What Is a Kidney Infection?
If it was not for our kidneys then the levels of toxins in our blood would gradually rise. They will continue to rise until the point where our own blood becomes too toxic for us, and we would die. This makes our kidneys very important to us, so we need to treat them with care.
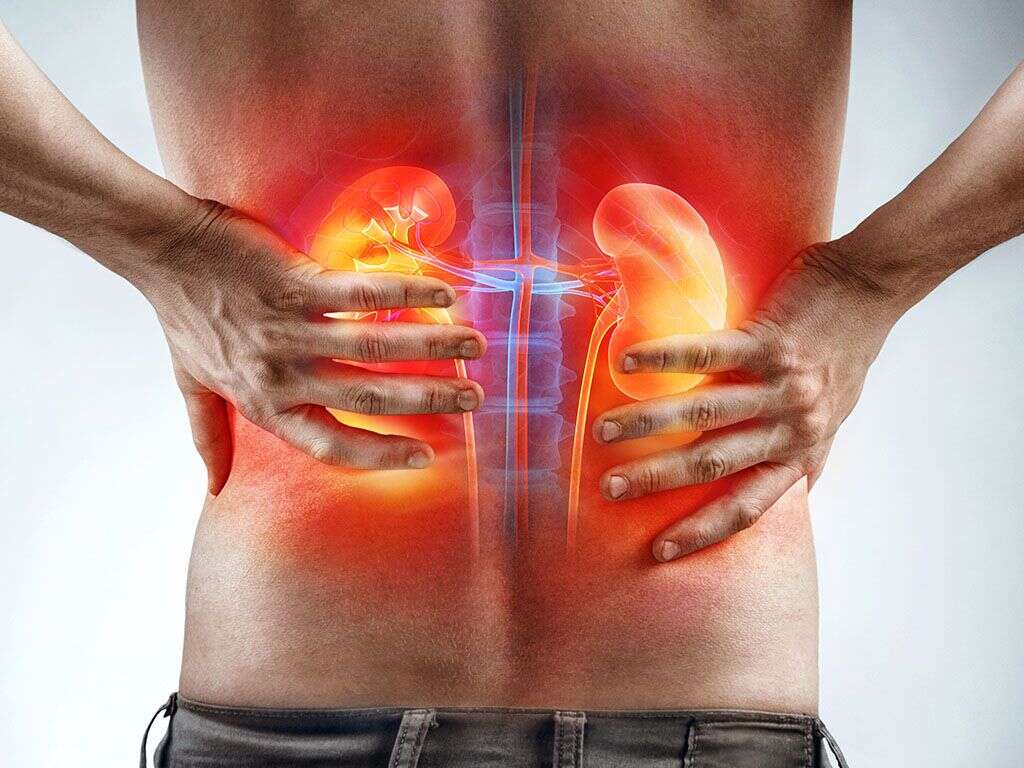
Because our kidneys are important for us then we should see a doctor as soon as we develop problems with them. Certain signs like pain in the region of the kidneys can be a sign that something is wrong. In some cases, it can be a sign of a kidney infection and it is something that we should get seen to as soon as possible.
1. Kidney Infection
A kidney infection is a type of urinary tract infection that tends to start elsewhere in the urinary tract. Bacteria from an infection elsewhere in the body will sometimes end up in the kidneys and, if they are able to get a foothold, they can proliferate and cause a problem.
Kidney infections are usually fairly straightforward to treat. However, they can cause severe damage if left untreated so it is essential the patient is found medical assistance as soon as possible. Depending on the severity of the infection, hospitalization may be necessary, and long term treatment will also be necessary in some cases.
2. Causes
As mentioned, kidney infections are often caused by bacteria that were causing an infection elsewhere in the body. This will often mean infections that started in the urethra or the bladder. This type of infection will themselves tend to be caused as bacteria manage to find their way to the entrance of the urethra from external sources.
In many cases, the bacterium has come directly from the anus, and the bacteria at fault will often be those that are commonly found in the digestive system. Other potential causes include infections after surgery, but such instances are not at all common.
3. Symptoms
The symptoms of a kidney infection can range in severity, and they are also likely to get worse if not treated. Patients with an infection will typically complain of a pain in one side at the back of the body. They are also likely to be experiencing a fever, chills, and aches and pains in their joints and muscles.
Other possible symptoms include a strong urge to urinate, and a need to urinate more frequently than usual. Nausea and vomiting are other potential symptoms, and the patient will experience pain when they are urinating. The patient’s urine can be cloudy and have a foul odor, while there may also be blood and/or pus in their urine.
4. Kidney Scarring
It is important to get treatment for a kidney infection as quickly as possible because otherwise it might cause permanent damage to the kidneys. If the infection is severe enough, it can damage the kidneys to the point where it causes extensive scarring. This scarring will then affect the organs’ ability to function.
This will result in chronic kidney disease, which the patient will have for the rest of their life. This, in turn, can lead to symptoms including high blood pressure, fatigue, shortness of breath, and itchy skin. Kidney disease can also progress to kidney failure, which is a potentially fatal condition.
5. Pregnancy Complications
It is a good idea for pregnant women to get regular check-ups to help identify potential problems early on. It is also a good idea for them to see a doctor as soon as a potential problem is noticed. There are numerous things that can jeopardize a pregnancy, and these include kidney infections.
If a pregnant woman does have an untreated kidney infection then there is a risk that the child will be born underweight. If the condition remains untreated, there is also a chance the fetus can be affected by complications the mother is experiencing. This includes potentially serious complications like sepsis.

6. Sepsis
Our immune system will respond to the presence of unwelcome bacteria in a number of ways. One of these is to release chemicals that will help to kill the bacteria. While this can be very helpful in helping to keep us safe, too many of these chemicals can be dangerous to us.
In cases of a severe infection, the immune system may respond by releasing a dangerous volume of chemicals into the body. This is a condition known as sepsis, and it is very dangerous. Symptoms of sepsis include a low body temperature, sweaty and clammy skin, pain, weakness, blotchy skin, and a fast heartbeat.

7. Risk Factors
No person is completely safe from developing a kidney infection. However, some people are more prone than others are. One of the main risk categories is women, and the female anatomy makes it more likely that bacteria from outside will end up in the urethra. Other risk categories include people that have a weakened immune system.
This can be caused by certain medication, and it can also be caused by other diseases like HIV. Blockages like kidney stones can also make a kidney infection more likely, and certain medical conditions with the urinary tract can also increase the chances of a kidney infection occurring.

8. Prevention
While we can’t be 100% safe from kidney infections, we can still take action to make ourselves safer from the disease. One of these is for women to wipe from front to back to help prevent infection from bacteria from the anus. Also, try avoiding female hygiene products that can be irritating to the urethra.
Drink plenty of fluids to help the body flush bacteria out of the kidneys and elsewhere in the urinary tract. You should also try to avoid holding in urine for too long, and make sure you go to the bathroom before you go out anywhere. Urinating after intercourse can also help to prevent kidney infections.

9. Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely need to ask about your symptoms and medical history. However, tests will still be necessary to confirm what is causing the symptoms. This will typically involve requesting a urine sample so the urine can be analyzed for signs of an infection. A blood sample may also be taken for the same purpose.
Other possible tests include imaging techniques that will help to get a clear picture of the condition of the urinary tract. This will sometimes include the use of a dye that will help structures like the bladder to show up clearly on the images.

10. Treatment
Kidney infections are bacterial infections, and this means that they will be treated with antibiotics. The dosage and the type of drugs used will vary on the patient’s overall health, and the severity of their infection. Antibiotics are usually very effective, and the patient should make a full recovery in just a few days or so.
If the infection is severe then the patient may need to be hospitalized, and antibiotics may be given intravenously. In some cases, it might be necessary to treat an underlying cause, and this will sometimes mean surgery to help repair an anomaly in the urinary tract.