What Is a Heart Attack?
One of the biggest killers of people is problems with the heart. Our heart is essential to us as it helps to ensure our bodies are supplied with oxygen and nutrients. If our heart was to stop working then we will simply die. Other problems with the heart can have a considerable impact on our health and quality of life.
One such problem is a heart attack, which is a very serious medical condition. Our methods of treating heart attacks are improving, however, and now around 90% of people in developed countries can expect to survive a heart attack. However, this relies on the patient being found medical assistance without hesitation.
1. Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction is the technical medical term for a heart attack. It occurs when there is a disruption of the flow of blood to the heart’s muscles. There are several different reasons this can happen, and the condition is to be considered an extreme medical emergency regardless of the cause.
If the flow of blood to the heart is blocked then the heart’s muscles will begin to die. If the patient is not found medical assistance in time then their heart may stop working altogether. A heart attack often can be treated provided the patient is found the assistance they need, however.
2. Cardiac Arrest
People often think that a cardiac arrest and a heart attack are the same thing, but they are different conditions. While a heart attack means the flow of blood to the heart has been impeded, it does not necessarily mean that the patient’s heart has stopped. In instances of a cardiac arrest, the patient’s heart has stopped beating altogether.
While both conditions are serious, a cardiac arrest is certainly the more serious of the two, and the patient can die within minutes. A heart attack will sometimes lead to the patient having a cardiac arrest, but there are also other causes of the condition.
3. Causes
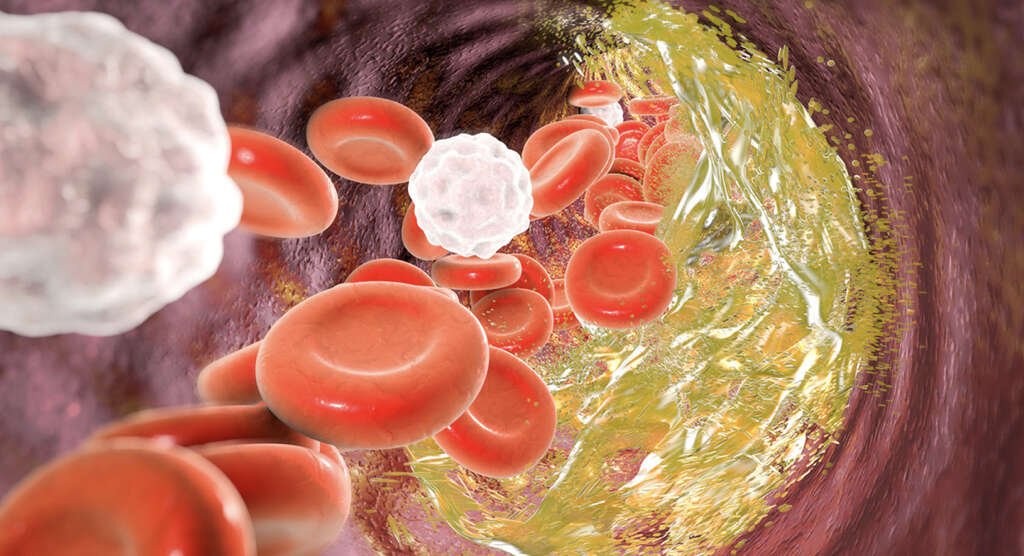
Heart attacks are caused by blockages in the coronary arteries, which help supply oxygenated blood to the heart’s muscles. These blockages are often a result of atherosclerosis. This is a condition where fatty deposits and other substances accumulate on the walls of the patient’s blood vessels.
These buildups can harden into what are known as plaques and, as they accumulate, they can begin to restrict the flow of blood through the blood vessels. When the flow of blood is impeded too much, a heart attack can occur. Another potential cause is spasms of the coronary artery preventing blood from flowing through.
4. Symptoms
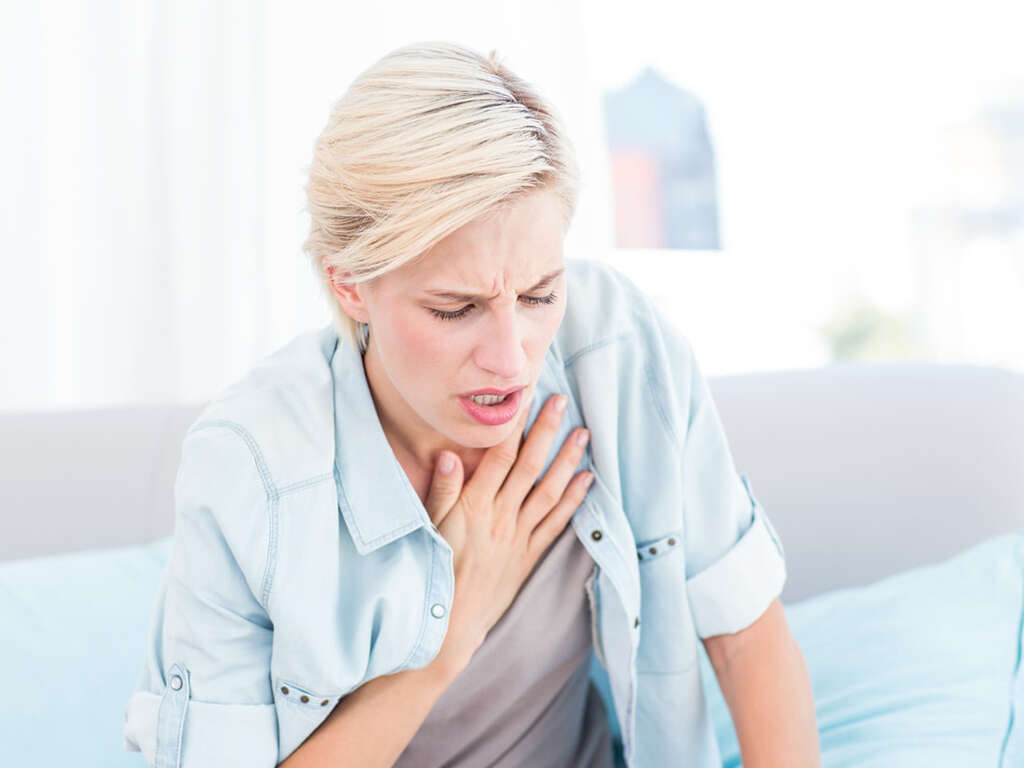
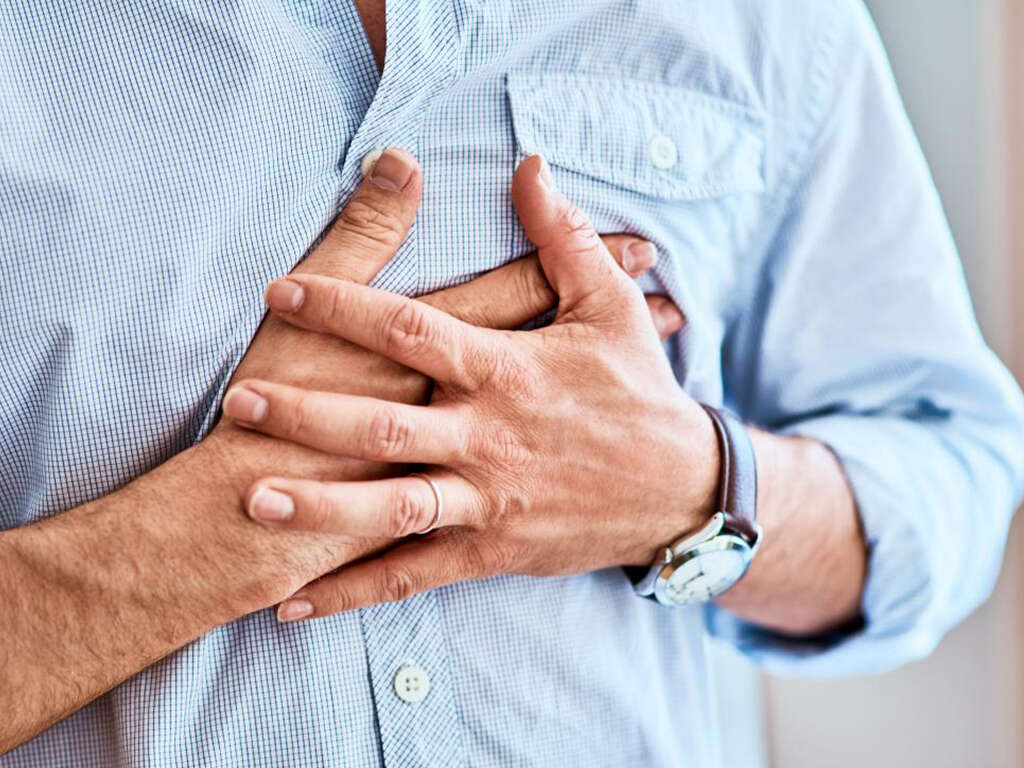
The symptoms of a heart attack can come on suddenly, although they will develop gradually in some cases. The symptoms will not always be the same in everybody, and they can also vary in severity. Perhaps the most common of all symptoms of a heart attack is that the patient will feel pain in the chest or arms.
The pain will sometimes radiate out to the neck, back, and jaw. The patient can also find it difficult to breathe, and they may also become dizzy. Cold sweats are also possible, and the patient can also experience nausea and pain in the abdomen. A heart attack will also sometimes cause the patient to feel fatigued.
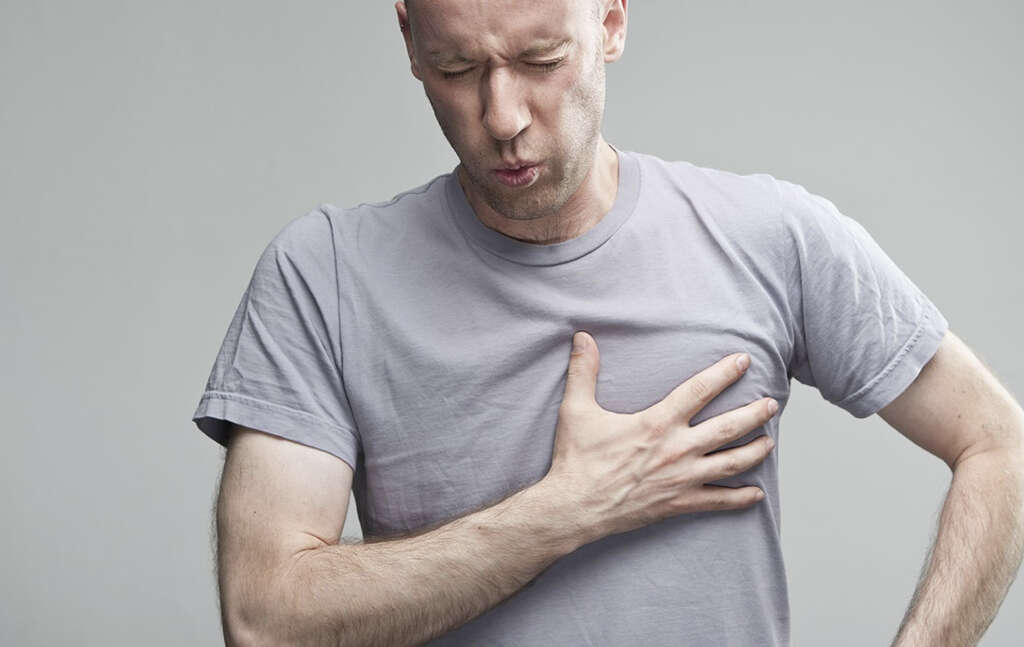

5. Complications
The lack of sufficient blood flowing to the heart can cause permanent damage to the heart. This can affect the patient in several ways, one of which is arrhythmias. These are abnormal heart rhythms that can be caused by abnormalities with electrical impulses in the heart’s muscles.
Another potential complication is heart failure. This means that the heart is less effective than it used to be, affecting the flow of blood around the body. This will sometimes only be temporary, but it can also be permanent. As mentioned, a heart attack can also lead to a cardiac arrest, which is an extremely dangerous situation.
6. Who’s At Risk
The people most at risk of having a heart attack are generally those that have atherosclerosis. However, atherosclerosis usually does not cause symptoms and by the time the patient is aware of a problem, it is often too late. People are more prone to heart attacks as they get older and women over 55 and men over 45 are more likely to experience one.
People who smoke are also more likely to have a heart attack, as are non-smokers who are exposed to cigarette smoke. Diabetes is another potential factor, as is obesity. A high blood pressure will also increase somebody’s risk of a heart attack, and high blood cholesterol levels will also increase the risk.
7. Prevention
With the right choices, we can make it a lot less likely that we will suffer a heart attack ourselves. This includes lifestyle choices like eating healthily, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking. It also helps to avoid being exposed to stress for too long and trying to take at least a little time to relax.
If you are in a high risk category, your doctor may be able to prescribe medication to help reduce the chances of a heart attack happening. This can include medication that will help reduce your cholesterol levels, and/or medication that will help to reduce your blood pressure.
8. Diagnosis
If you are able, your doctor will likely need to ask about your symptoms. They will also likely want to check your blood pressure, pulse, and temperature. You will also need to have your heart monitored so experts can see how well your heart is working, and to look for signs of a heart attack.
Blood tests may also be taken. This will help doctors to look for signs of high levels of certain proteins in the blood that would be a result of damage to the heart. An electrocardiogram can also be used to help experts to measure the electrical activity in the heart.

9. Medications
One of the first treatments provided for a heart attack is often aspirin. This is because aspirin helps to thin the blood, thus improving the flow. It also helps to prevent clotting. Nitroglycerin is also often the first drug used because it helps to widen the blood vessels.
Thrombolytics can also be used, and these will help to dissolve any blood clots that might be causing blockages. Beta blockers can be used as they will help to decrease blood pressure and relax the heart’s muscles. Statins may also be used to help reduce the patient’s cholesterol levels, and pain killers may be administered to help make the patient more comfortable.
10. Surgery
In addition to medication, surgery will be also sometimes be deemed necessary. In some cases, this will mean a coronary bypass surgery, and this will involve ensuring the blood can bypass affected blood vessels so they can reach the heart. This will be performed after the heart has had some time to recover where possible.
Another surgical option is a coronary angioplasty and stenting. In this option, a catheter is passed into the affected artery. The catheter comes with a small balloon which can then be inflated to help open the artery, thus allowing the blood to flow freely again. A permanent stent can also be inserted to help ensure that the blood vessel stays open.









