secondary.

1. What Is Primary Raynaud’s?
Primary Raynaud’s is the most common form of the disease. It occurs on its own, rather than as a secondary condition to another medical disease. It is generally a less severe form. Symptoms are mild enough that people frequently do not seek treatment.
This form of the disease tends to appear in people between the ages of 15 and 25 and in otherwise healthy individuals. Even without treatment, people can recover from primary Raynaud’s syndrome, as the condition frequently resolves itself.

2. What Is Secondary Raynaud’s
Secondary Raynaud’s is less common but more severe. This form of the disease occurs along with other medical conditions. The onset for secondary Raynaud’s is typically after the age of 40. It is associated most often with autoimmune and connective tissue disorders.
Some of the common conditions that are linked to the secondary form of the disease include lupus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders and blood disorders. A person who has had frostbite may also develop secondary Raynaud’s in the damaged tissue.

3. What Causes Raynaud’s?
The causes of Raynaud’s are not always known. Blood disorders that lead to a thickening of the blood are potential factors that lead to the disease. The excess platelets or blood cells associated with some blood disorders may be the reason they cause primary Raynaud’s.
The causes of secondary Raynaud’s can be attributed to the physical conditions of the underlying medical diagnosis. These diseases can alter the characteristics of surrounding tissues, blood vessels or nerves, leading to the condition. Smoking is an additional cause, as it results in constriction of the blood vessels.

4. What Are the Symptoms of Raynaud’s?
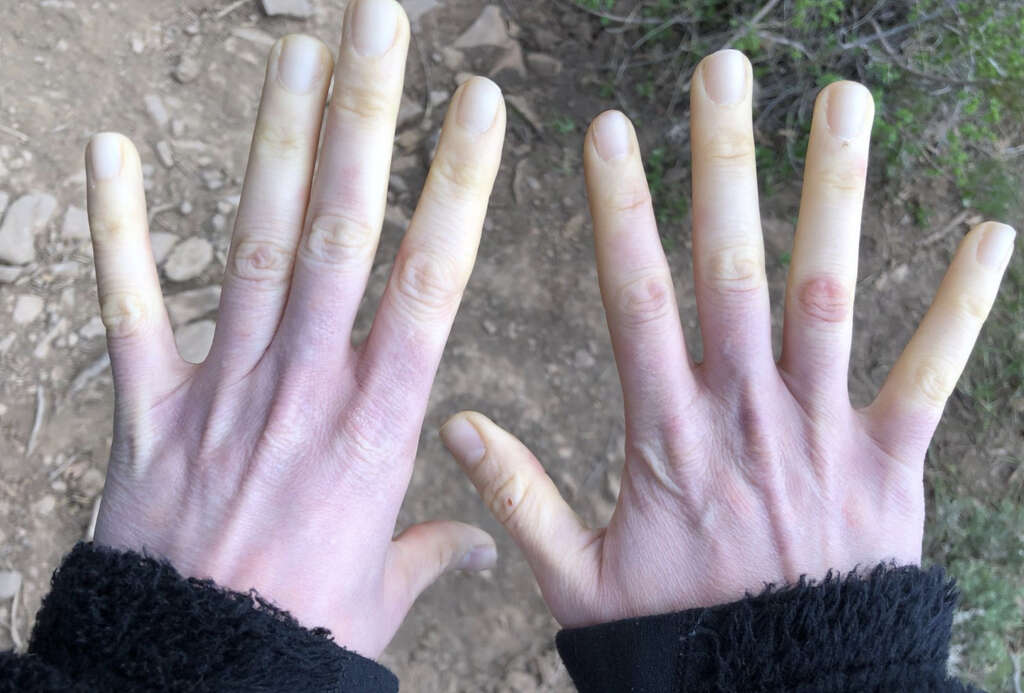
When a person has an attack of Raynaud’s, the affected area often first turns white and feels cold. After that, the skin can turn blue and go numb. Warming the area improves circulation, but it can result in pain, throbbing and tingling. The skin may also then turn bright red. Episodes can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
For those with the primary form of the disease, it is not unusual to have the same fingers or toes affected on both sides of the body. Secondary Raynaud’s can impact one or both sides of the body. In severe cases, sores can appear on the tips of the fingers. Very rarely, gangrene in the fingertips leads to an infection that requires amputation.
5. What Are the Risk Factors for Raynaud’s?
Primary Raynaud’s is more prevalent in women than in men. The condition can occur in people of any age but is most often seen in those between the ages of 15 and 30. There does appear to be an inheritance factor, as those with a primary family member with the disease are more likely to get it themselves. Furthermore, it is most often seen in people who live in colder climates.
People diagnosed with one of the associated diseases are at risk for secondary Raynaud’s. Smokers are also more likely than non-smokers to develop the condition. Engaging in certain repetitive motions that cause trauma on a routine basis can make a person more susceptible. People who are exposed to particular chemicals, such as vinyl chloride, and those who take medications that constrict blood vessels have an increased probability of secondary Raynaud’s.

6. What Are the Diagnostic Criteria for Raynaud’s?
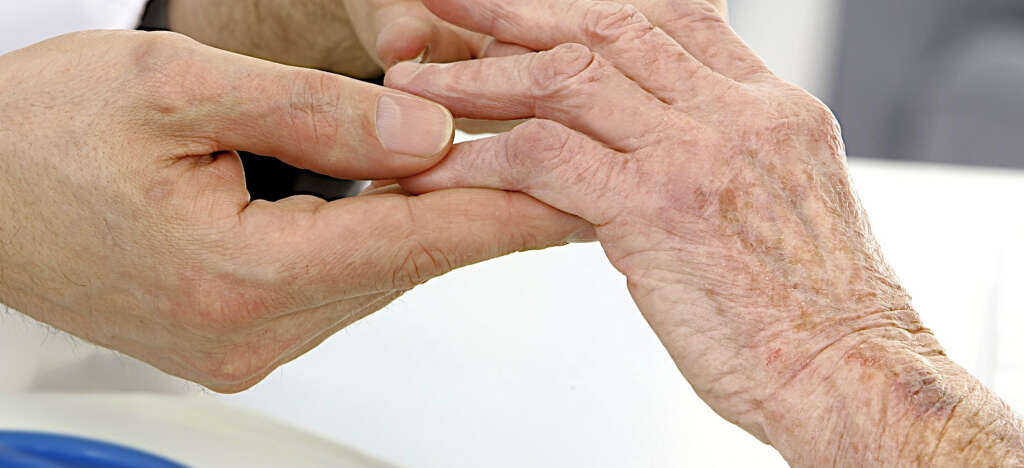
Diagnosis begins with a physical examination and an assessment of medical history. Often, the physician subjects the patient to a cold test to observe the changes to the skin in the affected area. In addition, the doctor is likely to examine the tiny blood vessels under a microscope to determine their condition.
For those who develop the condition after the age of 30, additional testing is likely. This is to determine whether there is an underlying condition causing Raynaud’s disease. Blood is drawn to test for antibodies that indicate a potential autoimmune deficiency.
7. What Are the Natural Treatment Options for Raynaud’s?
Changes in lifestyle habits are often effective in reducing the severity of Raynaud’s disease symptoms and are an important component in any course of treatment. The first step is to avoid substances that are vasoconstrictors, including nicotine and caffeine.
Getting regular exercise is beneficial as well. Cardio and strength-building exercises are both good for increasing blood circulation, which can reduce the severity and frequency of attacks. In addition, exercise alleviates stress, which can cause vasospasms. Reducing exposure to cold and keeping extremities warm are also beneficial.

8. What Are the Medical Treatment Options for Raynaud’s?
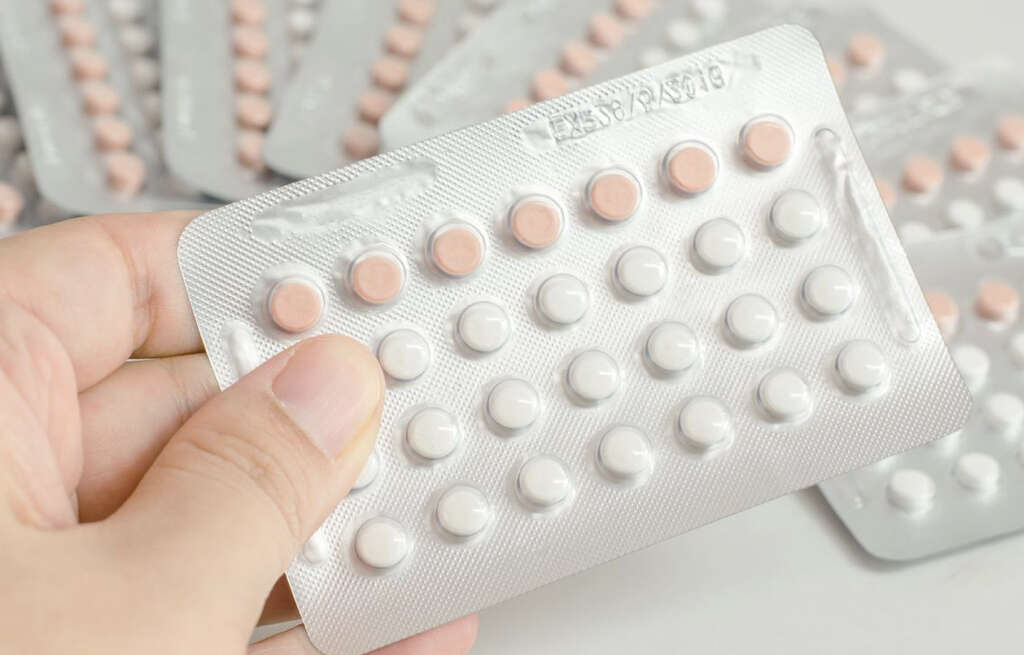
Certain medications can make Raynaud’s symptoms worse. These include birth control and migraine medicines as well as beta-blockers, some cold medications and estrogen-based drugs. Alternatives to using these types of medications are desirable when possible.
For people who have severe, frequent or long-lasting vasospasms, the doctor may prescribe a drug that helps with circulation by relaxing and expanding the blood vessels. The possibilities include antidepressants, antihypertension and erectile dysfunction medications.
9. What Can Be Done to Prevent Raynaud’s?
Preventative measures for some causes of secondary Raynaud’s include reducing repetitive motions and taking frequent breaks when those motions are required. Stopping, or never starting, a smoking habit reduces your risk of the disease. Taking care to avoid frostbite and trauma also lower the likelihood for secondary Raynaud’s.
Once a person is diagnosed with the condition, steps can be taken to reduce the likelihood of vasospasms. Keep warm when going out into the cold, taking particular care to bundle up extremities. Heat up the car on cold days before driving. Indoors, make it a practice to wear socks, and wear gloves when removing items from the freezer. Keep the thermostat dialed up a few degrees.

10. What Is the Prognosis for Raynaud’s?
Often, people who have the primary form of Raynaud’s find it an inconvenience rather than a serious issue. Many do not find their symptoms severe enough to seek medical attention. Frequently, the condition disappears of its own accord.
For secondary Raynaud’s, the prognosis depends on the severity of the underlying condition. In some instances, treating the associated condition is possible, making the prognosis for Raynaud’s good. In a number of other instances, managing the underlying condition can help decrease vasospasm attacks.