10 Turner Syndrome Symptoms
Turner syndrome is a chromosomal condition that affects the normal development of females. This condition affects approximately 1 out of every 2,000 females in the United States, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. It occurs when the X chromosome, which is otherwise known as the sex chromosome, is completely or partially missing.
Turner syndrome was described for the first time in 1938 by Dr. Henry Turner who noticed the same unusual developmental and physical features characteristic for this syndrome in a group of seven girls. There is no cure for Turner syndrome. Below are the 10 most common symptoms of Turner syndrome.

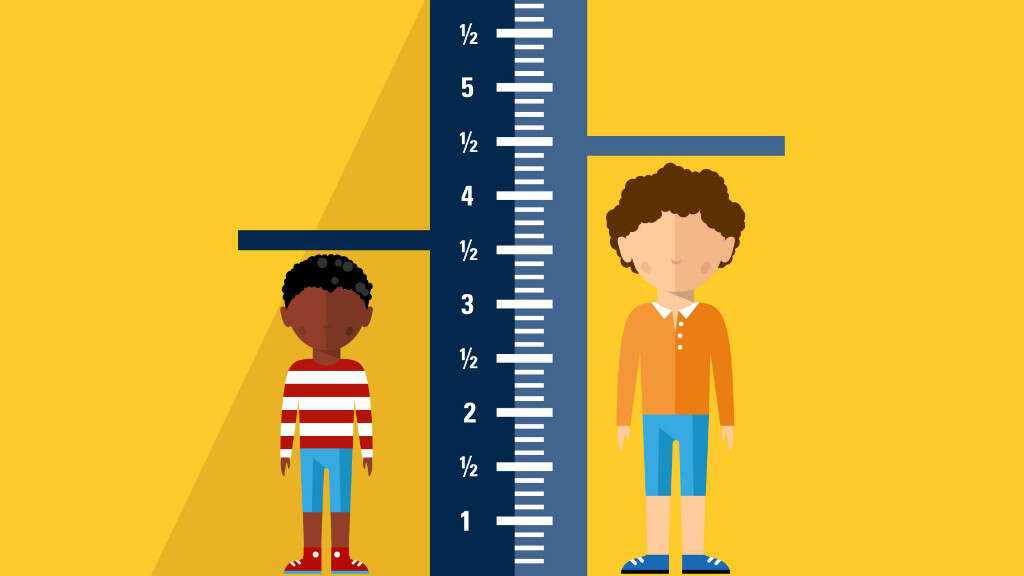
Symptom #1: Short Stature
A characteristic symptom of Turner syndrome is a short stature, which becomes evident by the age of 5. Children initially may display normal growth, usually for the first 5 years of life. However, in most cases, the growth rate becomes slower and the child will not experience normal growth spurts, finally leading to a shorter height than the average child of the same age.
If left untreated, those affected with Turner syndrome will have a final height of less than 5 feet. Those affected with Turner syndrome do not have a growth hormone deficiency; however, treatment with synthetic growth hormones does help with height.

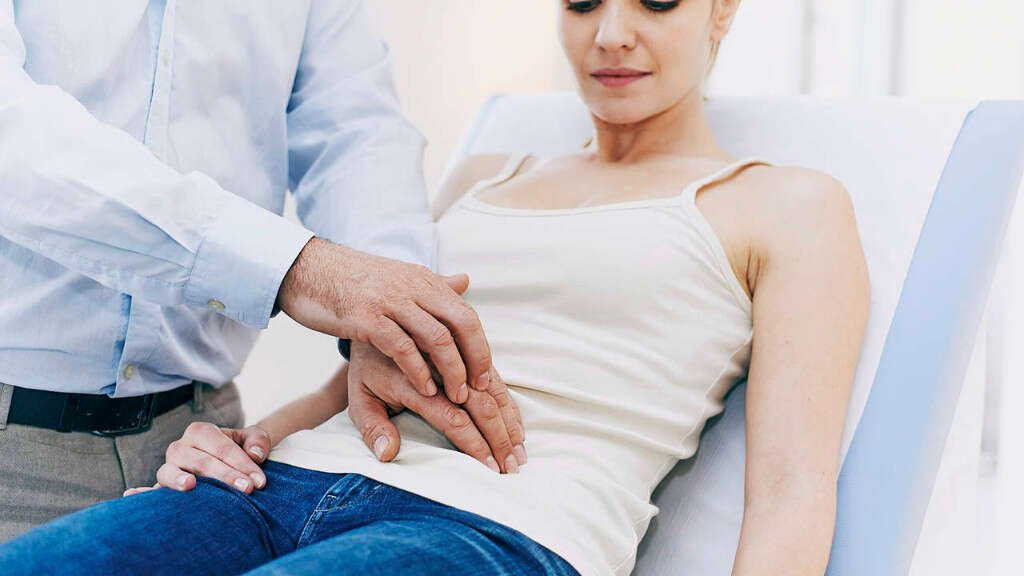
Symptom #2: Loss of Ovarian Function
Another common symptom of Turner syndrome is the loss of normal ovarian function. Even though the ovaries develop normally at first, the oocytes, which are the egg cells, usually die prematurely and most of the ovarian tissue degenerates even before birth leading to the development of ovarian hypofunction and premature ovarian failure. Those affected with Turner syndrome don’t undergo puberty normally so need to take hormone therapy in order to be able to conceive.
However, a small percentage of those affected with Turner syndrome retain a normal ovarian function, even in adulthood. They enter puberty normally and conceive on their own without needing hormone therapy.

Symptom #3: Excess Skin on the Neck
About 30% of those affected with Turner syndrome will have excess skin on the neck, otherwise commonly known as a webbed neck. Besides having these extra folds of skin on the neck, a low hairline at the back of the neck is also commonly seen.
In babies, this symptom looks like loose folds of extra skin, but as the child grows, the skin can stretch out and make it look like there is very little neck or no neck at all. Surgical treatments are possible to get rid of the excess skin on the neck.
Symptom #4: Mental Difficulties
Even though intelligence is usually normal in those affected by Turner syndrome, learning disabilities are quite common. An example of a learning disability that these person’s may encounter is right-left disorientation.
Other possible difficulties that they might have are problems with nonverbal memory, attention problems, difficulties in learning math, and difficulties with directional sense. All these mental difficulties will have a great impact on a person’s life, especially in certain social situations.

Symptom #5: Autoimmune Disorders
Girls and women affected with Turner syndrome have a higher risk of developing certain autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pernicious anemia, autoimmune hepatitis, thrombocytopenia, Addison disease, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
The increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease is because the patient has an increased prevalence of autoantibodies.

Symptom #6: Heart Defects
Estimates have shown that about one-third of individuals affected with Turner syndrome are born with heart defects, such as coarctation of the aorta, valve abnormalities, and septal defect. These heart problems require consistent medical check-ups and treatment. Complications can be life-threatening if not managed correctly.
In addition, some girls and women with Turner syndrome develop high blood pressure, and have a higher risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
Symptom #7: Ear Problems
Turner syndrome leads to development and normal functioning problems in almost every organ in the human body, including the ears. Common ear problems include chronic infections of the middle ear, cholesteatoma, conductive hearing loss, and sensorineural hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss develops as a result of the gradual loss of the normal nerve function. It appears in late childhood or early adulthood. Hearing aids or cochlear implants can help treat this problem, depending on the severity of the hearing loss.

Symptom #8: Kidney Abnormalities
Girls with Turner syndrome may have kidney abnormalities. Estimates have shown that about one-third of those affected with Turner syndrome have a malformation of the kidneys, although in most of the cases these abnormalities don’t initially cause any serious medical problems. Possible kidney abnormalities include a horseshoe kidney, duplex collecting systems, and crossed ectopic.
Kidney abnormalities will eventually lead to a higher risk for high blood pressure as well as urinary tract infections.
Symptom #9: Skeletal Problems
One of the main problems that girls with Turner syndrome experience is slow growth and bone development problems, which means that they have a higher risk of scoliosis or kyphosis. Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, while kyphosis is a forward rounding in the upper part of the spine.
They have also a higher risk of developing osteoporosis because of brittle and weak bones. Girls and women with Turner syndrome seem not to have a higher risk for bone fractures compared to the general population unless osteoporosis develops.

Symptom #10: Infertility
As mentioned, Turner syndrome occurs when the X chromosome, which is otherwise known as the sex chromosome, is missing, totally or partially. For this reason, it is quite understandable that these girls will have fertility problems. Because the ovaries will not develop normally or stop developing as they should, girls affected with Turner syndrome may not enter puberty and have menstrual periods like normal girls at the same age will have. However, a very small number of women with Turner syndrome can become pregnant spontaneously without fertility treatment.
One thing a person with Turner syndrome should keep in mind is that they have a higher risk of pregnancy complications such as high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and aortic dissections. Before and during pregnancy, women affected with Turner syndrome should be carefully and constantly evaluated by a cardiologist.