What Is a Tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy is a relatively common surgical procedure that is often used to save somebodys life in the short term, and/or to maintain their life in the longer term. It looks quite dramatic but it is actually quite straightforward, and often not nearly as bad as it may look, even though it can be uncomfortable for the patient.
While the procedure is quite straightforward, it is still only used as a last resort. It is usually only temporary and the hole created will be repaired once it is no longer needed. In some cases, however, there may be a need to have a tracheostomy permanently.

1. Trachea
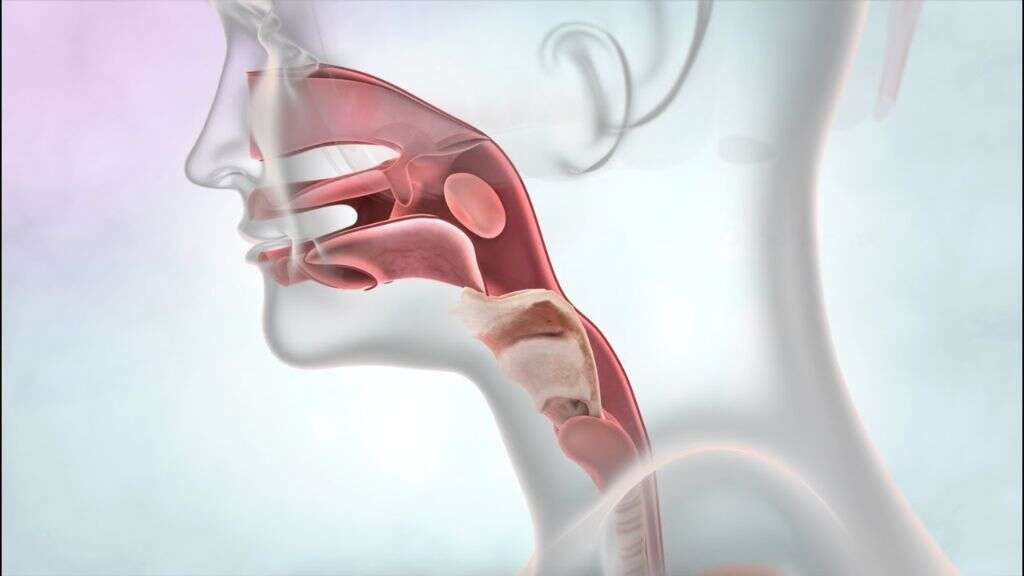
The trachea, which is more commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube that travels from our mouths down to our lungs and it allows for air to pass freely between the two. It is made mostly from cartilage, and it is found in the vast majority of animals that use lungs to take oxygen from the air. It begins just below the voice box, and forks at the bottom into two separate branches that feed air to and from the lungs. It is essential that this airway is kept clear at all times so that the body is continuously fed with oxygen, while the passages to and from the trachea must also remain open.
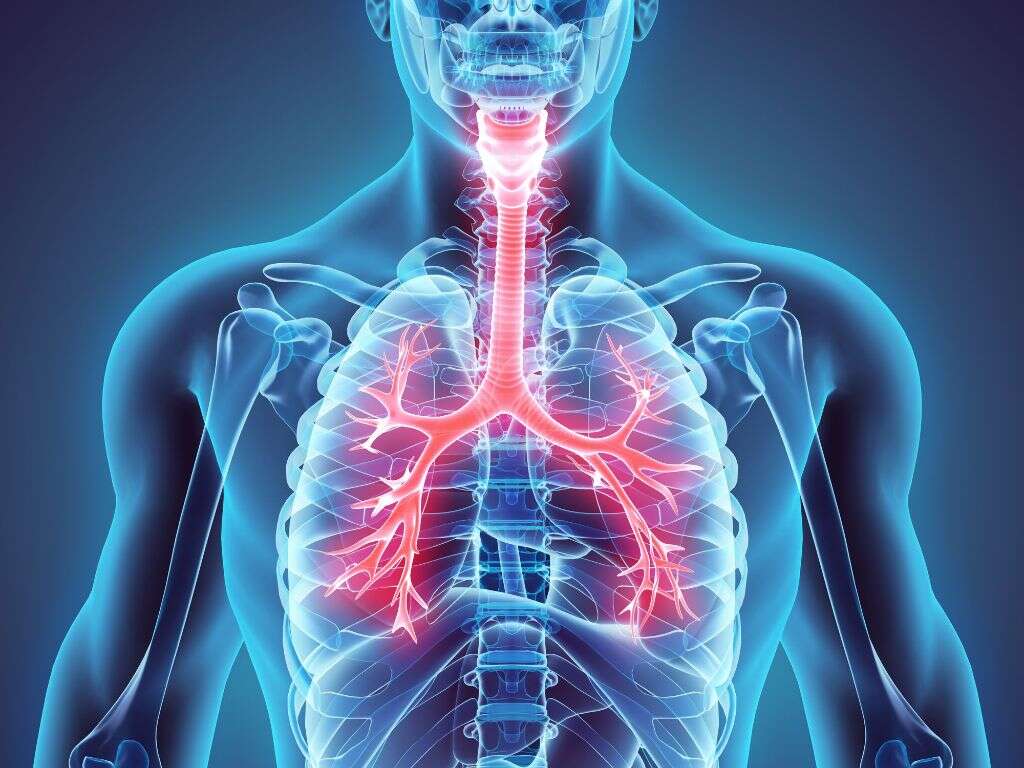
2. Tracheostomy
If, for whatever reason, the passageway into the windpipe is blocked then emergency steps need to be taken to ensure that air can still get into the windpipe and into the lungs. Sometimes, this means bypassing the rest of the airways and creating a passage directly into the windpipe itself.
In order to achieve this, a hole is cut directly into the windpipe just below the voice box. A tube can then be inserted so air can be slowly pumped in, feeding the lungs with oxygen. This is usually done in a hospital or ambulance, but in some extreme emergencies, this is done using more rudimentary equipment.
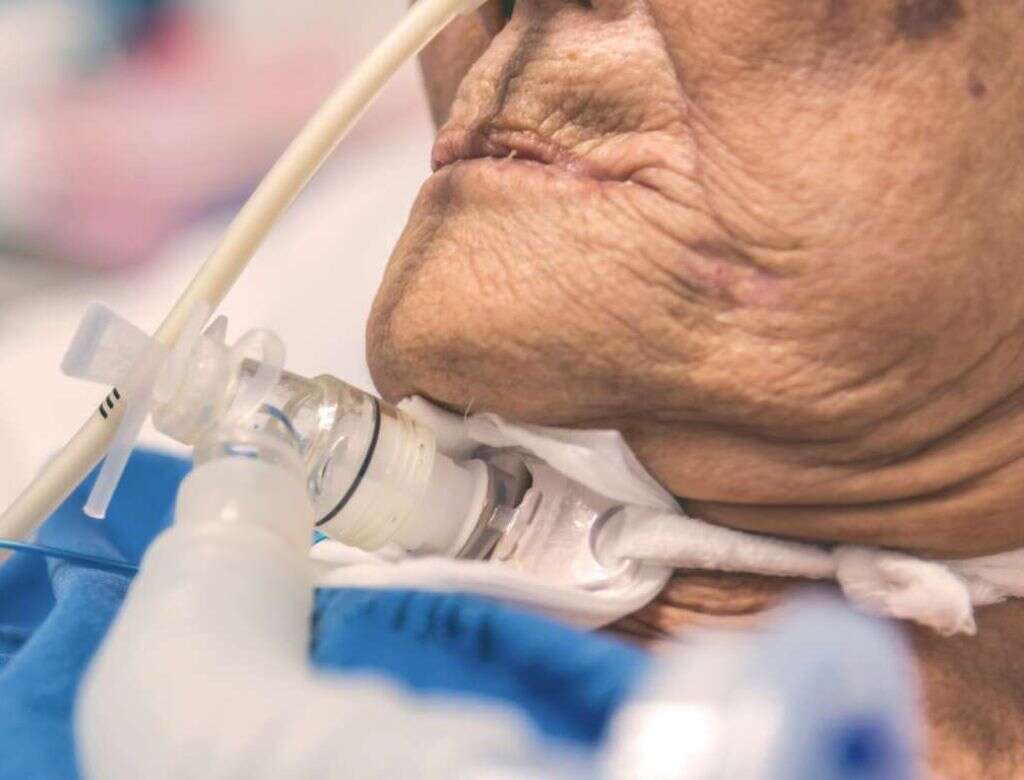
3. Anaphylaxis
Many people have allergies, and allergens that can cause reactions are also very common. For the most part, though, the reactions are relatively mild, causing symptoms that are irritating but harmless. In some instances, however, allergic reactions can be very dangerous indeed.
They can even pose a very real threat to the patients life. Anaphylaxis is a condition that occurs after an extreme allergic reaction. The body reacts by pumping too many chemicals into the body and this can be extremely dangerous. This can cause a dangerous swelling in the patients neck that can block the airways, in which case, a tracheostomy will be needed.

4. Injury
Whether it is a sporting injury, a road traffic injury, or an accident at home, we have a habit of hurting ourselves. In some cases, we can do ourselves damage that can pose a very real threat to our lives. This can mean that urgent steps need to be taken in order to save our life.
In some cases, the severity of the injuries will mean that we are unable to breathe freely. This will mean that an emergency tracheostomy is necessary to make sure we are able to breathe. In some cases, this might even mean having to cut a hole in the windpipe, even without the right equipment.
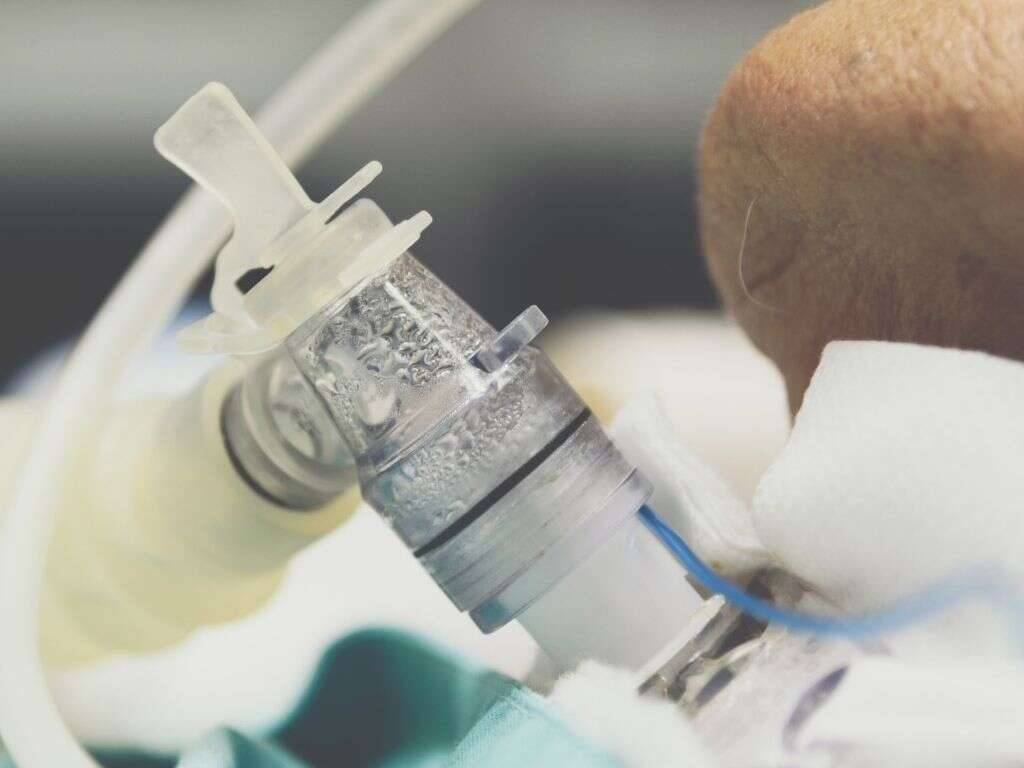
5. Birth Defects
It is unfortunate that some children are born with defects, and these can sometimes pose a real and immediate risk to their young lives. Some children will not be able to breathe after being born because of obstructions in the airways and this will need to be treated as a matter of emergency to save the child’s life.
Doctors and surgeons prefer not to operate on newborns because surgery in somebody so small will increase the risk of complications arising. Still, they are highly trained and will know just what to do should it be necessary that they take drastic action.

6. Coma
If the body is injured seriously enough then it can effectively shut itself down, except for vital organs. This can give the body a chance to try and repair itself, although it is obviously a very dangerous time for the patient. Thanks to modern medicine, the chances of making a recovery after going into a coma is on the rise.
Some people in a coma are still able to breathe freely, but this is not always the case. In some instances, they will need help from machines, and this will often require a tracheostomy. Some people will be in a coma for just a few days, whereas others can be in a coma for months or even years.
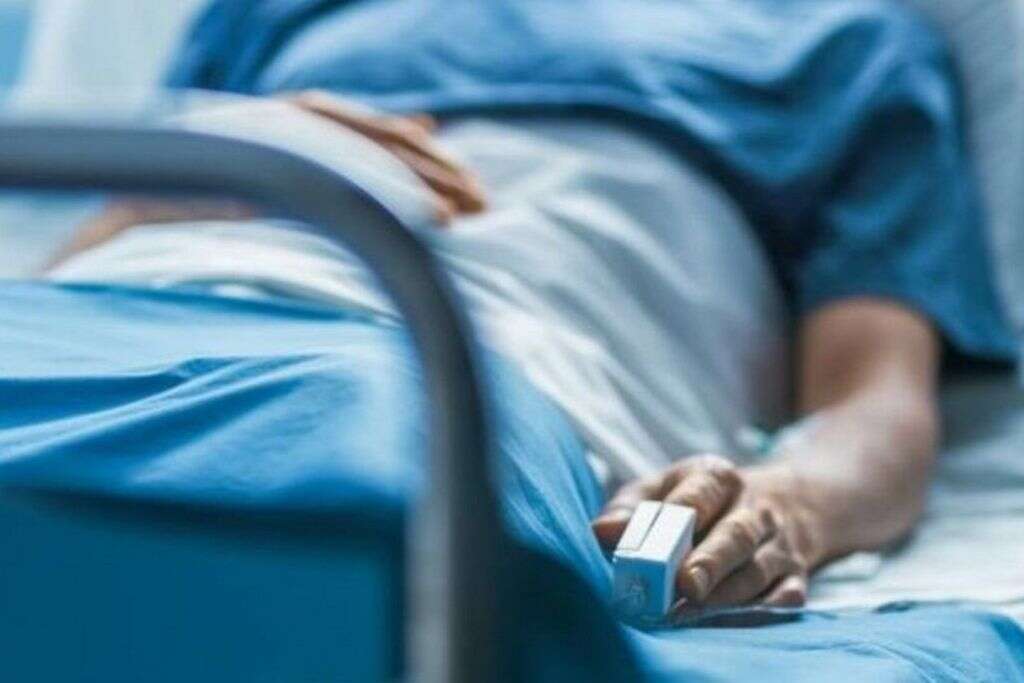
7. Lung Disease
We are able to breathe in and out thanks to the action of the lungs. With help from the diaphragm and other muscles, the lungs will expand and this will force oxygen rich air into the lungs. When they collapse again, the air is expelled, making way for a fresh load of oxygen-rich air again.
In cases of lung disease, the lungs may not be able to expand and compress properly, meaning the body will not get the oxygen it needs. If the condition is severe enough, machinery is needed to help ensure the breathing process is enabled, and this can mean a tracheostomy will need to be performed.

8. Diaphragm Problems
The diaphragm is a thin muscle that is located just beneath the lungs. When it contracts, it flattens out and pulls the bottom of the lungs down with it. This results in a vacuum in the lungs, and this causes fresh air to be sucked into the lungs. When it relaxes, the spent air is forced out and the process can start again.
In some cases, the patients diaphragm will develop problems, meaning that it is no longer able to pull down on the lungs as it usually would. Thus, the patient will need help with breathing, and this will often mean a tracheostomy is necessary to allow a tube to be inserted into the windpipe.
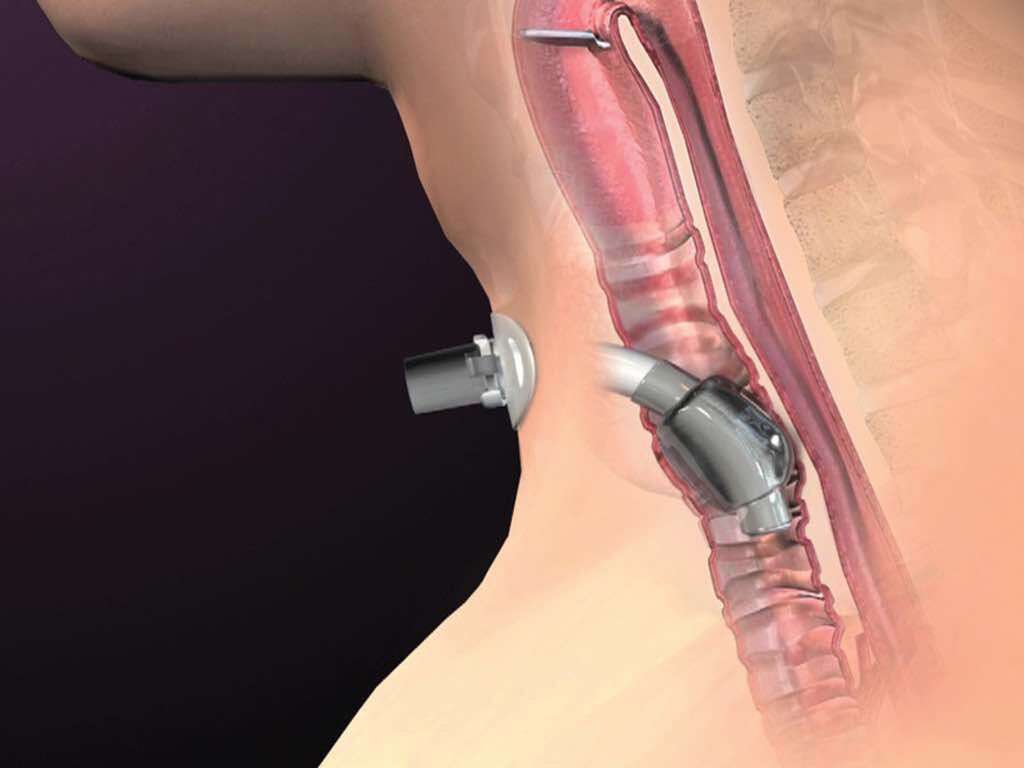
9. Obstruction
Most people have, at some point, choked on something that they have eaten. The vast majority of the time, the food will simply be coughed up, clearing the airways, but this is not always the case. If food or anything else is able to block the passage of air to the windpipe then the patient can be in a lot of trouble.
If the blockage cannot be immediately cleared then it may be necessary to turn to more drastic measures. This might mean a tracheostomy is needed in order to help bypass the blockage to allow air to get into the windpipe.

10. Cancer
Some types of cancers can affect the different parts of the throat and, depending on the problem at hand, surgery may be necessary to save the patients life. The patient will still need to be able to get oxygen during this time, however, so they may need assistance with breathing.
In some cases, a tracheostomy will only be temporary as the patient is treated to help the wound heal after surgery and/or to reconstruct the airways. In other cases, however, the surgery will be permanent and the patient will effectively have a hole in their throat for the rest of their life.