10 Subdural Hematoma Symptoms
A subdural hematoma is the name given to a condition in which blood collects outside the brain, usually as a result of some sort of serious head injury. The blood results in an increase in pressure in the brain, which can lead to a number of symptoms and, in some cases, be fatal.
There are several layers of tissue that surround the brain, the closest to the skull being referred to as the dura. In a subdural hematoma, the problem is located underneath the dura but before the next layer of tissue, which is referred to as the arachnoid. Subdural hematomas can vary in their intensity and duration; some of them come quickly and disappear on their own whereas others require medical intervention and drainage. If this does not occur, the increasing pressure on the brain can lead to a person losing consciousness and eventually dying. There are a number of things that can lead to a subdural hematoma, but the most common cause is a head injury. People have developed them as a result of a car crash, a blunt force injury, or a fall. A hematoma caused by an injury is referred to as an acute hematoma.
It’s also possible to develop what’s known as a chronic subdural hematoma. These are recurring hematomas and can be a result of veins in the brain becoming torn. The symptoms may not appear for a few days and they may persist for longer. Older people are more at risk to develop either type of hematoma. If you think that you or someone that you love has developed a subdural hematoma, it could be a good idea for you to check out this list of symptoms. If you’re experiencing some of these symptoms, you might want to seek further medical attention.

Symptom #1: Unconsciousness
One of the things that might happen if you develop a sudden, acute subdural hematoma as a result of an injury is unconsciousness. This is usually the result of the serious bleeding that can happen. This applies pressure to the brain and can lead to a person becoming unconscious.
This usually occurs immediately after the injury. There are many reasons that you might fall unconscious after an injury, however, so this isn’t necessarily an indication that you have developed a subdural hematoma.

Symptom #2: Confusion
This symptom generally indicates that a person has developed a fairly serious hematoma. Patients who develop these hematomas may not display any symptoms at all shortly after they are injured. As the days progress, they may become more and more confused and disoriented.
This is a result of the blood slowly leaking into their cranial cavity. This slowly increases the pressure put on the brain and leads to a gradual increase in the severity of symptoms.

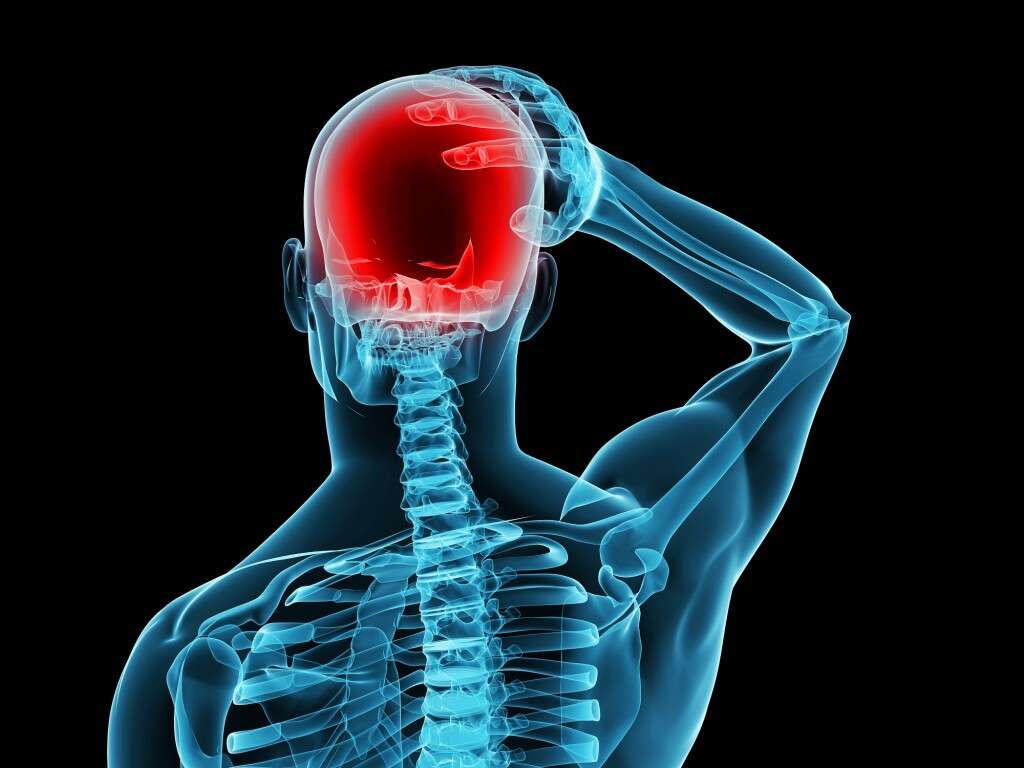
Symptom #3: Headaches
Subdural hematomas are well-known for causing headaches, and this can occur in either acute or chronic hematomas. Anything that puts pressure on the brain can lead to a headache, and the severity of the headache depends on the intensity of the hematoma.
In some cases, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs can help to reduce the discomfort associated with a hematoma. However, it’s important that you seek medical treatment if you think that you have developed a hematoma.

Symptom #4: Behavioral Changes
Some people may experience changes in their behavior after they have had an injury leading to a hematoma.
Some people may experience changes in their emotional behavior and act out irrationally or more aggressively. Other people may experience changes in their motivation or be inclined to act in a way that they wouldn’t have done before.

Symptom #5: Dizziness
Another symptom that’s common among hematoma patients—or any form of head injury—is dizziness. Dizziness is not generally dangerous on its own, but if it strikes at the wrong time, such as when driving a car or holding a knife, dizziness can be a hazard.
Dizziness can occur when blood applies pressure on the brain. The best way to cope with this is to sit down for a moment and get your bearings. If dizziness persists, you should check with your medical professional.

Symptom #6: Lethargy
Lethargy is a term used to describe a type of chronic and severe fatigue. Lethargic people often lack the energy to perform simple tasks or engage in activities that they would usually do.
If you are experiencing fatigue and lethargy, there are some herbal supplements that can be useful for helping you regain your energy without causing side effects; however, in the case of a head injury, it is most important to get yourself checked out first and ask your physician questions on how best to combat the symptoms.

Symptom #7: Nausea
Nausea is a queasy feeling that may or may not precede vomiting. Many of us are familiar with the sensation of nausea because of our experiences with flu, but people with head injuries often report that they experience nausea.
This is usually an indication that the hematoma is quite serious. If you experience any nausea after a head injury then you should get yourself checked out by a doctor immediately.

Symptom #8: Seizures
In much more serious cases, subdural hematomas have been known to cause seizures. Seizures are involuntary muscle contractions that can be very debilitating.
Seizures range in intensity from very mild muscle spasms to full-body convulsions in which a person loses control of their body and often loses consciousness. These seizures, referred to as grand mal seizures, often require hospitalization.

Symptom #9: Apathy
Another thing that may be experienced while suffering a hematoma or, indeed, other forms of head injury, is apathy. Apathy is essentially the opposite of empathy. When one is apathetic, they are unable to feel their emotions.
An apathetic person will seem unmotivated, unenthusiastic, and emotionally unavailable. This can be unhealthy for their personal relationships as they will become difficult to relate to.

Symptom #10: Coma
Many people lose consciousness when they receive an injury that leads to a hematoma. Unfortunately, some of these patients may not regain consciousness for days, weeks, or months after their injury.
Being in a prolonged state of unconsciousness is known as being comatose or being in a coma. Comatose patients generally require hospitalization so they can receive their hydration and nutrients until they regain consciousness.