What Is a Viral Infection?
Viruses are tiny germs containing genetic material encapsulated inside a protein coating. Viruses cause many different illnesses and diseases, ranging from mild to life-threatening.
It’s estimated that there are more viruses on the earth than there are stars in our universe. To keep yourself safe and well, it’s important to learn as much about viruses as possible, and what you can do to treat them if you become infected.
1. What Is a Viral Infection?
When a virus enters your body, it hijacks your healthy cells and uses them to reproduce more copies of itself. It’s like the virus takes over and creates its own little factory inside your body. Different types of viruses attack different types of cells. For example, some attack the respiratory system while others attack the blood or specific vital organs.
If your immune system is healthy, you may not even know that you have a virus. A healthy immune system can often fight viruses off before they have a chance to cause significant illness. However, even people with healthy immune systems may still become very sick from certain types of viruses.
2. Are Viral Infections Dangerous?
Viral infections can be mild or life-threatening. Some viruses cause only minor symptoms of illness that may subside in a day or two. Other viruses may cause serious illnesses that can lead to permanent damage or death.
Examples of viruses that can be mild in some people include warts and the flu. More serious viruses include Ebola, HIV/AIDS and COVID-19.
3. What Are the Symptoms of a Viral Infection?
Symptoms of a viral infection can be very diverse, depending on a variety of factors. Symptoms may be as mild as cough and sneezing or as serious as high fevers and swelling of the tissues around the brain.
If you think you may have a virus, visit your doctor. He or she can conduct tests to determine if a virus is causing your infection, and what type. A blood test may be conducted to detect viral infections.

4. What Are the Most Common Types of Viral Infections?
There are many different types of viruses, and some are more common than others. Annually, the common flu is a virus that causes millions of people to get sick. Other common viruses include Chickenpox, herpes, infectious mononucleosis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV/AIDS).
Some viruses are starting to make a comeback, though they were nearly eradicated in the past through vaccinations. These include measles and mumps. In certain areas of the world, other viruses such as polio and rubella are also on the rise.

5. How Does the Body Fight Off Viruses?
Your body is remarkable and knows how to defend itself from many different types of viruses. When a virus attacks the cells in the human body, the body responds by initiating an immune response. This response stimulates the body to send different types of white blood cells to identify and repel or destroy foreign invaders.
Your body makes about a billion protective white blood cells in its bone marrow every single day. When you overcome a virus, it means your body has successfully fought it off. Unfortunately, the body doesn’t always recognize foreign invaders until it’s too late and they’ve already overwhelmed too many cells. When this happens, you develop various symptoms of illness. Depending on the severity of the infection, your body may be able to bounce back after a few days or weeks, or you may require medical intervention to help your body fight off viral infections.

6. How Do Viral Infections Enter the Body?
Your body is pretty good at keeping unwanted substances out, but viruses are so tiny that they can often pass through your body’s openings undetected. Some of the most common entry points for viruses include the mouth, nose, wounds and sexual organs. You can also become infected during transfusion with contaminated blood.
Your body has a number of defenses against viruses, but they don’t always work. For example, nasal hairs may not prevent tiny viruses from entering your body, and your body’s natural blood-clotting defenses may not work quickly enough to keep viruses from entering wounds. That’s why it’s important to clean and bandage any wounds quickly before they can become infected.
7. How Do Viral Infections Differ from Bacterial Infections?
It can be hard to differentiate between viral and bacterial infections based on symptoms alone. Both can cause many of the same types of symptoms, including sneezing, coughing and runny noses. However, bacterial infections are caused by bacteria, while viral infections are caused by viruses. It’s important to know which type you have before seeking treatment, since they are both treated in very different ways.
Bacteria are single-celled creatures that can reproduce on their own and are relatively complex when compared to viruses. They often have rigid walls with a rubbery membrane and fluid inside. Most bacteria are relatively harmless, and some are actually good for the body. In fact, fewer than 1% of bacteria cause harmful symptoms in humans. Viruses, on the other hand, can’t reproduce or survive without a host. Most types of viruses are harmful to humans and can even target healthy bacteria.

8. What Are the Risk Factors for Viral Infections?
Viral illnesses can affect practically anyone, regardless of age or gender. However, there are certain lifestyle choices or genetic factors that can cause some people to be more prone to viral infections.
Risk factors for viral infections include poor hygiene, pre-existing medical conditions, excess stress, age and drug use. Disadvantaged populations are also at higher risk of developing viral infections.

9. When Should You See a Doctor for a Viral Infection?
It’s not always necessary to see a doctor if you’re sick with a viral illness, but there are situations when prompt medical attention is essential. If you have a fever that lasts longer than five days or keeps returning, you should visit your doctor. A severe sore throat, intense sinus pain and wheezing are also indications that you need care.
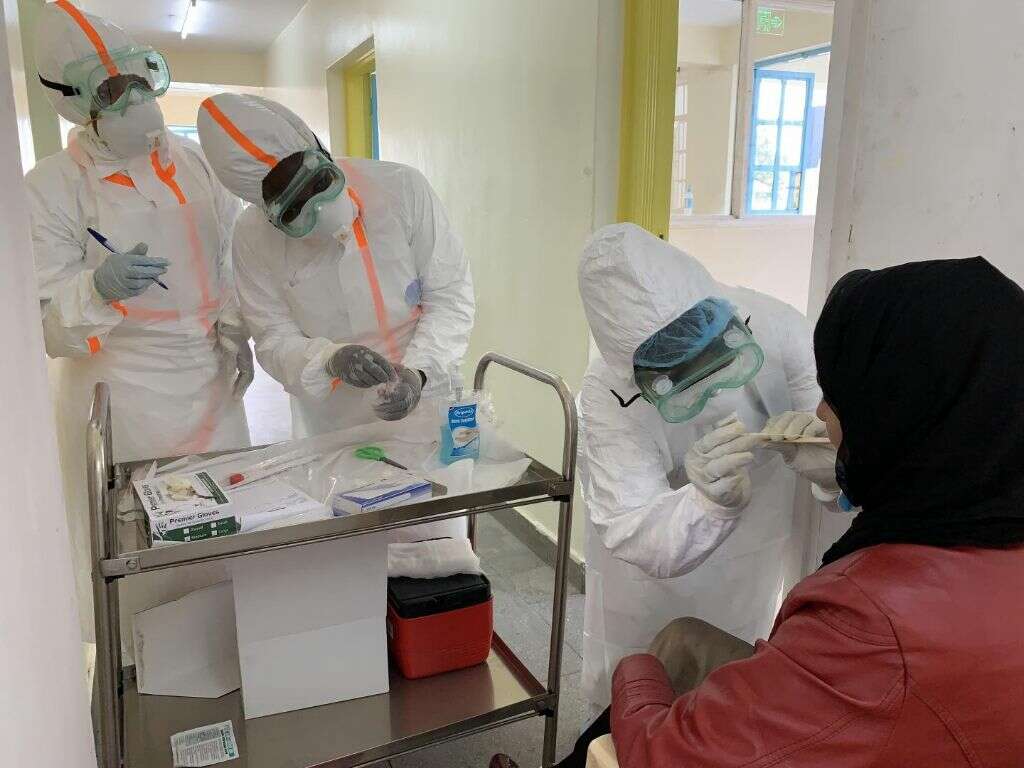
With the current COVID-19 pandemic going on, it’s also important to see your doctor or be tested if you experience any of the following symptoms: loss of smell or taste, fever or chills, fatigue, headache, muscle or body aches, cough, and shortness of breath.

10. What Are Treatment Options for Viral Infections?
Viral infections are treated in different ways, depending on the type and cause of the infection. Vaccines are commonly used to prevent viral infections in the first place, but if you do develop a viral infection, your doctor may treat you with antiviral medicine.
Every case is different, which is why treatment should be recommended on a case-by-case basis. It’s important to talk to your doctor about treatment options that are available for your specific type of viral illness.