10 Symptoms of Tooth Infection
A tooth infection or tooth abscess is usually the result of untreated decay or a cracked tooth. This enables the bacteria to penetrate the enamel and infect the nerves located in the pulp of the tooth leading to an abscess. An abscessed tooth is a collection of pus that causes troubling symptoms. There are several types of tooth infection or abscess such as periapical abscess, periodontal abscess, gingival abscess, pericoronal abscess, and combined periodontic endodontic abscess. Management of a tooth infection is important as if left untreated, can lead to sepsis and airway compromise.
The risks of complications are higher in those with suppressed or weakened immune systems. The diagnosis of a tooth infection can be made based on the patient’s history, examination, and supported by a dental radiograph. The goal of treatment is to kill the offending pathogen using antibiotics and pus drainage. If the tooth can be restored, a root canal therapy can be performed. However, extraction and curettage should be done for a non-restorable tooth.

Symptom #1: Swelling
Swelling or edema is one of the hallmarks of inflammation. It can be defined as an enlargement of the affected area due to the accumulation of fluid in the affected area and its adjacent tissues. Systemic swelling involves the whole body while localized swelling is confined to one area.
Swelling usually occurs when there is inflammation or infection. In a tooth infection, the involvement of the gums may result in the swelling of the surrounding tissues and can even be seen on the jaw. Patients who experience swelling should seek dental care to prevent it from becoming a chronic infection.

Symptom #2: Pain
The pain in a tooth infection or abscess is often described as an excruciating pain that is radiating, sharp, throbbing, or shooting. The pain may radiate upwards causing a headache or downwards causing pain in the neck. It can be aggravated by warmth and pressure.
Other associated symptoms of pain usually include swelling, fever, redness, and more. To help manage the pain, patients can take painkillers such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).

Symptom #3: Heat
Heat or warmth is also a cardinal sign of inflammation along with pain, swelling, redness, and loss of function. The process of inflammation occurs as a response to injury, irritants, damaged cells, or harmful pathogens.
It is the body’s natural way to attempt to eradicate the cause of injury, clear necrotic cells and repair damaged tissues. However, internal inflammation does not cause apparent increase in heat. In a tooth infection, the affected region is warm to the touch.

Symptom #4: Redness
Redness is often seen in areas that are infected or inflamed. Other associated symptoms are pain, swelling, and loss of function. In a tooth infection, there may be fever and swollen lymph nodes. Redness occurs when there is increased blood flow to the area of inflammation or infection.
There is exudation of fluid and emigration of leukocytes that help initiate the process of removing the offending pathogen. Redness can be reduced by applying ice packs and usually resolves once the inflammation subsides.
Symptom #5: Loss of Function
Loss of function is also one of the cardinal signs of inflammation along with heat, pain, swelling, and redness. Loss of function was a late addition to the first four cardinal signs of inflammation. It is usually caused by a combination of factors believed to help prevent further movement so there is less damage.
Depending on the affected area, loss of function means that the specific part of the body is no longer able to function normally. In a tooth infection, the patient may not be able to chew their food.

Symptom #6: Malaise
Malaise is an uneasy feeling where there is discomfort. There may or may not be pain and is often one of the earliest symptoms of a disease or infection. Malaise is a common and non-specific symptom that can be seen in even the slightest ailments such as hunger or stress.
It can also be present in serious conditions such as cancer, stroke, heart attack, and more. Patients often describe it as a feeling where “something does not feel right”. It is believed that malaise occurs due to the release of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of immune response.

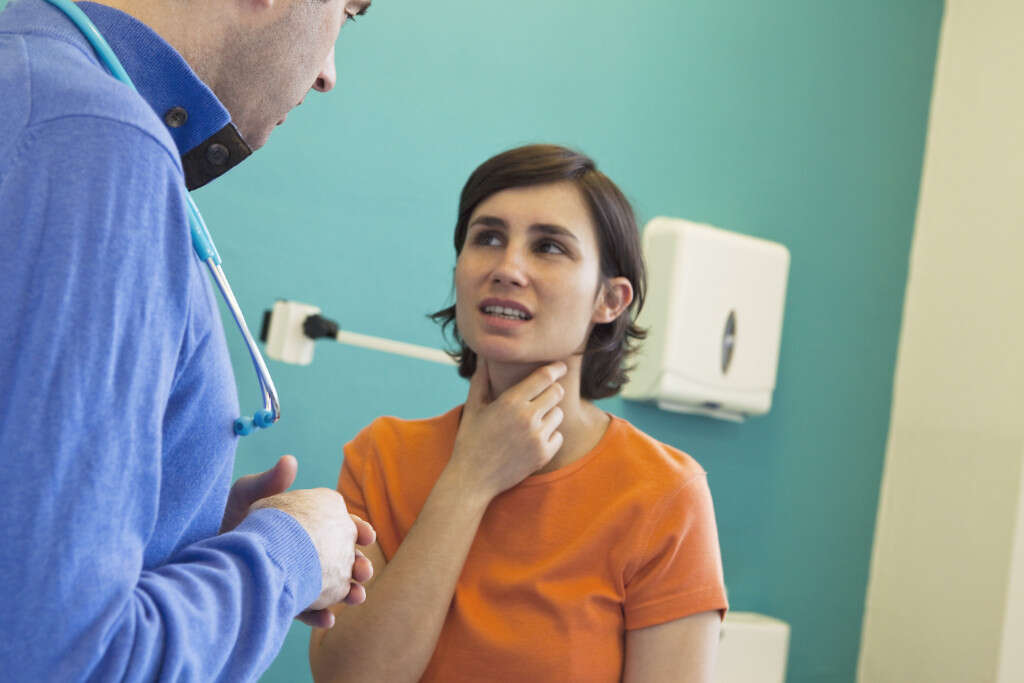
Symptom #7: Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy is defined as lymph nodes that are different in terms of number, size, or consistency. It can be seen in both minor and serious infections, cancers, autoimmune disorders, and more. Lymph nodes are part of the immune system that help to combat against pathogens or abnormal cells.
They can be likened to filters that trap pathogens and swell up when near a site of infection. In a tooth infection, the lymph nodes involved are usually located in the neck.
Symptom #8: Fever
Fever or pyrexia is an increase in the set point of body temperature that causes a feeling of coldness and resulting in muscle contractions to produce and conserve more heat in an attempt to reach the higher set point of body temperature. It is a common and non-specific symptom that can be seen in all infections (bacterial, viral, or parasitic) and non-infectious causes such as deep vein thrombosis and vasculitis.
Low grade fever is one of the body’s natural responses against infection as it helps enhance the immune system. To lower the temperature, antipyretics such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be useful.

Symptom #9: Headaches
A headache refers to pain that occurs anywhere in the head or neck. There are several types of headaches such as cluster headaches, tension type headaches, migraines, and more. A tooth infection may result in a headache or migraine due to the distribution of the trigeminal nerve.
A migraine is a recurrent type of headache ranging from moderate to severe. It usually affects one half of the head and can be described as pulsating. Migraines are usually associated with photophobia, phonophobia, nausea, vomiting, and exacerbation with activity.

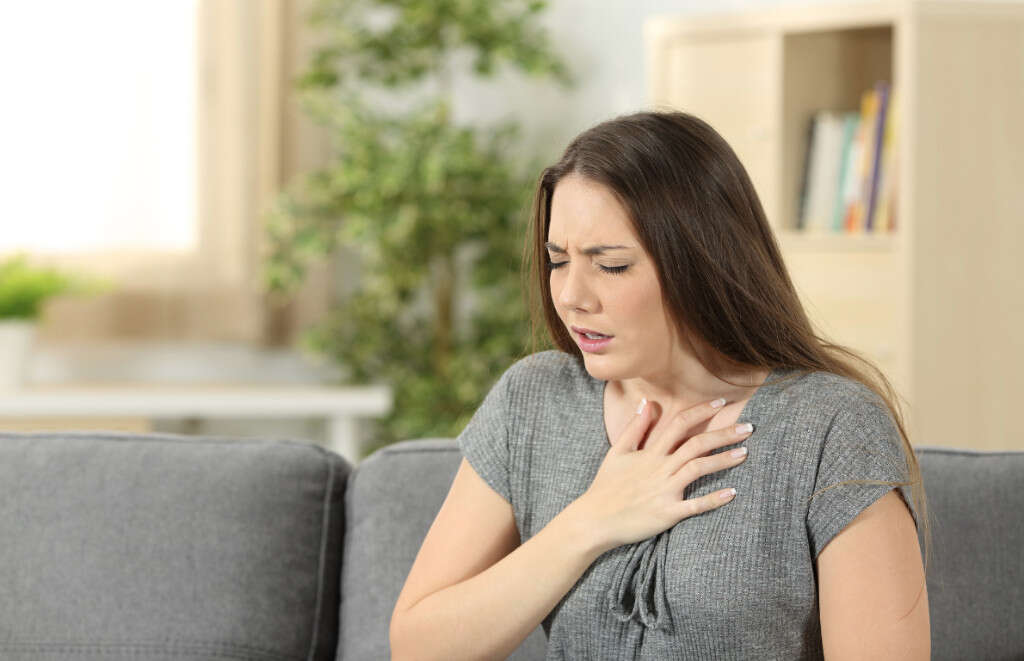
Symptom #10: Dyspnea
Dyspnea or shortness of breath is a feeling where one is unable to breathe well enough. Patients may experience air hunger, increased effort to breathe, and chest tightness. Dyspnea can be seen in patients with pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure, and more.
In a tooth infection, the involvement of the fascial planes where there is swelling can cause difficulty swallowing, opening the mouth, and breathing. Patients who experience these symptoms should seek medical attention as soon as possible.